.jpeg)
Algorithmic stablecoin
Recently, stablecoins have been a very hot topic, so I think a very advanced getting started guide might be helpful. There are many kinds of stablecoins, including stablecoins that are centralized by fiat currency pledges, and there are also stablecoins that are more decentralized based on algorithms and do not require pledges.
Stablecoin overview
Stable currency is a token supported by legal currency on the public chain, and its value is linked to a stable traditional currency (such as the US dollar). This token minimizes the volatility of tokens, so that some exchanges and DEXs can remit and settle in US dollars, and traders can also enjoy BTC, ETH and other cryptocurrency belts without price volatility. The benefits come.
In 2020, the DeFi market is booming, and stablecoins have also achieved impressive growth. In fact, the U.S. Currency Administration (OCC) announced last week that under federal supervision, banks can use stablecoins for payments and other activities. OCC stated in a letter that blockchain has the same status as other global financial networks such as SWIFT, ACH, and FedWire, and supports the use of stablecoins and cryptocurrencies as legal alternatives to other real-time payment systems. The total value of stablecoins has now exceeded US$30 billion, reflecting the rising demand for price-stable assets from investors during turbulent times.
At present, more than 200 stable currencies have been developed, mainly USDT and Centre's USDC. The market value of the most popular stablecoin USDT has soared to more than $21 billion in recent weeks. Since the beginning of 2020, the market value of USDT has more than quadrupled, accounting for more than three-quarters of the stablecoin market.
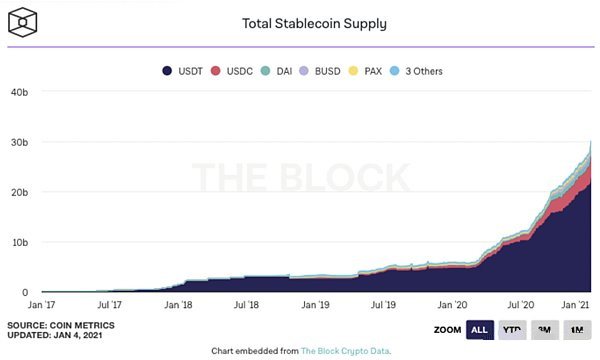
The cryptocurrency market is changing with each passing day. Despite this, the share of stablecoins continues to surge. Unlike the real US dollar, investors can easily hold or trade stablecoins and enjoy the benefits of blockchain technology and peer-to-peer value transfer. Many traders view stablecoins as an intermediate step in the process before investing in riskier cryptocurrencies. After buying stablecoins with U.S. dollars or other government-issued currencies, traders can transfer them to exchanges and trade cryptocurrencies such as BTC and ETH.
The principle of algorithmic stablecoin
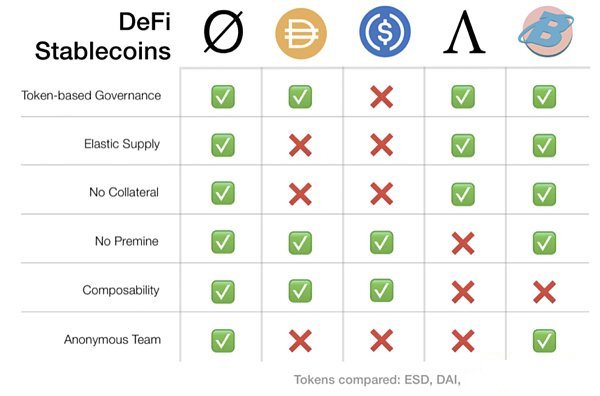
Algorithmic stablecoins use price-stabilization algorithms to track the price of a specific currency unit-usually $1. Algorithmic stablecoins run on the public chain. Some algorithmic stablecoins are supported by basic cryptocurrencies such as ETH, and some have no guarantees. Price parity is supported by the market and technical mechanisms, which are based on smart contracts and lock cryptocurrency collateral to achieve price stability. Unlike other types of stablecoins, algorithmic stablecoins cannot be exchanged for U.S. dollars at a 1:1 ratio, nor are they secured by cryptocurrency assets, and are usually highly reflexive. Its demand is mainly driven by market sentiment and market conditions, which affects supply.
The first batch of algorithmic stablecoins was launched on the Bitshares blockchain in 2013. Now, the longest running algorithmic stablecoin is Ampleforth (AMPL), although the DeFi boom in 2020 has brought projects such as Yam and Based.
For stablecoins similar to AMPL, if the token price deviates from the target asset price, the supply will also change accordingly (called Rebase), which will affect each account. The interval at which rebase occurs is preset to maintain the activity of the blockchain network. The algorithm issues more tokens when the price rises, and reduces the supply when the price falls, so that supply and demand balance. For example, after an algorithm is designed, when a stable currency worth $1 drops to $0.70, the algorithm will automatically set a market buy order to push the price higher. If the price is higher than $1, the algorithm will sell stablecoins.
Some traders want to make money by taking the risk of stablecoins. Therefore, for such traders, new projects such as Basis Cash and Empty Set Dollar will limit the number of rebases and eliminate the impact of token supply changes on each wallet.
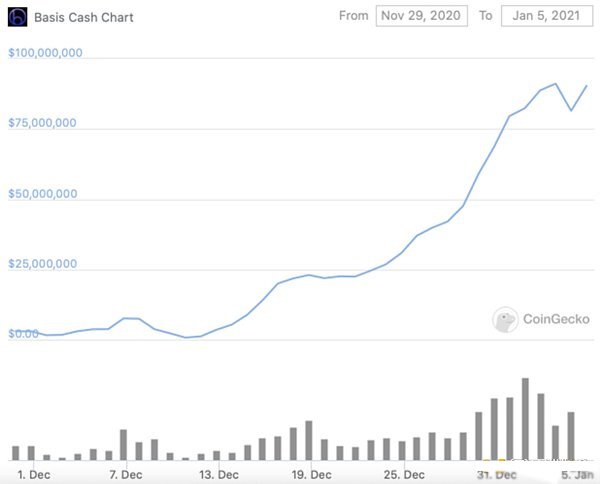
Basis Cash is a new multi-token protocol based on the stable currency Basis. Basis is an algorithmic stable currency project that raised $133 million in funds in 2018 but never went online. Basis Cash consists of the following three tokens:
1. BAC-algorithmic stablecoin, the current supply of BAC is close to 90 million.
2. Basis shares-in the case of blockchain network expansion and inflation, holders can obtain BAC.
3. Basis bond-In the case of deflation of the entire blockchain network, investors can buy the bond at a discount. After the deflation ends, the bond can be redeemed in exchange for BAC.
The purpose of Basis shares and Basis bonds is to pull the price of Basis Cash back to $1. For example, when the price of Basis Cash is lower than $1, users can destroy Basis Cash, buy Basis bonds, and reduce the supply of Basis Cash. Basis bonds have no interest and no maturity date. When the price of Basis Cash exceeds $1, it can be redeemed. On the contrary, when the price of Basis Cash exceeds $1, the smart contract allows the redemption of Basis bonds. As the demand for BAC increases, more new BACs will be minted and distributed to Basis bond holders.
The initial distribution of Basis Cash is 50,000 in total, and priority is given to users who deposit DAI, yCRV, USDT, sUSD and USDC in the smart contract. After that, in Uniswap v2, users who provide liquidity for the Basis Cash (BAC)-DAI trading pair can obtain token distribution, and they can deposit LP tokens into the distribution smart contract to obtain Basis shares.
Basis went live on November 30, 2020, with a total lock-up value of up to nearly 200 million U.S. dollars, and then dropped to 169 million U.S. dollars. Initially, DeFi traders provided liquidity for the project one after another, and the BAC stablecoin liquidity pool reached an annual rate of return of about 10,000%. The current BAC/DAI daily and annualized returns are 1% and 365% respectively. The daily and annualized returns of DAI/BAS are 2% and 365% respectively.
Under the influence of Basis, the Empty Set Dollar project developed an ESD stable coin, which was launched at the end of August, and its current market value exceeds 100 million US dollars. The core of the agreement is the ERC-20 token ESD, which is both a stable currency of the US dollar and the governance token of the agreement. The total supply of tokens currently exceeds 500 million, and the DAO daily and 30-day yields are 4% and 206%, respectively. The LP and 30-day returns are 1% and 40% respectively.
Although Basis Cash is still in its early stages of development, ESD has experienced multiple cycles of inflation and contraction. ESD has the following three main characteristics:
1. Stability-ESD uses the algorithm to stabilize its price at around 1USDC, and uses Uniswap's liquidity to incentivize the time-weighted average price algorithm oracle of the trading pool, allowing the supply to automatically expand and contract, and reward those who stabilize the price within the agreement user.
2. Compatibility-ESD conforms to the ERC-20 protocol and can seamlessly access various DeFi infrastructures.
3. Decentralization-governance on the ESD chain is decentralized. In the community, ESD holders can vote on protocol changes and upgrades.
In fact, so far, ESD has experienced more than 200 supply epochs (epochs), of which nearly 60% occurred when the TWAP of ESD reached the range of $0.95 <x <$1.05. This means that the stability of ESD is more than twice that of Ampleforth, the longest running algorithmic stable coin, even though the former has a shorter running time.
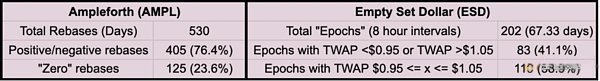
Similarities and differences between ESD and Basis Cash
Like Basis Cash, ESD uses bonds ("coupons") to finance the agreement. If you want to buy ESD bonds, you must destroy the ESD. After the agreement is inflated, the bonds can be redeemed and exchanged for ESD. Basis Cash has 3 token models. In contrast, ESD does not have a third token. After paying off the debt, if the blockchain network is inflated, users will not be rewarded. In order to cope with this problem, ESD holders can pledge ESD to the ESD DAO, and obtain additional ESD according to a certain proportion, the upper limit of which is 3%.
The "staging" model of ESD will eventually play a role similar to the three-token system in Basis Cash Shares. In this mode, after a period of time, the ESD in the DAO can be converted to a non-bond state. During this period, the ESD tokens will be temporarily stored in the DAO for 15 epochs (that is, 5 days), and everyone can neither trade nor Obtain cumulative inflation returns.
In the face of liquidity risk, users will convert ESD into a bond state in the DAO, and in the face of price risk, they will buy Basis Cash stock, both of which may allow users to obtain inflationary returns in the future. However, in staging mode, there are specific requirements for converting the bond state of ESD in DAO, which will cause additional time and fluidity risks, which are unique to ESD.
Stablecoins also bring new regulatory challenges. A new US Congress bill, "Stablecoin Constraints and Bank License Enforcement Act" (STABLE) will require issuers to obtain bank licenses and regulatory approvals before issuing any stablecoins. Algorithmic stablecoins such as Basis Cash, as well as many stablecoin issuers that currently do not have a bank license, will obey this rule. Basis.io was shut down. Faced with more supervision in the future, the founders of Based and ESD remain anonymous. Although the regulatory environment is constantly changing, algorithmic stable currency innovation is shaping the future of DeFi currency, while stabilizing prices, while playing a key role in ensuring secure digital transactions.
The bifurcation of Basis and ESD
Many new algorithmic stablecoins have been launched one after another, all of which are forks of Basis Cash and ESD. On December 30, Basis's fork Mithril Cash went live. For Mithril Cash's economic model, its function is similar to the process by which the central bank determines the target value of fiat currency. By buying and selling bonds, Mithril controls the entire supply of tokens and achieves a target value of $1. The smart contract supporting the MIC algorithm maintains the token price between US$0.99 and US$1.01, ensuring long-term prediction of price trends and maintaining stability.
The Mithril Cash protocol has the following three tokens:
1. Mithril Cash (MIC)-the stablecoin in the Mithril system, with a target value of US$1, and the current circulation is close to 29 million.
2. Mithril Stock (MIS) —— This token can prove the owner of the stock. After inflation occurs, the token holder can receive rewards, because only after the assets are pledged in the smart contract can they own Mis tokens, and the total supply of Mis The quantity reaches 1 million pieces.
3. Mithril Bond (MIB)-one represents the price of 1 MIC. After the price of MIC exceeds 1 USD, it can be redeemed and exchanged for 1MIC. The purpose of MIC and MIB is to achieve the target value of MIC through price fluctuation.
The demand for a variety of stablecoins with stable prices is on the rise. Mithril Cash provides a promising model to create more reliable stablecoins.
As a fork of ESD, Dynamic Set Dollar is a new algorithm stable currency. The Dynamic Set Dollar protocol has two major features. They are a price-sensitive ERC-20 algorithm stable currency, which aims to maintain a stable value. The second is that the price of $DSD fluctuates during the inflation and deflation phase, which brings investors Come for arbitrage opportunities. DSD has made many important improvements to the ESD protocol, including the addition of coupon redemption penalties to reduce the impact of robots. The epoch time has been shortened to 2 hours, and it can respond faster to price changes.
The impact of stablecoins expands
The emergence of stablecoins has facilitated transactions and value transfer, combining the efficiency, security and speed of digital currencies with the stability of legal currencies. At present, the global market value of stablecoins is billions of dollars, and the demand for them continues to grow.
Now, both the economy and technology are constantly evolving. As far as large technology companies are concerned, the financial products and systemic businesses they provide are replacing traditional bank services. Stablecoins can represent the disruption of the traditional payment and financial industries. For example, if stable currency projects such as Facebook's Libra coin can usher in large-scale applications, it may reshape the digital payment landscape, but it will also bring new risks to the global financial system and the circulation of sovereign legal tender and pose challenges to monetary policy.
The regulatory environment in the United States continues to evolve. For example, the OCC recently approved banks to use stablecoins, highlighting the growing demand for stablecoins in banks and authorized payment activities. In the next ten years of the global economy, approximately 70% of the added value is expected to come from digital platforms. Stablecoins provide a new secure and price-stable payment system, which is very suitable for the vibrant financial market.
mass adoption coming
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
Source of plagiarism
Direct translation without giving credit to the original author is Plagiarism.
Repeated plagiarism is considered fraud. Fraud is discouraged by the community and may result in the account being Blacklisted.
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #appeals in Discord.
Please note that direct translations including attribution or source with no original content are considered spam.