Pattern Formation And Solitons
Angular and radial correlation scaling in stochastic growth morphodynamics: a unifying fractality framework (1803.03715v2)
J. R. Nicolás-Carlock, J. M. Solano-Altamirano, J. L. Carrillo-Estrada
2018-03-09
Fractal/non-fractal morphological transitions allow for the systematic study of the physical mechanisms behind fractal morphogenesis in nature. In these systems, the fractal dimension is considered a non-thermal order parameter, commonly and equivalently computed from the scaling of quantities such as the two-point density radial or angular correlations. However, persistent discrepancies found during the analysis of basic models, using these two quantification methods, demand important clarifications. In this work, considering three fundamental fractal/non-fractal transitions in two dimensions, we show that the unavoidable emergence of growth anisotropies is responsible for the breaking-down of the radial-angular equivalence, rendering the angular correlation scaling crucial for establishing appropriate order parameters. Specifically, we show that the angular scaling behaves as a critical power-law, whereas the radial scaling as an exponential, that, under the fractal dimension interpretation, resemble first- and second-order transitions, respectively. Remarkably, these and previous results can be unified under a single fractal dimensionality equation.
High-order couplings in geometric complex networks of neurons (1907.06765v1)
A. Tlaie, I. Leyva, I. Sendiña
2019-07-15
We explore the consequences of introducing higher-order interactions in a geometric complex network of Morris-Lecar neurons. We focus on the regime where travelling synchronization waves are observed out of a first-neighbours based coupling, to evaluate the changes induced when higher-order dynamical interactions are included. We observe that the travelling wave phenomenon gets enhanced by these interactions, allowing the information to travel further in the system without generating pathological full synchronization states. This scheme could be a step towards a simple modelization of neuroglial networks.
Self-Localized Solitons of the Nonlinear Wave Blocking Problem (1907.03857v2)
Cihan Bayindir
2019-07-08
In this paper, we propose a numerical framework to study the shapes, dynamics and the stabilities of the self-localized solutions of the nonlinear wave blocking problem. With this motivation, we use the nonlinear Schr"odinger equation (NLSE) derived by Smith as a model for the nonlinear wave blocking. We propose a spectral renormalization method (SRM) to find the self-localized solitons of this model. We show that for constant, linearly varying or sinusoidal current gradient, i.e. dU/dx, the self-localized solitons of the Smith's NLSE do exist. Additionally, we propose a spectral scheme with 4th order Runge-Kutta time integrator to study the temporal dynamics and stabilities of such solitons. We observe that self-localized solitons are stable for the cases of constant or linearly varying current gradient however, they are unstable for sinusoidal current gradient, at least for the selected parameters. We comment on our findings and discuss the importance and the applicability of the proposed approach.
Inverse scattering transform for two-level systems with nonzero background (1907.06231v1)
Gino Biondini, Ildar Gabitov, Gregor Kovacic, Sitai Li
2019-07-14
We formulate the inverse scattering transform for the scalar Maxwell-Bloch system of equations describing the resonant interaction of light and active optical media in the case when the light intensity does not vanish at infinity. We show that pure background states in general do not exist with a nonzero background field. We then use the formalism to compute explicitly the soliton solutions of this system. We discuss the initial population of atoms and show that the pure soliton solutions do not correspond to a pure state initially. We obtain a representation for the soliton solutions in determinant form, and explicitly write down the one-soliton solutions. We next derive periodic solutions and rational solutions from the one-soliton solutions. We then analyze the properties of these solutions, including discussion of the sharp-line and small-amplitude limits, and thereafter show that the two limits do not commute. Finally, we investigate the behavior of general solutions, showing that solutions are stable (i.e., the radiative parts of solutions decay) only when initially atoms in the ground state dominant, i.e., initial population inversion is negative.
Spontaneous and engineered transformations of topological structures in nonlinear media with gain and loss (1907.06180v1)
B. A. Kochetov, O. G. Chelpanova, V. R. Tuz, A. I. Yakimenko
2019-07-14
In contrast to conservative systems, in nonlinear media with gain and loss the dynamics of localized topological structures can exhibit unique features that can be controlled externally. We propose a robust mechanism to perform topological transformations changing characteristics of dissipative vortices and their complexes in a controllable way. We show that a properly chosen control carries out the evolution of dissipative structures to regime with spontaneous transformation of the topological excitations or drives generation of vortices with control over the topological charge.
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
 sigma models described through hypergeometric orthogonal polynomials (1905.06351v2)
sigma models described through hypergeometric orthogonal polynomials (1905.06351v2)
N. Crampe, A. M. Grundland
2019-05-15
The main objective of this paper is to establish a new connection between the Hermitian rank-1 projector solutions of the Euclidean
sigma model in two dimensions and the particular hypergeometric orthogonal polynomials called Krawtchouk polynomials. We show that any such projector solutions of the
model, defined on the Riemann sphere and having a finite action, can be explicitly parametrised in terms of these polynomials. We apply these results to the analysis of surfaces associated with
models defined using the generalised Weierstrass formula for immersion. We show that these surfaces are homeomorphic to spheres in the
algebra, and express several other geometrical characteristics in terms of the Krawtchouk polynomials. Finally, a connection between the
spin-s representation and the
model is explored in detail.
An Index for Quantum Integrability (1907.07186v1)
Shota Komatsu, Raghu Mahajan, Shu-Heng Shao
2019-07-16
The existence of higher-spin quantum conserved currents in two dimensions guarantees quantum integrability. We revisit the question of whether classically-conserved local higher-spin currents in two-dimensional sigma models survive quantization. We define an integrability index
for each spin
, with the property that
is a lower bound on the number of quantum conserved currents of spin
. In particular, a positive value for the index establishes the existence of quantum conserved currents. For a general coset model, with or without extra discrete symmetries, we derive an explicit formula for a generating function that encodes the indices for all spins. We apply our techniques to the
model, the
model, and the flag sigma model
. For the
model, we establish the existence of a spin-6 quantum conserved current, in addition to the well-known spin-4 current. The indices for the
model for
are all non-positive, consistent with the fact that these models are not integrable. The indices for the flag sigma model
for
are all negative. Thus, it is unlikely that the flag sigma models are integrable.
Benney-Lin and Kawahara equations: a detailed study through Lie symmetries and Painlevé analysis (1907.06918v1)
Andronikos Paliathanasis
2019-07-16
We perform a detailed study on the integrability of the Benney-Lin and KdV-Kawahara equations by using the Lie symmetry analysis and the singularity analysis. We find that the equations under our consideration admit integrable travelling-wave solutions. The singularity analysis is applied for the partial differential equations and the generic algebraic solution is presented.
 gauge theory, free fermions on the torus and Painlevé VI (1901.10497v2)
gauge theory, free fermions on the torus and Painlevé VI (1901.10497v2)
Giulio Bonelli, Fabrizio Del Monte, Pavlo Gavrylenko, Alessandro Tanzini
2019-01-29
In this paper we study the extension of Painlev'e/gauge theory correspondence to circular quivers by focusing on the special case of
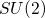
theory. We show that the Nekrasov-Okounkov partition function of this gauge theory provides an explicit combinatorial expression and a Fredholm determinant formula for the tau-function describing isomonodromic deformations of
flat connections on the one-punctured torus. This is achieved by reformulating the Riemann-Hilbert problem associated to the latter in terms of chiral conformal blocks of a free-fermionic algebra. This viewpoint provides the exact solution of the renormalization group flow of the
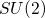
theory on self-dual
-background and, in the Seiberg-Witten limit, an elegant relation between the IR and UV gauge couplings.
Algebra of Dunkl Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector (1907.06706v1)
Misha Feigin, Tigran Hakobyan
2019-07-15
We introduce Dunkl version of Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector associated with a finite Coxeter group
acting geometrically in
with multiplicity function
. This vector commutes with Dunkl Laplacian with additional Coulomb potential
, and it generalises the usual Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector. We study resulting symmetry algebra
and show that it has Poincar'e-Birkhoff-Witt property. In the absence of Coulomb potential this symmetry algebra is a subalgebra of the rational Cherednik algebra
. We show that its central quotient is a quadratic algebra isomorphic to a central quotient of the corresponding Dunkl angular momenta algebra
. This gives interpretation of the algebra
as the hidden symmetry algebra of Dunkl Laplacian. On the other hand by specialising
to
we recover a quotient of the universal enveloping algebra
as the hidden symmetry algebra of Coulomb problem in
.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.