Introduction
The blockchain must constantly adjust to new demands. It is a recent technology which is in frank evolution.
Sometimes to meet the needs of growing demographics, platform expansion, crypto space evolution, scalability, adaptability and vulnerability to cyber attack risks.
What is a FORK?
"Different types of updates for the improvement of a blockchain may require major changes in the protocol which must be accepted in consensus by the node operators in order to become operational, such modifications or Forks are implanted in a block with a specific creation date; they may be contained in the same chain or give rise to a new one, depending on the nature, concept and object of its creation."


What is a HARD FORK?
Hard Fork
It is the splitting of a blockchain from a block created to update the project or develop a new derivation with certain rule changes oriented, usually, to the improvement of the system from the point of view of security or scalability.
The fork will be executed with the nodes that adopt the new protocol and conform to the new update because the update is incompatible with the original chain and the two do not recognize each other for operational purposes.
What is its usefulness?
"Despite being an independent project, the Hard Fork shares the genesis block of the original project, as well as, part of its history, only up to the creation of the block with the protocol change information."
It should be noted, that a hard fork will give rise to the creation of a new cryptocurrency which will operate and store its accounting record in the new chain created, therefore, additionally we are talking about the origin of an ecosystem that will not keep any relation with the original blockchain from which it comes since the chain starts from the block where the hard fork occurred.

Example of HARD FORK
For this occasion I wanted to take as an example the Bitcoin Diamond cryptocurrency (BCD), which comes from a fork of the 495866 block of Bitcoin.
The BCD cryptocurrency was created with the aim of improving common problems with the bitcoin blockchain related to: Speed, transactional cost and mining.
Hard Fork BCD Case Count
Corresponds to a scheduled hard fork that took place on 11/24/2017 where a group of miners reached an agreement to create the "Bitcoin Diamond" blockchain and stop operating on the original Bitcoin chain. They bid for the time of the snapshot an equivalent of 10:1 BCD for each BTC estimating that this would reduce operational fees, likewise, would work on a new proof-of-work algorithm (X13) optimized which uses the "Lightning" network to streamline off-network payments guaranteed speed and unlimited operations at low cost.
The source was consulted: link

In the following part I have consulted the BTC and BCD blocks using a block explorer in order to find the record corresponding to the block where the fork occurred, as well as, the BTC genesis block data which is common for blockchain masters.
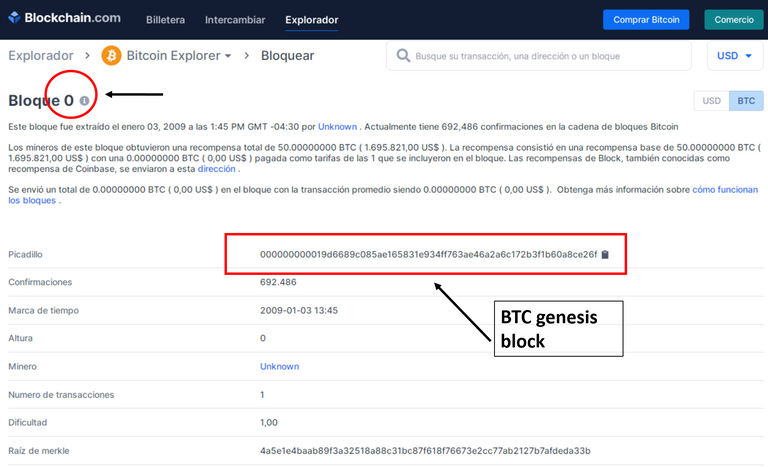
In the graph we observe that BCD and BTC share the same genesis block:
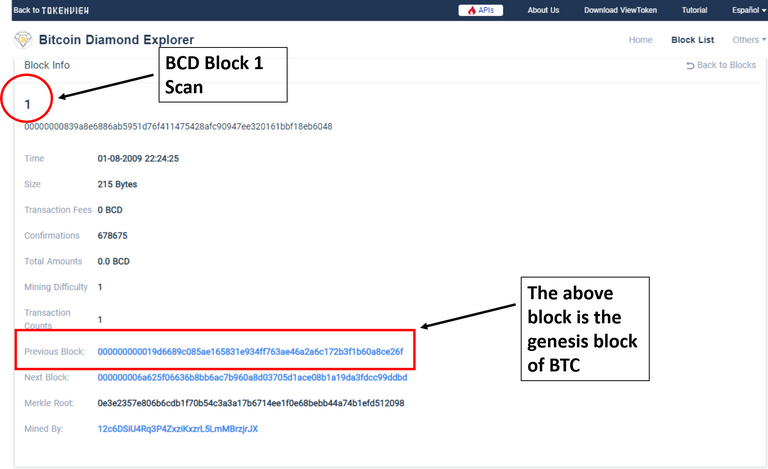
It may also be noted that the "block 0" BTC is not chained to a previous block as it refers to the first consensus reached by the nodes in the Bitcoin chain.
Final Thoughts
A Hard Fork is a scheduled process that serves to update the protocol of a blockchain, it must be taken into account that the technology is constantly evaluating and growing and in the same way it is also susceptible to possible cyber attacks or restructuring of the CEO.
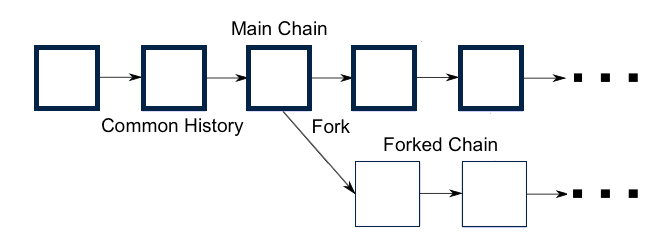
"In the example in the graph we observe, how after the Har Fork, the chain splits into two independent protocols that share the same history only up to the block where the FORK occurred. From then on the chains are not linked at all."
Finally, the update is executed on the cryptocurrency; it can be the native cryptocurrency or a new cryptocurrency created, which has been improved, therefore, the genesis block is recognized, but not necessarily the entire chain which will be characterized as independent and decentralized (autonomous).
The Hard Fork is necessary to solve the problems that arise in the computing structure of a blockchain and may come to represent a benefit for users as much as for the sustainable future of an ecosystem.

Original content
2021
