For this portion of the Ethereum Guide, let's give a look into the workings of Ethereum.
INTRODUCTION: What follows is a very simplified and truncated explanation of the basic workings of the Ethereum blockchain. It is simply a 'jumping off' point for an understand of how this blockchain works and in no way is meant to be exhaustive.
BLOCKCHAIN: The operative work of Ethereum occurs on a blockchain network. The blockchain is a decentralized, distributed public ledger where all transactions are verified and recorded.
Let's understand what these terms mean. A blockchain is 'distributed' in that all participants within the Ethereum network possess an identical copy of the ledger (where all past transactions may be viewed). A blockchain is 'decentralized' in that it exists and operates without a centralized governance (instead the network is managed by all distributed ledger holders). For Ethereum network security and verification of transactions cryptography is used in each blockchain transaction.
Mining: Anyone can use computers to 'mine'. Mining is using computers to solve complex mathematical equations, in essence by guessing the solution. The result of this 'mining' is to confirm each blockchain transaction and add new blocks to the blockchain which is the basis of the system. The reward for participation in this activity is cryptocurrency tokens which in the Ethereum ecosystem are called 'Ether' (ETH).
Trustless: Anyone may create a financial contract, keep debt, or maintain ownership registries on the ledger in the absence of an outside recordkeeper or trust officer. Transactions of this nature are called 'trustless'. These transactions are 'trustless' due to the elimination of the need for trusting the counterparty in that the underlying contract, by code, is self-fulfilling.
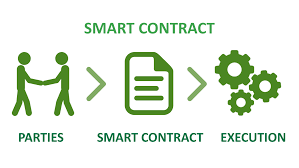
SMART CONTRACTS: Simply put, a smart contract is nothing more than a software program which runs on a blockchain. In other words, it is a digital automated agreement or terms and conditions that only execute when certain agreements within the contract have been met. Smart contracts are one type of Ethereum account, meaning they have a balance and can send transactions over the network.
The smart contract is not controlled by one party or the other in the transaction. Instead, smart contracts are deployed on the network and operate as programmed by code. Interaction by a user with the smart contract occurs when transactions are submitted that execute a function defined within the parameters of the specific smart contract. The smart contract defines the rules of the underlying transaction (much the same way as a regular contract), and automatically enforces the terms of the transaction by the code of the programmed smart contract.
DECENTRALIZED APPLICATIONS: The Ethereum Blockchain is unique as it is so much more than merely a distributed ledger. This blockchain allows for the construction of software coded applications to be built on top of the existing chain. These decentralized applications (DApps) operate on the Ethereum blockchain much like the way software runs on a computer. DApps are coded applications which can store and transfer personal data as well as handle complex financial transactions (such as in the area of decentralized finance ['DeFi']).
GAS FEES: Gas is the fuel needed to operate the Ethereum network, much the same way a motor vehicle requires gas to run. On this blockchain, gas refers to a unit of measurement corresponding with the required computational effort needed to execute a specific operation on the network. In that each individual Ethereum transaction requires computational resources to run, each individual transaction requires paying gas. Gas is the required fee to be paid to successfully execute a transaction on the Ethereum blockchain.
Gas fees are paid in Ether and are denoted in 'gwei'. 'Gwei' itself is merely a denomination of Ether equivalent to 10 to the -9th power of Ether (0.000000001 Eth).
For a further understanding of gas fees, reference is made to the following video:
Video Source
CONCLUSION: As stated at the onset of this article, this consisted of a very short and simplified look into the working of the Ethereum Blockchain. If you would like further information on this topic, reference is made to the following materials:
"Ethereum 101". Coindesk. https://www.coindesk.com/learn/ethereum-101/what-is-ethereum. (Accessed June 15, 2021).
"Community guides and resources". Ethereum.org. https://ethereum.org/en/learn/. (Accessed June 15, 2021).
"Ethereum". Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethereum. (Accessed June 15, 2021).
"What is Ethereum and how does it work?". IG. https://www.ig.com/en/ethereum-trading/what-is-ethereum-and-how-does-it-work. (Accessed June 15, 2021).
"What is Ethereum: Understanding Its Features and Applications". Simplilearn. https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/blockchain-tutorial/what-is-ethereum. (Accessed June 15, 2021)
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
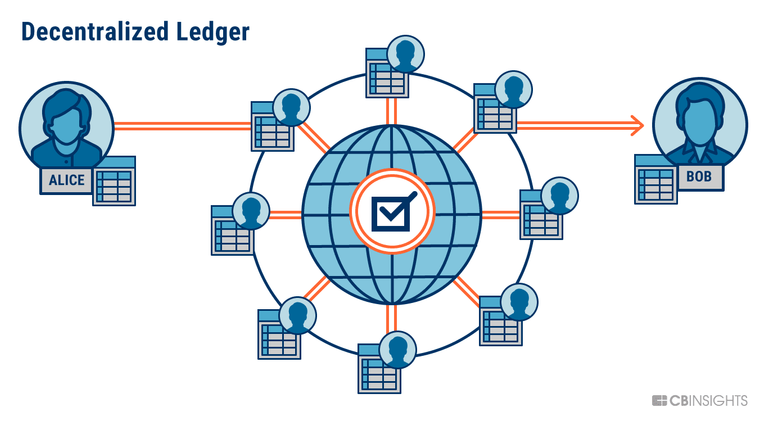
Like all cryptocurrencies, Ethereum works on the basis of a blockchain network. A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed public ledger where all transactions are verified and recorded. .
Congratulations @kevinnag58! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Your next target is to reach 2750 upvotes.
Your next target is to reach 1500 replies.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP