Testicular torsion represents a real urological urgency to be more specific, and this is the product of one of the testicles contained in the scrotal pouch rotating on its own axis or vascular pedicle, thus generating an obstruction and if the ischemia and necrosis of the same is not reversed.
This pathological entity is more frequent in those between 12 and 18 years of age; however, cases have been reported in neonatal age and in geriatric patients.

Public domain Pxfuel
Anatomy
Testicles
The testicles are two oval-shaped glands, one on each side of the penis, contained and protected by the scrotal sac and suspended by the spermatic cord. They weigh an estimated 10 to 15 grams.
Thanks to the internal constitution of each testicle, which includes seminiferous tubules, made up of two groups of cells called spermatogenic cells and Sertoli cells, whose purpose is to give rise to sperm. There is an underlying connective tissue made up of Leydig cells, which are responsible for secreting testosterone and androgens.
Epididymus
In number of two and in the shape of a coma, with an approximate length of 4 cm, attached or attached to each testicle in its upper and postero-lateral portion, its function is to store the sperm and to release it during sexual excitement, by means of peristaltic contractions, triggered by the smooth wall muscles and through the Urethra.
Scrotum
As described above, the scrotum represents a sac of skin tissue, whose function is to contain and protect the testicles. It is located below and behind the penis and the pubic symphysis.
In addition, it contains the so-called cremaster muscle, which is no more than a small band of striated muscle, and its purpose is to protect the testicles when they are subjected to low temperatures.
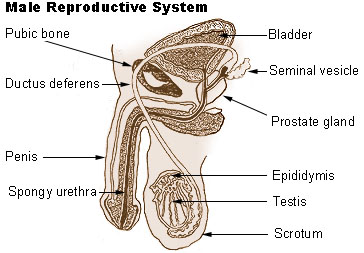
Male Reproductive System Anatomy. Public domain from wikipedia
In general terms, the male reproductive system is made up of:
External genitalia: penis, testicles and scrotum.
Internal organs: seminal vesicles, ejaculatory ducts, and deferens.
Genital glands: bulb-urethral, prostate.
Physiopathology
Testicular obstruction obstructs the vascular irrigation of the testicles, which generates edema and finally, by causing complete arterial obstruction, leads to ischemia and necrosis.
Complete vascular occlusion will produce irreversible and permanent damage rather than partial vascular obstruction.
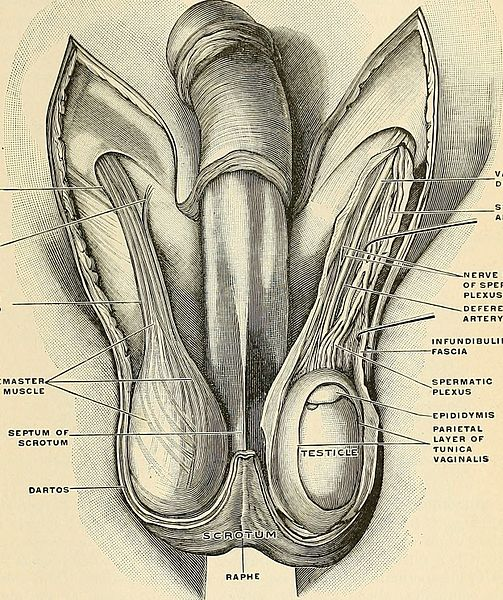
Structures involved in testicular torsion. Public domain form wikipedia
Most of the literature agrees that such a twist should resolve within 6 to 24 hours, with better results seen in that which is treated within the first 6 hours. Testicular torsion can be classified as extravaginal and intravaginal.
Extravaginal torsion affects newborns, where the testicle with its epididymis and the tunic albicans rotate on its vertical axis. The product of this torsion is the fact that the gutter is not attached to the scrotal wall, allowing free rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord.
In relation to intravaginal torsion, it affects peri-pubertal men, associated with the bell-shaped clapper deformity, which is given by the vaginal tunic completely covering the testicle, epididymis and the base of the cord, which facilitates their free rotation within the tunic.
We must take into account that both intravaginal and extravaginal torsion always occurs inwards or towards the middle.
Current recommendations suggest the removal of a necrotic testicle or one that remains necrotic after detorsion, and the preservation of any viable testicle.
Several theories have been put forward regarding the immune role and future fertility. One theory argues that ischemic damage to the testicle breaks down the hematotensive barrier, allowing the body to produce antibodies that attack the contralateral testicle.
Another theory explains that abnormal or subfertile testicles present a greater risk of torsion.
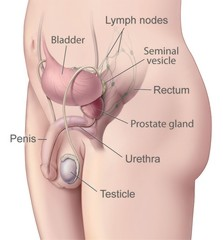
Male Genitourinary Anatomy. NIH Medical Arts. National Cancer Institute (NCI). Public domain
Indications
Attempts should be made to manually reduce all suspected testicular torsion. If torsion resolves within the first 6-8 hours of the onset of symptoms, the survival of the testicle is up to 100%.
Manual detorsion after prolonged periods of time is difficult due to oedema, but since the complications are minimal compared to those that do not occur, regardless of the time of evolution, if testicular torsion is suspected, it should be untwisted.
Contraindications
There is no absolute contraindication for attempting to manually reduce the torsion of a testicle, but there are cases where this manoeuvre is contraindicated.
If the testicle has been fixed to the scrotal wall, it is probable that it is already necrotic and this manoeuvre may no longer be possible, but rather that management is already surgical.
If intense pain and oedema prevent the doctor from manipulating this area, such as putting firm pressure on the testicle and therefore not carrying out the detorsion.
In those cases where the suspicion of testicular torsion is very low, it is suggested that a Doppler ultrasound be requested to certify said diagnosis.

Human testicle. Public domain Wikipedia CC BY-SA 3.0
Preparation the patient
As is customary and correct, we must explain to the patient and/or represent the medical technique to be performed. Inform him/her that the technique will be quick, simple but painful.
In most cases, the administration of pain relief drugs can interfere with the success of the maneuver, as it can generate false positives. Although the use of anesthesia is clearly not contraindicated, it can be useful according to the patient's age and the physician's preference.
What we should avoid is intravenous sedation, or blocking the spermatic cord, since it interferes with the patient's ability to assess pain and determine the success of the detorsion. Remember that local spermatic cord anesthesia may compromise future testicular blood flow.
The potential complications are severe pain, edema, and ultimately the inability to successfully shrink the testicle. Similarly, whether the detorsion is satisfactory or not, it will be necessary to take the patient to an operating table to correct the alterations that have precipitated new episodes of testicular torsion in the future.
Technique
It has been described that more than 90% of the twists occur in an internal or medial direction. Therefore, in order to carry out a reduction, the testicle must be rotated outwards or in a lateral direction.
Another way is to visualize the patient in a supine position, rotating the affected testicle. If the right one is rotating in a clockwise direction, the left testicle would be counting in a clockwise direction.
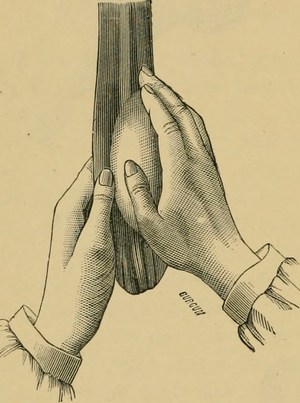
Another option is to place the patient in the supine or semi-supine position. Place the right hand on the affected testicle, grasp the spermatic cord with the other hand to fix it. Hold the testicle firmly, but gently, and rotate the testicle with the scrotum about 180 degrees outward.
However, it is recommended to reduce the torsion of the testicle until the patient experiences relief from pain, which will give us the certainty that everything is already in place.
We must bear in mind that there is a small part of the affected population where the testicles rotate outwards or sideways, and it is for this reason that if during their outward detorsion, which is common, the patient experiences more pain and edema, we must stop and rotate in the opposite direction.
Public domain Flickr
Confirmation
The successful reduction is manifested by the patient's feeling of relief and by the restoration of normal anatomy and good coloring of the area.
The normal anatomy is delimited by the elongation of the spermatic cord and the vertical position of the testicle. In relation to the decrease in edema, this will depend on the degree and duration of the ischemia (absence of blood flow, product of torsion), but it will never be as immediate and evident as the relief of pain.
If the patient refers to relief during the manoeuvre, but it is evident that the testicles remain in a horizontal position, we must continue to twist or reduce them until they take on a vertical position that is anatomically correct.
After care
Every patient who brings a testicular torsion to the emergency department should try to reduce and solve it manually. If this is not achieved, take the patient to the surgical table by the urology service, a specialist doctor, to correct this pathology.
In those cases, where the reduction was satisfactory, the patient should also be admitted by the urology service and plan surgery to correct the anatomical alteration that is precipitating the presentation of clinical pictures of testicular torsion, thus avoiding the reappearance of future testicular torsion.
The bell clapper deformity involves many cases of testicular torsion bilaterally, therefore, it is likely that the patient will experience contralateral testicular torsion soon after.
Due to the high risk of altered fertility in these cases, following torsion, every effort should always be made to preserve the function of at least the contralateral testicle in those severe and long-standing cases.
Some important recommendations
All emergency physicians are advised to have a knowledge of this testicular torsion technique and be prepared to reduce it rapidly by hand.
It is important to notify the urology service on call immediately, since the time of ischemia and the probability of saving the testicle are inversely related.
Manual reduction of torsion may alleviate and reduce ischemia, increase survival and guarantee the preservation of testicular fertility.
Always remember that all patients with testicular torsion should receive definitive treatment in the operating theatre.
Sources:

steemSTEM is a project of the chain of blocks that supports the scientific content in different areas of science. If you want to know more about this wonderful project you can join the server in discord
This article will be published at https://www.steemstem.io/

link
If you have any questions about any topic of medicine or present any disease you can comment the publication or write me in discord and I will attend you.
Dr. Ana EstradaI hope you enjoyed my content.
aua 😂
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie and @minnowbooster.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness @stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Thanks for having used the steemstem.io app and included @steemstem in the list of beneficiaries of this post. This granted you a stronger support from SteemSTEM.
Thank you for support
A friend of mine had this. It occured when he was running and he dropped to his knees in the middle of his run. Had to go to the emergency room for treatment. He started wearing a jock strap on his runs after he recovered.
painful enough :(