Photochemical halogenation:
Photochemical halogenation, which is used to create numerous halogen derivatives, including the well-known insecticide hexachlorane (hexachlorocyclohexane), is of great practical significance. The following reactions are included in the overall scheme of photochlorination:
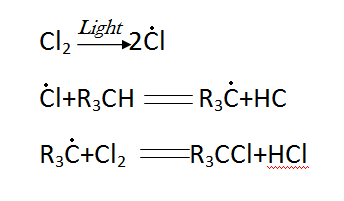 where R is a hydrocarbon radical.
where R is a hydrocarbon radical.
[Created by using microsoft paint and word]
- Alkyl sulfochlorides with industrial significance are produced by passing a chlorine+sulfur anhydride mixture through a hydrocarbon solution in tetrachloromethane:
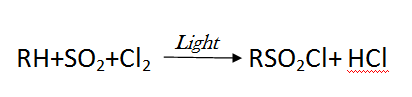
[Created by using microsoft paint and word]
Photopolymerization:
The process of photopolymerization is made possible by the radicals that are created when light interacts with a substance. Vinyl acetate is converted into polyvinyl acetate through photopolymerization (wavelength is in the visible range between 3000 and 6000A°).
Hydrolytic reactions:
Additionally, light can start some hydrolytic processes. Under the influence of light, amino acids are hydrolyzed in solution to produce oxyacids and ammonia; occasionally, ketonic acids are also produced. An example of how alanine reacts in a 0.1N HCl solution is as follows:
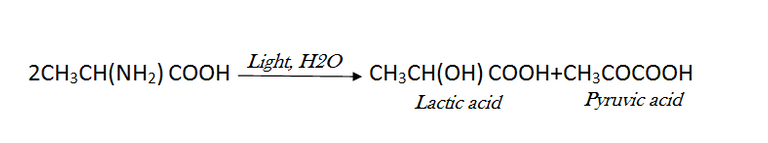
[Created by using microsoft paint and word]
- Irradiation is a potent way to produce radicals, so using radiation in the synthesis of polymers is becoming increasingly important. Radicals play important roles in polymerization and other processes that give rise to macromolecular compounds.
Irradiated polymerizations are typically performed in gaseous or liquid media. Water is the most commonly used solvent because organic radicals, due to their low activity, cannot decompose water molecules. The acrylic polyamide is formed from the acrylic amide through this process. Radiation polymerization is also used to make polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, and other materials.
When an already-formed polymer is exposed to radiation, it goes through a process known as cross-linking, which involves the creation of new bonds between the molecules' chains at transverse junctions, raising the melting point and viscosity of the polymer. The polymer becomes less soluble in solvents. The irradiation results in the polymer's disaggregation if, on the other hand, the CH2 groups and substituted groups are arranged alternately in the polymer. Teflon, polymethyl methacrylate, and other materials degrade due to radiation in the same way.
References:
[Smail Meziane: Livre Chimie générale- Structure de la matiére. Berti edition, Alger, 2006]
[Principles & Applications of Photochemistry, Brian Wardle,Wiley, ISBN 0470014938]
[R. OUAHES et B. DEVALLEZ- Chimie générale- Office des publacations universitaires- Alger]
[Norman S. Allen- Photochemistry and Photophysics of Polymeric Materials]
T. Mill- Reactions and Processes: Chemical and Photo Oxidation
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.