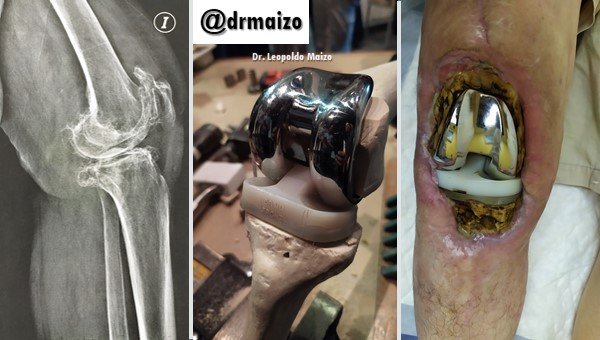
Peri-prosthetic infections
Technological progress has allowed undeniable progress in joint replacement surgery, however peri-prosthetic infections (PPI) remain one of the most serious problems that patients and medical staff face when talking about post-surgical complications.
Peri-prosthetic infections (PPI) remain one of the most serious problems that patients and medical staff face when post-surgical complications are discussed. The present work describes the case of a post total arthroplasty infection of the knee in a female patient with bilateral gonarthrosis.

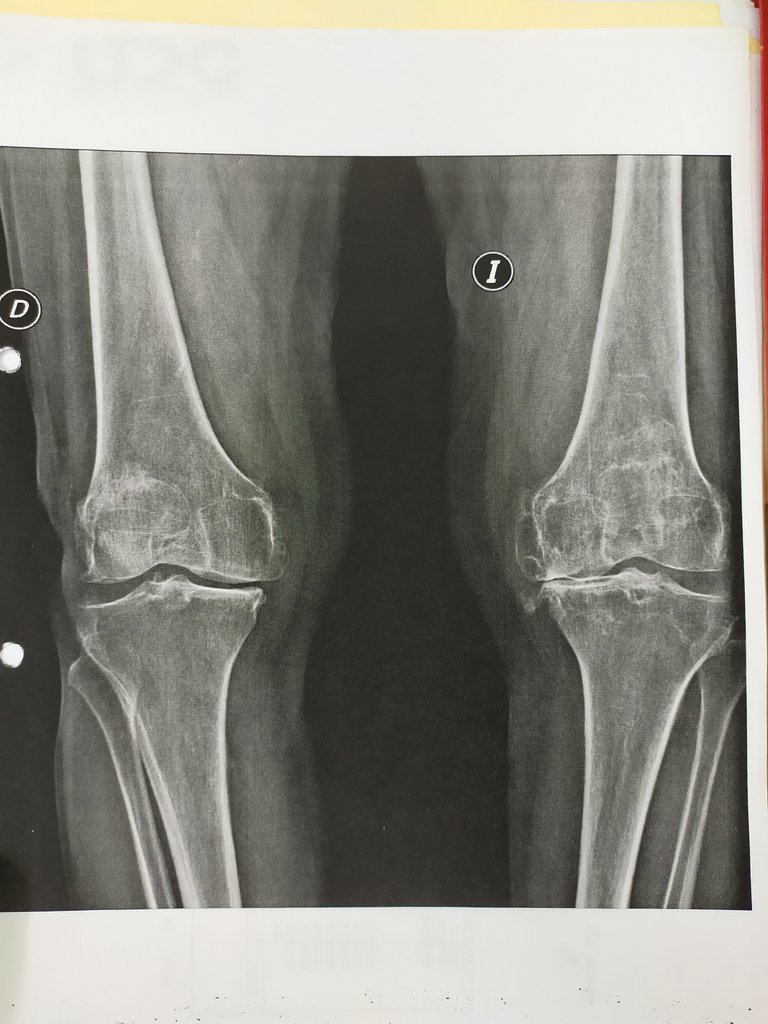
Early postoperative infection
Appears within 1 month after implant. There are local symptoms and signs (pain, erythema, swelling) associated in many cases with infection of the surgical incision. Early post-surgical infection, which is allowed to develop without surgery > 1 month, is considered a chronic infection. It presents dehiscence and suppuration of the surgical wound that extends to the prosthesis; presence of arthrocentesis with positive culture or purulent synovial fluid or surgery proves periprosthetic pus or that the infection of the surgical wound extends to the prosthesis. A synovial fluid with the presence of more than 27,800 leukocytes/µL and more than 89% neutrophils is predictive of early postoperative knee infection. Also a culture of the surgical wound exudate: aerobes and anaerobes. Arthrocentesis: cellularity and synovial fluid cultures for aerobes and anaerobes. Ultrasound to locate peri prosthetic collections, especially on the hip. Percutaneous puncture of peri prosthetic collection: aerobic and anaerobic cultures.

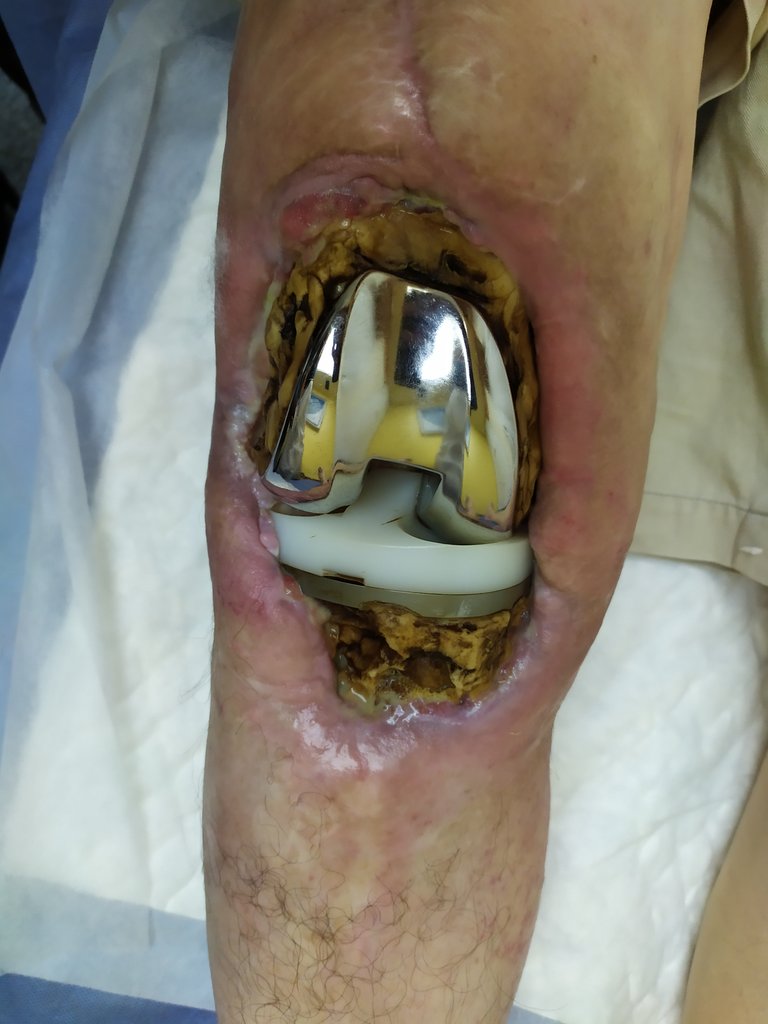
Late or chronic post-surgical infection
It is diagnosed from the first month after implantation until 1-2 years later. Insidious evolution with persistent inflammatory pain for months, few local signs, no fever. There may be joint effusion, abscesses and fistulization. The equal presence of microorganism in more than 2 cultures of synovial fluid, periprosthetic membrane or periprosthetic bone tissue from 5-6 samples taken during surgery; preoperative synovial fluid culture + 1 positive intraoperative culture for the same microorganism and communicating fistula with the prosthesis with obvious periprosthetic suppuration during surgery.
Many criteria are used to identify a late periportesic infection and the treatment is more insidious with many complications.
Dr. Leopoldo Maizo - Orthopedic Surgeon


Firma diseñada por @themonkeyzuelans, contáctalos vía Discord "themonkeyzuelans#9087"
Great projects from the Steemit community:
- My Fundition campaign: https://fundition.io/#!/@drmaizo/6f88ggj8h

.png)
That’s a brutal knee infection ugh!
Really brutal man :(
Thanks friends :D