Emotional well-being alludes to mental, social, and close to home prosperity. Everything revolves around individuals' thought process, feel, and act. Individuals at times utilize the expression "psychological wellness" to mean the shortfall of a psychological problem.

A mental patient
Emotional well-being can influence everyday living, connections, and actual wellbeing.
In any case, this connection additionally works in the other bearing. Factors in individuals' lives, relational associations, and actual elements can add to mental medical affliction.
Taking care of psychological well-being can safeguard an individual's capacity to appreciate life. Doing this includes adjusting life exercises, obligations, and endeavors to accomplish mental strength.
Stress, discouragement, and nervousness can all influence psychological well-being and upset an individual's everyday practice.
In spite of the fact that wellbeing experts frequently utilize the term emotional well-being, specialists perceive that numerous mental issues have actual roots.
This article makes sense of what individuals mean by psychological wellness and dysfunctional behavior. We likewise depict the most widely recognized sorts of mental problems, including their initial signs and how to treat them.
The WHO expresses that psychological well-being is "something other than the shortfall of mental problems or inabilities." Peak emotional well-being isn't just about overseeing dynamic circumstances yet in addition taking care of progressing health and joy.
It likewise stresses that saving and reestablishing emotional wellness is critical exclusively and at a local area and society level.
In the United States, the National Alliance on Mental Illness assesses that just about 1 of every 5 grown-ups experience emotional well-being issues every year.
In 2020, an expected 14.2 million adultsTrusted Source in the U.S., or around 5.6%, had a serious mental condition, as per the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
Risk factors for mental health conditions
Everybody is at some gamble of fostering a psychological wellness problem, paying little mind to mature, sex, pay, or identity. In the U.S. also, a large part of the created world, mental issues are one of the main sources of handicap.
Social and monetary conditions, unfriendly youth encounters, organic elements, and hidden ailments can all shape an individual's emotional well-being.
Many individuals with a psychological well-being problem have more than each condition in turn.
It is critical to take note of that great emotional well-being relies upon a sensitive equilibrium between variables and that few components might add to fostering these problems.
The accompanying elements can add to psychological wellness disturbances.
Continuous social and economic pressure
Having restricted monetary means or having a place with an underestimated or oppressed ethnic gathering can build the gamble of emotional well-being issues.
A 2015 Iranian studyTrusted Source depicts a few financial reasons for emotional well-being conditions, remembering neediness and living for the edges of an enormous city.
The scientists likewise depicted adaptable (modifiable) and firm (nonmodifiable) factors that influence the accessibility and nature of psychological well-being treatment for specific gatherings.
Modifiable variables for psychological well-being problems include:
financial circumstances, for example, whether work is accessible in the neighborhood
occupation
an individual's degree of social 1) inclusion
- instruction
- lodging quality
- orientation
Nonmodifiable variables include: - orientation
- age
- nationality
- ethnicity
The analysts tracked down that being female expanded the gamble of low psychological well-being status by almost multiple times. Individuals with a "frail financial status" likewise scored most elevated for psychological wellness conditions in this review.
Childhood adversity
Numerous studies A growing child's mental and physical health are greatly impacted by traumatic childhood events such child abuse, parental illness, loss, and separation, according to reliable sources.
Additionally, there are links between unfavorable events and other psychotic diseases, including childhood maltreatment. Additionally, these events increase a person's risk of developing post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Biological factors
According to the NIMH, a person's genetic family history may A person is more likely to develop mental health issues as a result of particular genes and gene variants that increase risk.
However, a variety of additional factors also play a role in the emergence of these illnesses.
The presence of a gene linked to a mental health illness does not ensure that the disorder will manifest. Similar to how those with linked genes or a family history of mental illness can still experience problems with their mental health.
Chronic physical health issues like cancer, diabetes, and chronic pain can lead to mental health diseases like depression and anxiety as well as chronic stress.
Types of mental health disorders
Due to traits they share, particular mental diseases are categorized. Here are a few examples of mental illnesses:
- anxiety disorders
- mood disorders
- schizophrenia disorders
Anxiety disorders
The most prevalent mental illness, according to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, is anxiety disorders.
People who have these illnesses experience intense fear or anxiety in relation to particular things or circumstances. Most individuals with anxiety disorders make an effort to limit their exposure to anything that makes them anxious.
Here are a few illustrations of anxiety disorders.
Generalized anxiety disorder
An excessive amount of concern or fear that interferes with daily life is a symptom of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
Physical signs that people may experience include:
- restlessness
- fatigue
- poor concentration
- tense muscles
- interrupted sleep
In patients with GAD, an anxiety attack does not always require a specific cause.
When confronted with routine scenarios like housework or appointments that don't directly endanger them, they may get overly anxious. Anxiety can occasionally strike a person with GAD with no apparent trigger.
Panic disorder
Regular panic attacks characterized by extreme anxiety or a sense of impending doom affect people with panic disorders.
PTSD
After experiencing or witnessing a highly stressful or traumatic event, PTSD may develop. The person believes that their life or the lives of others are in risk during this kind of incident. They might experience fear or the notion that they are powerless over the situation.
PTSD may then result from these trauma and fear-related feelings.
Mood Disorder.
Affective disorders and depressive disorders are other terms used to describe mood problems.
These illnesses cause severe mood swings in sufferers, which are typically either mania—a period of extreme vigor and joy—or sadness. Mood disorders include, for example:
Major Depression: A person with significant depression has a persistently depressed mood and loses interest in things and situations they once found enjoyable (anhedonia). They may experience intense sadness over extended periods of time.
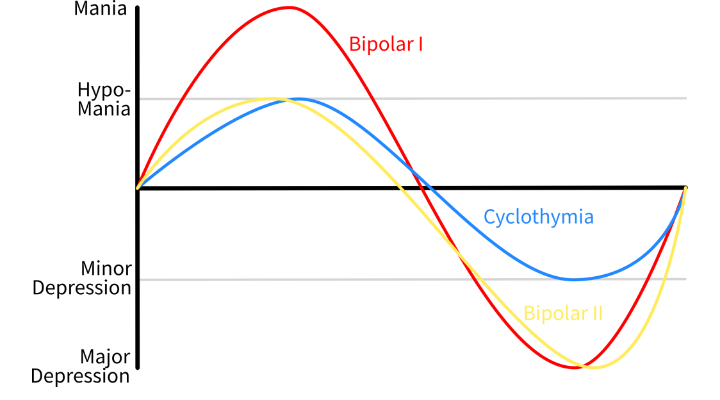
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar disorder causes unusual fluctuations in a person's mood, energy level, amount of activity, and capacity to go about their daily lives. Manic phases are times of extreme mood, while depression phases are times of extreme low mood.
Seasonal Affective Disorder: This sort of serious depression is brought on by less daylight in the fall, winter, and early spring. dependable source It is especially prevalent in nations that are far from the equator.
Schizophrenia disorders:
The term "schizophrenia" is frequently used to describe a range of illnesses marked by severe psychotic symptoms. These are extremely difficult circumstances.
The NIMH reports that symptoms of schizophrenia often appear between the ages of 16 and 30Reliable Source. The person may also have trouble processing information and have scattered ideas.
Both negative and positive signs of schizophrenia exist. Delusions, thought disorders, and hallucinations are instances of positive symptoms, whereas withdrawal, a lack of desire, and an unsuitable or flat mood are examples of negative symptoms.