Last Wednesday, March 11, 2020, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, current Director General of the World Health Organization (WHO), declared the Coronavirus (Covid-19) as a PANDEMIC, this due to its accelerated spread worldwide, which is why, in this new issue I will socialize some introductory elements about Covid-19, essentially those related to in vitro treatments based on Chloroquine, Interferon α, and Interferon β.

Fig. 2 Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director General of the World Health Organization (WHO), declared the Coronavirus (Covid-19) as a Pandemic. Captured image
Introduction
According to the official reports of the World Health Organization [1], since December 31, 2019, the first cases of Covid-19 were registered in Wuhan, a city located in the China province of Hubei, whose symptoms, infection process, outbreak and affectation do not behave in a similar way to the viruses known so far, an extremely worrying situation, because it does not know how these new viruses can affect people, essentially because the pathogenesis generated does not behave the same as the normal pathogenesis.
The abnormal pathogenesis of Covid-19 is the main reason why, to date, there are no drugs or vaccines that can be used to initiate treatments to lower mortality levels, an alarming situation if we consider that the disease is highly contagious, and patients in a serious condition only receive support care, such as respiratory assistance.
Therefore, and considering that the disease has caused the death of more than 30,000 people worldwide, due to respiratory conditions known as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV), the objective of the present post is to present some scientific reports on the antiviral effect of Chloroquine, Interferon α, and Interferon β on the Coronavirus.
Conceptual overview
Coronavirus
To understand a little about the subject, from the conceptual point of view the Coronaviruses (CoVs) are the biggest group of viruses belonging to the order of Nidovirals, which includes the families; Coronaviridae, Arteriviridae and Roniviridae, on the other hand, the Coronavirinae are subdivided in turn in four groups, the alpha, beta, gamma and delta coronaviruses, characterized for causing numerous diseases in animals like; pigs, bovines, chickens, dogs and cats, according to research developed on these viruses in the last half of the 20th century, where diarrheas of epidemic scope in pigs were reported, as well as severe gastroenteritis in young piglets, leading to morbidity, mortality and economic losses.
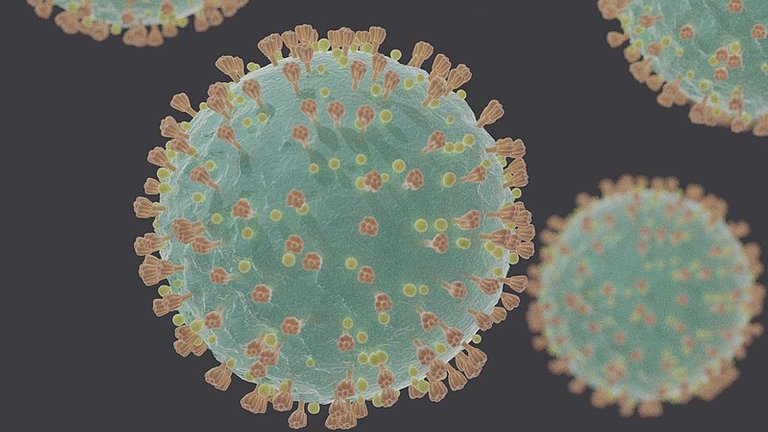
Fig. 3. This image is a computer generated representation of COVID-19 virions (SARS-CoV-2) under electron microscope. Public domain image. Author: Felipe E, 2020 / CC BY-SA 4.0
Chloroquine
Chloroquine (CQ), is a synthetic antimalarial compound based on quinine, the main characteristic of this substance, is that it has weak bases that raise the pH in human cells called organelles and are normally acidic, favorable biological behavior, because it interferes with the ability of pathogenic microorganisms to enter and multiply at the cellular level.
It is estimated that the incorrect application of CQ, can cause serious side effects because of its considerable toxic load, such as loss of vision, heart problems or death, however, its natural equivalent (tree quinine), has been used for hundreds of years in South American countries to treat multiple viral conditions.
Interferon α
Interferon α (IFN-α), is a protein with a bio-signaling capacity known as cytokine, produced and secreted by host cells in response to the presence of various pathogenic microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, parasites and cancer cells. The main function of IFN-α is to regulate metabolic function at the cellular level, generating an activation of antiviral defenses in nearby cells.
The bio-capacity of IFN-α signaling, triggers a defense network in the protective cells within the immune system, by participating and interfering in the replication and elimination of pathogenic microorganisms, in other words it is a modifier of the biological response, which protects cells from infections mainly from viral attacks.
Interferon β
Interferon β (IFN-β), is a cytokine family of IFN-α, and from the pharmacological point of view, it presents basically the same capacity of IFN-α, by stimulating the production of neutralizing antibodies on pathogenic microorganisms, hence, in an homologous way it reacts with receptors in the cell membrane but the effect occurs in the nucleus.
In multiple in vitro tests, it has been demonstrated that IFN-β has the biological characteristic of slowing down the advance of viral infections, provided that its application is made in the early stages and continues during the duration of the pathological incubation process.
In vitro treatments
The World Health Organization has issued reports indicating that Covid-19, in addition to producing mild, self-limiting respiratory infections in humans as normal viral processes do, usually causes fever and respiratory symptoms (coughing and dyspnea or difficulty breathing), and in the most severe cases, can cause pneumonia, severe acute respiratory syndrome, kidney failure, and even death. Hence, the main affected countries (China, Italy, Spain and the USA) are seeking to produce drugs and vaccines to stop the uncontrolled mortality that has generated this pandemic in the early 2020.
Chloroquine Antiviral Bioassays

Fig. 4 Article on: Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight Covid-19. Captured image
In China, antiviral trials with chloroquine have been developed, the clinical results of these in vitro investigations are favorable in patients with coronavirus by significantly reducing the occurrence of pneumonia, however, the optimal dose has not yet been determined, since different doses were used in different trials [2] .
Antiviral Interferon α Bioassays

Fig. 5 Article on: Characterization of the antiviral effects of interferon-α against a SARS-like coronoavirus infection in vitro Captured image
According to the results obtained in in vitro tests, where antiviral activity was induced using IFN-α in Coronavirus infections, the antiviral generation mediated by IFN-α, determines direct antiviral activity of IFN-α against Coronavirus infections, by interfering in viral multiplication, creating an inhibition mechanism in the first level of response of the organism [3] .
Antiviral Interferon β Bioassays

Fig. 6 Article on: Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV Captured image
In in vitro trials, recently developed by [4], in the search to determine the therapeutic efficacy of IFN- β on coronavirus, it was shown that Interferon β slightly reduces viral load by improving lung function, however, it fails to affect other disease parameters by not reducing virus replication or severe pulmonary pathology.
SCIENTIFIC CONTRIBUTIONS OF THIS PUBLICATION
- In the present issue, the three main treatments that are currently most accepted for their positive effects against Covid-19 were outlined. However, considering that the results are not so encouraging, and that the epidemiological risk factors are high, the best government measures to control the coronavirus revolve around a strong public health surveillance system, along with rapid diagnostic and quarantine tests when necessary to prevent local outbreaks, while the common citizen is advised to practice good hand and respiratory hygiene (covering the mouth and nose when coughing and sneezing) and to cook meat and eggs thoroughly, and to avoid close contact with anyone who shows signs of a respiratory condition, such as coughing or sneezing.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES CONSULTED AND CITED:
[1] OMS (Organización Mundial de la Salud. Electronic domain:
[2] Colson P., Rolain J., Lagier J., Brouqui P., and Raoult D. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight Covid-19. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. Article: Online access
[3] Zorzitto J., Galligan C., Ueng J. Characterization of the antiviral effects of interferon-α against a SARS-like coronoavirus infection in vitro. Cell Res. 2006; 16: 220–229. Article: Online access
[4] Sheahan T., Sims A., and Leist S. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat Commun. 2020; 11: 222. Article: Online access
[5] Ronald T., Alma F., Kenneth K., Douglas K., ad Carlton K. Prevention of Experimental Coronavirus Colds with Intranasal α-2b Interferon, The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1986; 154; 3: 443–447. Article: Online access
ATTENTION
Readers and followers
If you wish to read more scientific articles in English or Spanish, of excellent academic quality, do not hesitate to visit #SteemSTEM at Hive for the moments #HiveSTEM and #STEM-espanol, communities that promote scientific content mainly in the areas of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics.


If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness @stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Please consider using the stem.openhive.network app and including @steemstem as a beneficiary of this post. This could yield a stronger support.
Thanks for sharing these valuable information,
stay healthy
best
Chapper