[ESP]
En el mundo de la tecnología moderna, hay componentes invisibles que juegan roles cruciales en casi todos los dispositivos electrónicos que usamos a diario, desde nuestros teléfonos móviles hasta los sistemas de energía solar. Entre estos componentes esenciales, los semiconductores y, más específicamente, los diodos, son los héroes silenciosos que hacen posible el funcionamiento eficiente y efectivo de innumerables aparatos. Pero, ¿alguna vez te has preguntado qué son exactamente los diodos, cómo funcionan y por qué son tan vitales en la electrónica? Si tienes curiosidad por descubrir la magia detrás de estos pequeños pero poderosos componentes, estás en el lugar correcto. ¡Acompáñanos en este viaje fascinante al corazón de la electrónica moderna!
¿Qué son los Semiconductores?
![]()
Los semiconductores son materiales que tienen una conductividad eléctrica entre la de los conductores (como los metales) y los aislantes (como el vidrio). Los semiconductores más comunes están hechos de silicio, pero también pueden estar compuestos de otros materiales como germanio y compuestos de elementos del grupo III-V (como arseniuro de galio).

Diodos
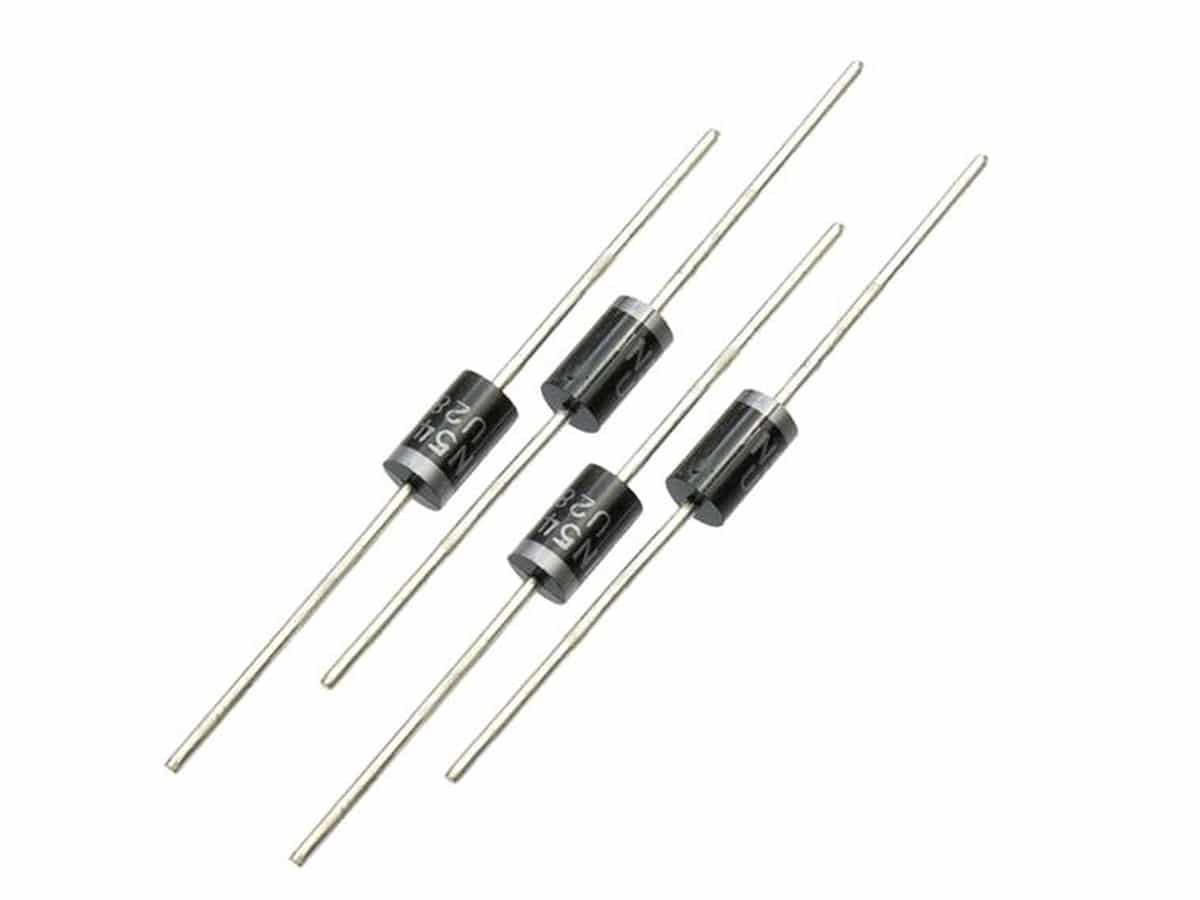

Composición y Estructura
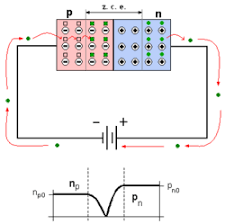
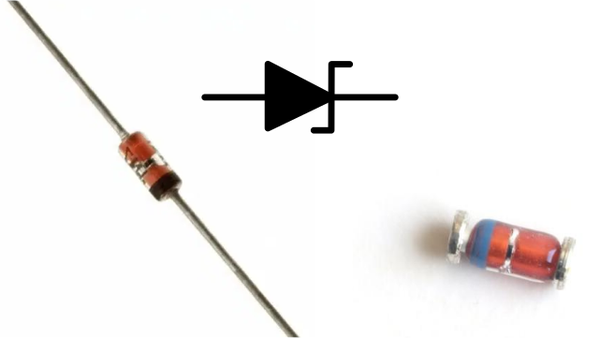
Los diodos son dispositivos semiconductores que permiten el paso de corriente en una sola dirección. Están compuestos por dos regiones de material semiconductor: una con carga positiva (tipo P) y otra con carga negativa (tipo N). La unión de estos dos tipos de semiconductores se llama unión PN.
- Región Tipo P: Tiene un exceso de huecos (portadores de carga positivos).
- Región Tipo N: Tiene un exceso de electrones (portadores de carga negativos).
Cuando estas dos regiones se juntan, se forma una barrera de potencial en la unión PN que impide el flujo de corriente en dirección contraria.
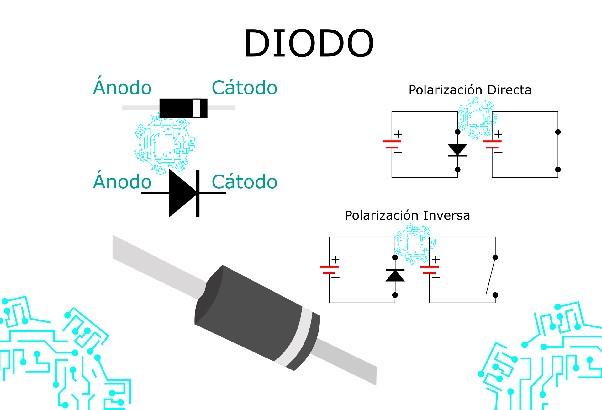
Funcionamiento
- Polarización Directa: Cuando el terminal positivo de la fuente de voltaje se conecta a la región P y el terminal negativo a la región N, la barrera de potencial disminuye, permitiendo el flujo de corriente.
- Polarización Inversa: Si se invierte la conexión, la barrera de potencial aumenta, impidiendo el paso de corriente.
Usos en Electrónica
Los diodos tienen diversas aplicaciones en electrónica, algunas de las más comunes son:
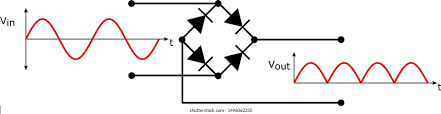
- Rectificación: Convertir corriente alterna (CA) en corriente continua (CC). Esto es fundamental en los adaptadores de corriente y en las fuentes de alimentación.
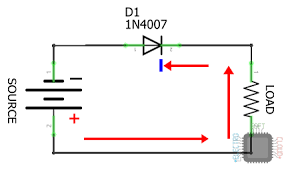
- Protección de circuitos: Proteger los componentes sensibles de voltajes inversos, como en los diodos de protección contra transitorios.
- Diodos Zener: Utilizados para regular voltajes y estabilizar fuentes de alimentación.
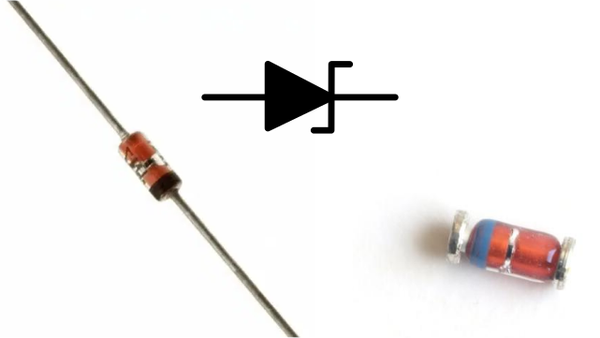
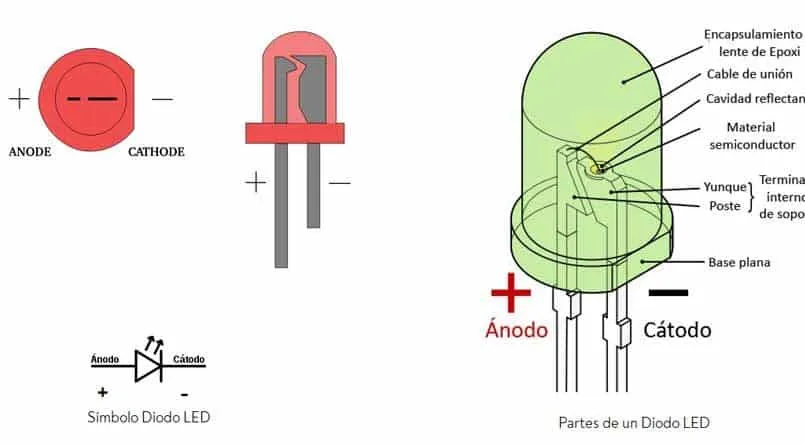
- Diodos LED (Light Emitting Diodes): Emiten luz cuando están polarizados directamente y son utilizados en indicadores, pantallas y luces.
Variedades de Diodos
Existen varios tipos de diodos, cada uno con características y aplicaciones específicas:
- Diodo Rectificador: Utilizado principalmente en la rectificación de corrientes.
- Diodo Zener: Opera en la región de ruptura inversa para mantener un voltaje constante.
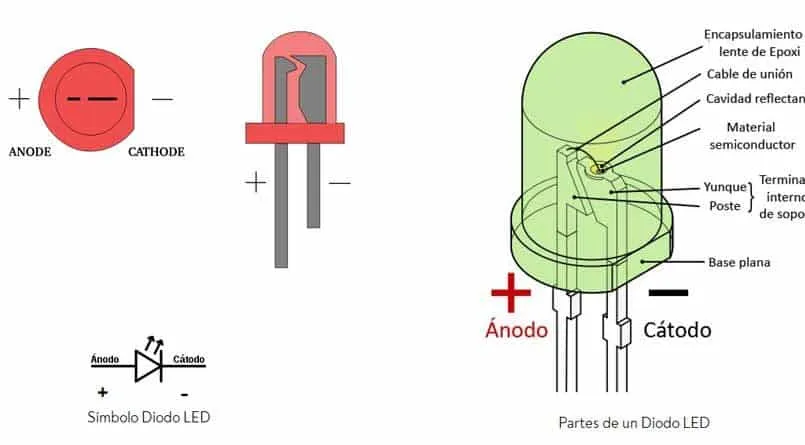
- Diodo LED: Emite luz cuando la corriente lo atraviesa en sentido directo.
- Diodo Schottky: Tiene una caída de voltaje directa más baja y una conmutación más rápida, utilizado en aplicaciones de alta velocidad.
- Diodo de Avalancha: Utilizado para proteger circuitos contra sobretensiones.
- Fotodiodo: Convierte luz en corriente eléctrica, utilizado en sensores y aplicaciones de detección de luz.
[ENG]
In the world of modern technology, there are invisible components that play crucial roles in almost all the electronic devices we use daily, from our mobile phones to solar energy systems. Among these essential components, semiconductors and, more specifically, diodes, are the silent heroes that enable the efficient and effective operation of countless devices. But, have you ever wondered what exactly diodes are, how they work and why they are so vital in electronics? If you are curious to discover the magic behind these small but powerful components, you are in the right place. correct place. Join us on this fascinating journey to the heart of modern electronics!
What are Semiconductors?
![]()
Semiconductors are materials that have an electrical conductivity between that of conductors (such as metals) and insulators (such as glass). The most common semiconductors are made of silicon, but they can also be composed of other materials such as germanium and compounds of group III-V elements (such as gallium arsenide).

Diodes
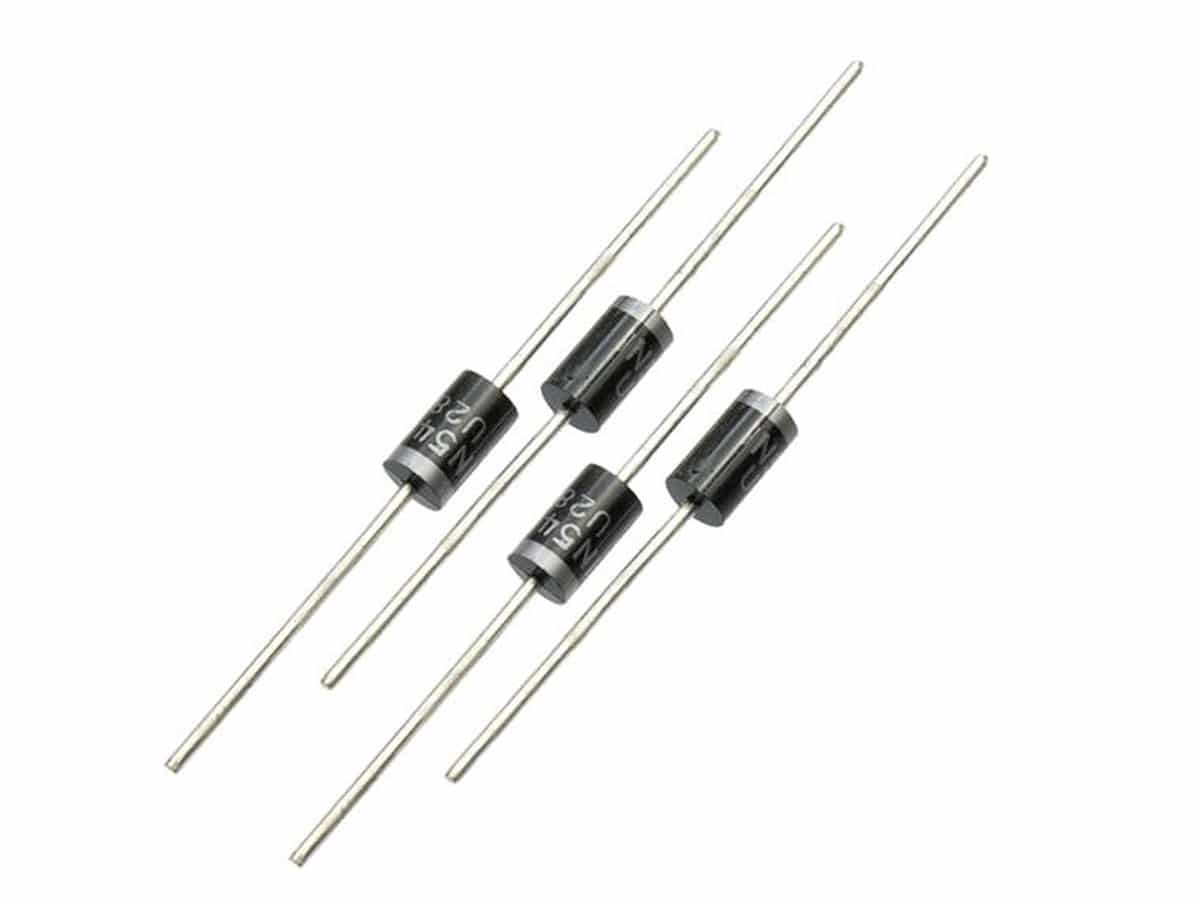

Composition and Structure
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are composed of two regions of semiconductor material: one with a positive charge (P type) and another with a negative charge (N type). The union of these two types of semiconductors is called PN junction.
- Type P Region: Has an excess of holes (positive charge carriers).
- Type N Region: Has an excess of electrons (negative charge carriers).
When these two regions come together, a potential barrier is formed at the PN junction that prevents current flow in the opposite direction.
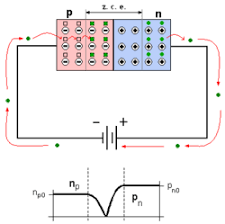
Functioning
- Forward Bias: When the positive terminal of the voltage source is connected to the P region and the negative terminal to the N region, the potential barrier decreases, allowing current to flow.
- Reverse Polarization: If the connection is reversed, the potential barrier increases, preventing the passage of current.

Uses in Electronics
Diodes have various applications in electronics, some of the most common are:
- Rectification: Convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This is essential in power adapters and power supplies.

- Circuit protection: Protect sensitive components from reverse voltages, such as transient protection diodes.

- Zener diodes: Used to regulate voltages and stabilize power supplies.
- LED diodes (Light Emitting Diodes): They emit light when they are directly polarized and are used in indicators, displays and lights.
Varieties of Diodes
There are several types of diodes, each with specific characteristics and applications:
- Rectifier Diode: Mainly used in the rectification of currents.
- Zener diode: Operates in the reverse breakdown region to maintain a constant voltage.
- LED diode: It emits light when current passes through it in a direct direction.
- Schottky diode: Has lower forward voltage drop and faster switching, used in high speed applications.
- Avalanche Diode: Used to protect circuits against surges.
- Photodiode: Converts light into electrical current, used in sensors and light detection applications.
Congratulations @profwhitetower! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 50 replies.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP