Hi everyone!
This is the next episode of my series dedicated to the learning of anatomy, for drawing use. 😉
Here are the previous topics :
- Intro
- Head & Neck
-> + Bonus How to draw hairs ? - The torso & the pelvis
-> + Bonus How to draw breasts ?
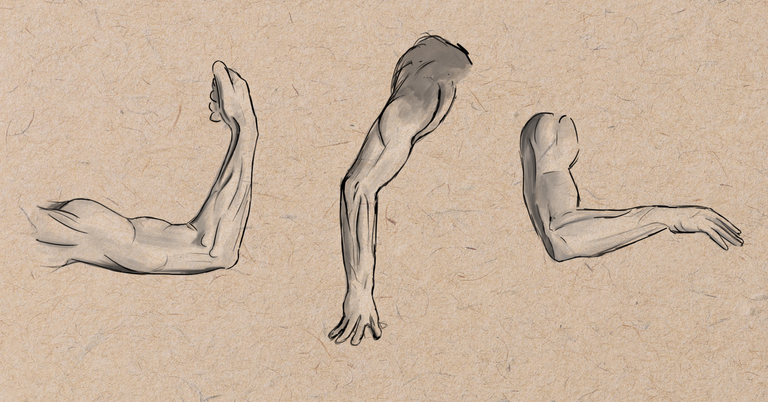
For this part, we will speak about arms, and its implantation to the body.
First, let's have a little reminder about proportions.
Proportions of the arms
 The distance between shoulders to the elbow is equal to the one between elbow to the metacarpals.
The distance between shoulders to the elbow is equal to the one between elbow to the metacarpals.
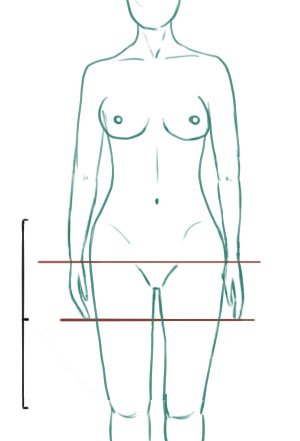
Also, the wrist comes near of the end of pubis. Depending on the person, the wrist something comes in the level of the legs intersection.
The end of hand comes about the middle of the distance between beginning of the leg (marked by the pelvis) and the knee.

Bones of the arms
There are 3 arm bones : The Humerus, Radius and Ulna.
The humerus
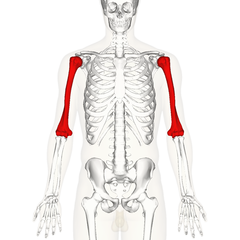
The humerus is the top bone between shoulder to elbow. It fits into the cavity of the shoulder girdle (Clavicle + scapula).
We can see a triangular form in the bottom of the humerus.
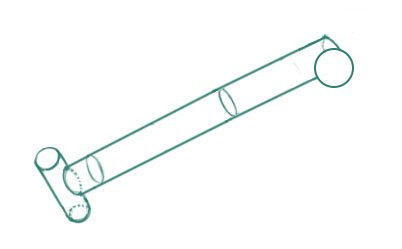
We can resume its form like a hammer.
 In the bottom of the humerus, we see two form that are junctions for the next bones.
In the bottom of the humerus, we see two form that are junctions for the next bones.
The ball is the connector of the radius, and the "speaker" the one for the ulna.
The radius
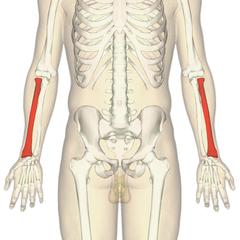
It's one of the two bones in the forearm. He is always on the side of the thumb. Its form is a cylinder at the top, and be more like a box when he approach to the hand.
The purpose of the radius is rotation of the forearm.
The ulna
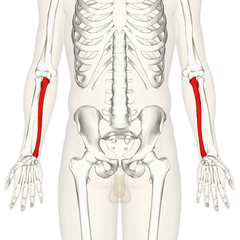
It's the other bone of the forearm. He is always on the side of the little finger. He becomes finer and rounder as he approach to the hand.
It is the bone we see in the elbow.
The purpose of the ulna is flexion/extension of the forearm.
Relation between radius and ulna :
- The ulna is bigger on the top than on the bottom. This is the opposite thing for the radius.
In fact, it's a kind of triangles puzzles that fit together.
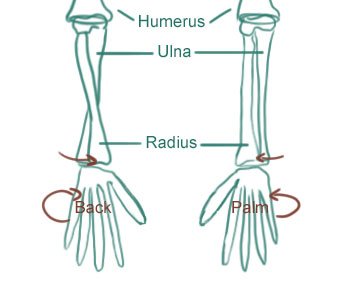
- We call pronation the left position, with back of hand, and supination the right one, with palm side.
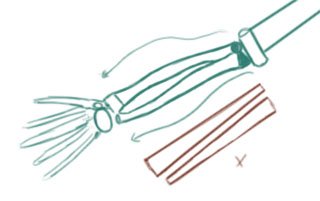
- These bones are not straight. There are curvy!

Muscles of the arms
Shoulders muscles
The complex form of the armpit is caused by the presence of many muscles. Let's check them together.
The deltoid
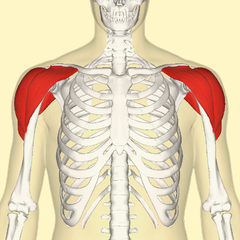
The deltoid has a form of a triangle. He's placed on the shoulder.
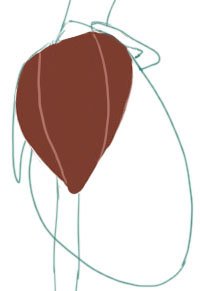 He is divided in 3 parts.
He is divided in 3 parts.
It is located in continuity with the trapezius. The deltoid end near of the sternum ball.
Notice that the deltoid don't come straightly on the arm bone, he is curvy and come a bit in the interior of arm.
The deltoid joins the pectoral at the bottom.
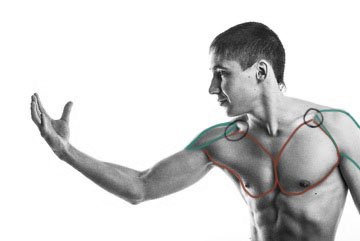 They are separate by the clavicle at the top, which forms a gap, called infraclavicular fossa (here circled in black).
They are separate by the clavicle at the top, which forms a gap, called infraclavicular fossa (here circled in black).
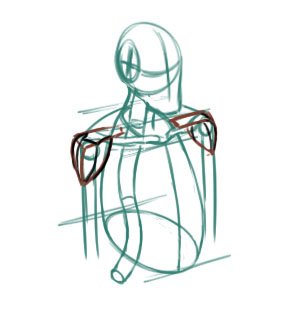
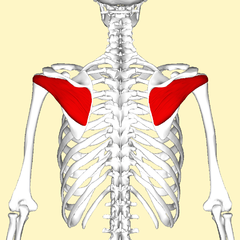
The infraspinatus
He takes its origin on the scapula, and finish on the head of the humerus.
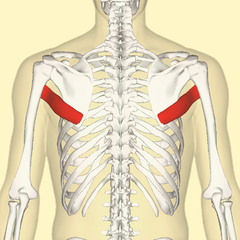
The teres major and minor
This is two little muscles, that like the infraspinatus, take origin on scapula and finish on the head of humerus.
They help on different movement of arm and scapula.
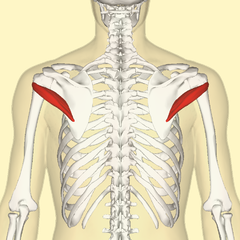
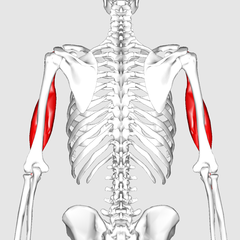
Biceps
It is call biceps because this muscle has two heads.
It is the big arm muscle on the face side.
They take origin from scapula. The first head passes under the shoulder joint, during the other passes next to. They join together to finish in one point on the radius bone.
In fact, the biceps is never attached to the humerus, because it is attach from the scapula and shoulder to the radius.
When the muscle is at rest, he is long and thin. And when he contract, he look more little and more bigger.
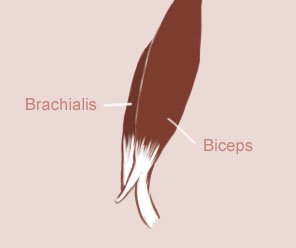
Brachialis
As the biceps finish in the radius, the brachialis finish in the ulna.
 The brachialis is placed under the biceps.
The brachialis is placed under the biceps.We only see a little part of the brachialis, because the biceps is in front.
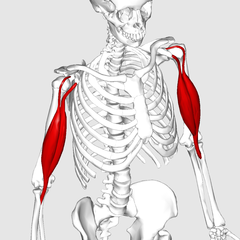
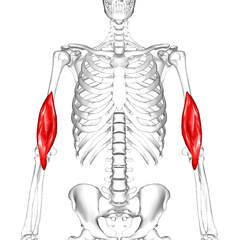
Triceps
You should understood, Triceps is named like that because it has three heads.
It is the other big muscle of the arm, located in the back side.
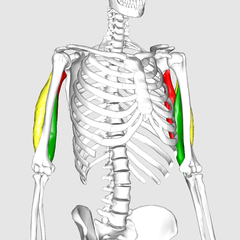
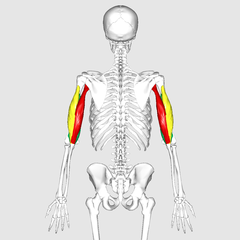
At the end of the triceps, you find the triceps tendon, which joins to the elbow.

Forearm muscles
Drawing forearm is not simple at all. There is a lot of little muscles which forms a complex shape.
I will try to simplify all of this!
About the general form of the forearm, keep in mind that at the level of the elbow, it is swollen and full of muscle. At the wrist, it is rather full of bones and tendons and narrow, so that you can simplify the end of the arm with a rectangular box shape.

--> In the forearm, we have a 3 groupes of muscles : the Flexors, the Extensors, and the Brachioradialis.
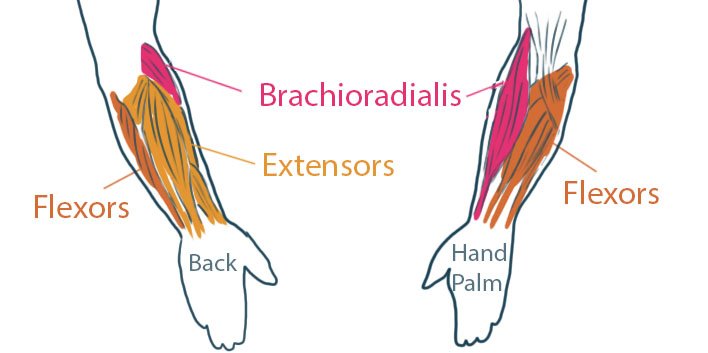
- The role of the Flexors is to bend the wrist and the fingers.
They are mostly visible on the palm side. It takes origin from the humerus extremity (called the medial epicondyle). We can resume it into a big round form.
- The role of the Flexors is to bend the wrist and the fingers.
- The role of the Extensors is to straighten up the wirst and fingers. It starts from the lateral epicondyle.
This is a group of different complex muscles.
.
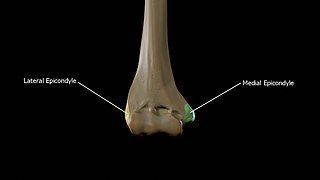 The two visible extremity of the humerus.
The two visible extremity of the humerus.
- The role of the Extensors is to straighten up the wirst and fingers. It starts from the lateral epicondyle.
- The Brachioradialis muscles takes origin outside of the humerus.
It is composed of the Brachioradialis and the Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus.
These muscles are visible on the top on the back side, and on the side of the palm side.
The function is to flex the forearm at the elbow.
- The Brachioradialis muscles takes origin outside of the humerus.
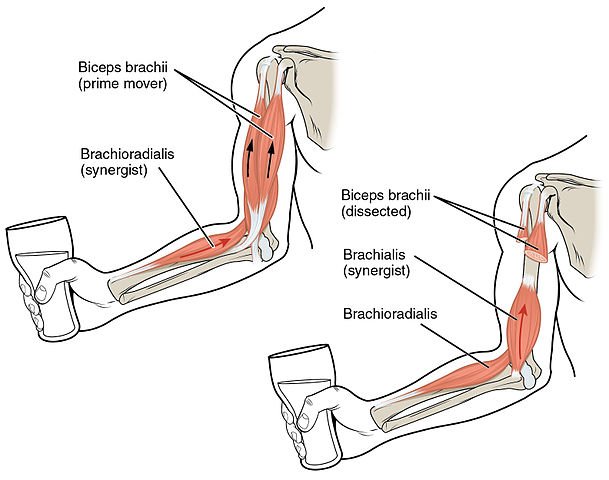
OpenStax College, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

That's all for this tutorial. 😊
Hope you will like it, don't hesitate to leave a comment or question something unclear.
And remember, after the theory, the best exercise is to practice on live models ! 😉
See you soon!!
Your content has been voted as a part of Encouragement program. Keep up the good work!
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more