In the previous episode of climate change saga, it was deduced that climate change was caused just by a degree Celsius (1 oC) rise in average global temperature, and human-induced greenhouse gases are the major causes of climate change of the 20th and 21st century, and the effect of global warming is climate change. However, the 3 basic theories by which global warming are caused are by:
(i) Entrapment and reflection of infra-red radiations into the earth surface by atmospheric greenhouse gases,
(ii) Depletion of ozone layer by chlorine radicals released by halocarbon derivatives and
(iii) Deforestation of trees and clearing of land vegetation.

** IMAGE 1: FULANI-HERDSMEN AND CROP FARMER CONFLICT IN NIGERIA DUE TO DROUGHT AND DESERTIFICATION.
Further, global warming involved the increase of the average global temperature as a result of the 3 aforementioned factors, most especially the atmospheric CO2 which is heavily liberated into the atmosphere through the incomplete combustion of organic matter such as fossil fuel, wood, plastics, nylons, and coal etc. Therefore, increased average global temperature is absorbed by the bodies of land, sea and ice. Especially the ice bodies such as Antarctica polar ice, land, river and sea polar ice, mountain ice sheets and snow are the receiving ends of the increased global temperature, thereby causing their melting, disappearance, shrinking and extrusion of their waters into the oceans and sea, hence increasing the sea level than usual level.
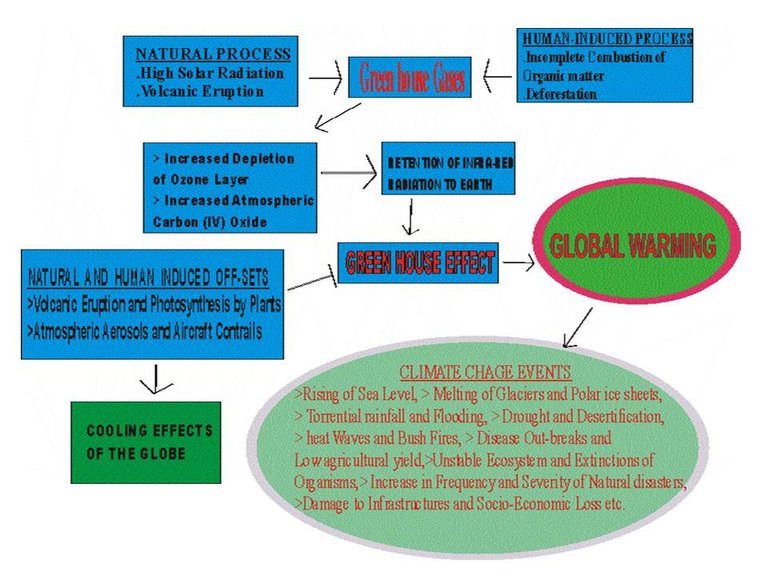
IMAGE 2: THE SUMMARY OF PATHWAYS LEADING TO GLOBAL WARMING-INDUCED CLIMATE CHANGE AND CLIMATE CHANGE EVENTS
More rises in sea level implies more energy transfer into the atmosphere in the form of water vapour and more heavy rainfall in a torrential manner, likewise more high energy storms such as hurricane, cyclones, tornado etc that extract energy from the sea with increased temperature. Areas with low rainfall will be suffered with drought, desertification, bush fires, sand storm and heat waves in response to increased global temperature. Coastal areas such as delta, island and riverine areas will be prone to extreme flood, thereby causing damage to life and properties, as well as relocations of dweller to alpine settlement as the sea level rises due to seepage of melted polar ice water into the sea. Food, water and health security become threatened with drought, desertification and heat waves; the ecosystem will not be safe anymore because of acidified sea water due to increase in the dissolution of atmosphere CO2, permafrost breakage and precipitation of sea’s sinking CO2 that will lead to reduced coral shell formation, increased coral death and fish migration from their natural niches, and also because of tree falling that will expose some animals to more danger with humans etc. The low yield of crops will be common in area with low rain fall especially during drought season in Sahel and Sudan tropical Savannah, hence causing pastoralists migrations to areas of green pastures for their cattle which might eventually lead to farmers and herdsmen clashes that results to loss of lives and properties (SEE FIG. 1).
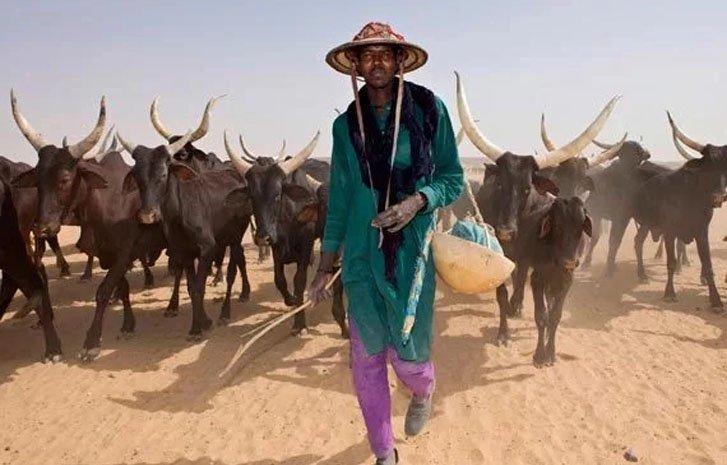

IMAGE3 HERDSMEN MIGRATION DUE TO DROUGHT AND DESERTIFICATION.
However, the aforesaid effects may be cascaded in a concerted manner with regional and local variability, depending on the prevailing micro-climate conditions of different areas and continents. Although as the effects are negative, there are also positive impacts in some areas with increased atmospheric CO2 to have increased food production due to CO2 fertilization, and much colder and snowed areas to have a reduced cooling and cold-related diseases. Therefore, we can then come to conclusion that as global warming causes some ill-effects, there are positive effects of this climate change. This article is directed to look at both the positive and negative consequences of presence and future of climate change due to global warming, as well as some pictorial and past real life evidences.
THE POSITIVE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE
(i) It was believed that area of the world with increased atmosphere CO2, though will have surface temperature, but will have also an increased agricultural yield due to CO2 fertilization if they increase their practice of agriculture since plants utilise CO2 to produce food, thereby increasing food security.
(ii) Areas in Europe, Asia, America and Australia with snows are prone to many cold-related diseases, therefore by the advent of global warming; the climate change event will result into less cold scenario, as a result reducing the prevalence of these cold-related diseases, vulnerability of patients and the number of people leaving the country due to winters.
(iii) Increased sea level will lead to increased fresh water through overflowing flood and lateral seepage; this will help in hydroelectric generation.
THE UNDESIRABLE CONSEQUENCES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
**SEA LEVEL RISE **
saline water invasion into nearby fresh water bodies, hence reducing fresh water availability for domestic use,
torrential rainfall and coastal flooding to coastal areas such as islands, deltas and riverine settlements, thereby destroying lives and infrastructures,
migrations of some aquatic organisms from area of water body with high temperature to a colder temperature zone,
acidification of ocean water due to the dissolution of atmosphere CO2 and precipitation of sea’s sinking CO2 that will lead to reduced coral shell formation and increased death death,
shrinking, falling and disappearance of glaciers and polar ice sheets on land, sea and mountain, and
extraction of energy by storms such as hurricane, cyclone and tornado etc from the increased ocean temperature, will wretch havoc on ships, nearby coastal settlements and infrastructures

**IMAGE 4: INVASIVE FLOODING OWING TO RISING SEA LEVEL BUCK LANDS BEACH IN NEW ZEALAND.
DROUGHT
This dry weather event may lead to: desertification in most arid areas, reduce agricultural yield, increased heat waves, increased sand storms, increased emigration of pastoralists to more greenish zones, green-zone population pressure and communal clashes of herdsmen and residential farmers due intrusion of cattle on farmlands, lack of fresh water for hydroelectric power generation and human consumption, wild bush-fire and migration of some animals from northern to southern zone, and finally spores of vectors and parasites are conveyed to different southern areas by storms, as well as human migration, can generate a rare episode of diseases (SEE IMAGE 1 & 3).
OUT-BURST OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND VECTOR-CARRYING PARASITES
There is now a possibility that some seasons will be longer than usual due to global warming, therefore increasing the associated infectious diseases (e.g protozoan, virus and bacteria) and vector-borne diseases (malaria, yellow fever and dengue fever), since they required the increased temperature for their incubation period,
Some displaced vector such as rats and bats etc as well as some average small animals such as monkeys can be a point of zoonotic transmissions of infectious diseases as their habitats have been destroyed by industrial encroachment, agriculture and resettlement due to global warming which in turn expose them to danger of being killed and consumed by men,
Geographical range of certain infectious diseases and their vectors that carry them will increase as their spores and the whole organisms can be supported by heat-waves and winds, thereby causing their occurrences in many areas of the world where they had previously being eradicated and where they had not witnessed before,
Also as people migrated from one locality, region, country and continent to another, due to unexpected global warming-induced intensity and severity of natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes etc that claim lives and infrastructures, there is possibility of distribution of and cross missing of rare infectious disease into the new locations as well as spontaneity of new diseases as these people intermarried.
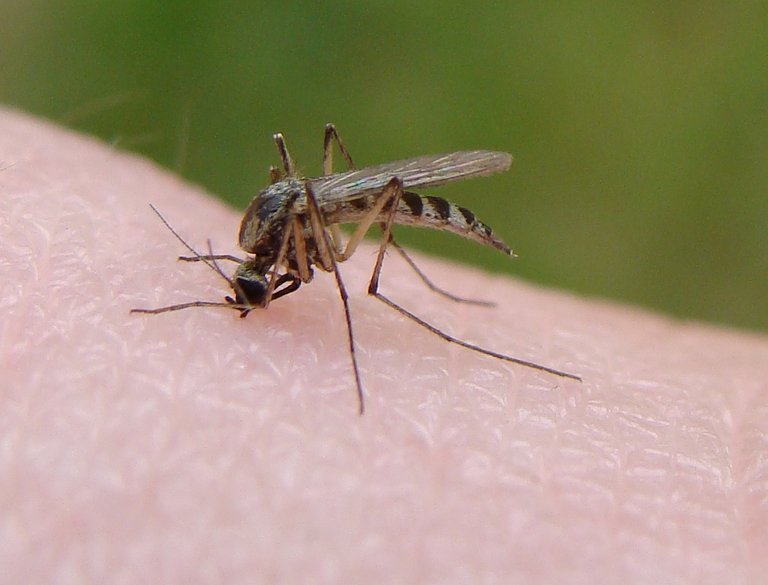

IMAGE 5: MOSQUITOES EXTENDING THEIR GEOGRAPHICAL REGIONS
HEAT WAVES
Induce certain homeostatic disorders on dwellers such as dehydration, gastroenteritis and kidney stones,
Transfer many spores of infectious disease-causing viruses and bacteria to beyond their geographical range, thereby increasing the death toll of which the heat wave itself caused if proper treatments are not administered and under poor medical facility,
Can lead to drought, desertification and finally low food security in an area of low rain water,
Bush fires that are uncontrollable will be common because the vegetation is so dried that it can serve as fuel to increase the energy of the fires and this can extend in destroying infrastructures and lives if spontaneous and planned measures are not taken when there is a sign of heat waves,
Reduce the availability of drinkable fresh water bodies in an area of high rainy season since the water will be so hot from the heat absorbed by the heat waves and may induce eutrophication (i.e bacterial proliferation in standing water bodies with high nutrient content) provided there is seepage of nutrients into it from industrial effluent and undiscriminating waste dropping and
Reduce the availability of enough water bodies to drive hydroelectric power, thereby causing electric power shortage and reducing the electric supply to demands by customers that needed it to power their air-conditions.
BUSH FIRES
The current increase in surface temperature has spontaneously ignited an intense wild fire in many parts of Europe and America owing to over-dried vegetation and forest and of which the ultimate effort to extinguish it has many time proven abortive. This uncontrollable could last for days or weeks, thereby claiming lives, destroying infrastructures and properties worth billions of dollars depending on the duration of the fires, as well as damage to the ecosystems and underlying soils, and displacement of animals from their habitats .

IMAGE6: WILDFIRE DESTROYING ECOSYSTEM AND DISPLACING ANIMALS FROM THEIR HABITAT
INFRASTRUCTURES
Many high-cost facilities have been engulfed by floods and wild fires, as well as hurricanes, cyclones, tornado and earth quake as a result of frequency and severity of these natural disasters which are common in places like Asia, Europe, America and Australia. Recently, there are growing evidences of the correlation of increased climate change to these spontaneous occurrences that have also claimed lives and properties in a whopping economical loss. Likewise, permafrost can flake away, thereby causing collapse of buildings and bulging of roads.
TORRENTIAL RAINFALL AND FLOODING
Coastal dwellers such as those residents on the island, delta and riverine settlements, since the floods will claim lives and properties, which will in turn causing their resettling to areas high far higher than the sea level such as alpine settlement, which may also generate new episodes of infectious diseases as the people interbreed to one another,
Agricultural farms bed at the banks of the rivers will be prone to invasive erosion by energized flood from the downpour, therefore reducing food security,
Infectious diseases (e.g cholera etc) and vector-borne diseases (such as malaria, sleeping sickness etc) that go with presence of water bodies flies etc will be on the rampage, and coupled with low immunity in dwellers as a result of low agricultural products for consumption, hence causing increased number of sick people and influx of patients into health service centers,
Places with low rainfall will experience heavy precipitations with high severity in a short duration, that will destroy lives and properties, and also in an irregular manner that will affect agricultural or planting patterns to weathers, thereby destroying crops and reducing agricultural yields
The torrential rains may associate with some natural disasters such as hurricanes, cyclone and tornado that are capable of wrecking ships with high exported goods, terminating lives on ships and on lands and destroying infrastructures and
Aquatic organisms may be displaced and go into by other aquatic lives carried by high-energy flood due to lateral seepage into fresh water at the water-shed or the new aquatic fishes may die as a result of inability to adapt to the physio-chemical parameters of the new environment.

**VIDEO 1: TORRENTIAL RAINFALL AND FLOODING CLAIMING LIVES AND PROPERTIES AT SULEJA (NORTH-CENTRAL) NIGERIA.
SOCIOECONOMIC LOSS
This can be inferred in the aspects of economic loss of high-asset infrastructures and facilities due to floods, hurricanes and the likes, and bush fires as a result of a degree rise in surface temperature of the globe. Therefore, this could lead many countries to poverty because more debts will be incurred in order to rebuild the destroyed infrastructures, which will in turn cause some countries to seek international aids for survival. Likewise, many lives and properties will be prone to destruction due to current and impending herdsmen and farmers’ clashes as a result of diminishing green folders for cattle consumption, as well as meat production and meat derivative products will scares and expensive(SEE IMAGE 1).
ECOSYSTEM
The flora and fauna will continuously be brought into constant instability as a result of climate change such as floods, bush fires and relative disasters, thereby causing some organisms to go into extinctions as they find it difficult to adapt to the new prevailing environment. Thus, continuous reduced biodiversity can lead to loss of evolutionary trend and loss of vital organisms (i.e plants and animals) as source of medicinal requirements. Likewise, this event can also bring some new organisms as a result of interbreeding that can be deleterious or advantageous to human existence.
SECONDARY EFFECTS
It is very possible that global warming effects cause by highly industrialized countries may be felt in developing countries in Africa and also other climate-regulated developed countries, provided the former doesn't put check and balance in the manner of their greenhouse emissions. Countries that are wealthy and scientifically aware of climate change will be able to adapt to this global menace for several years by putting up sustainable measures to tackle it but developing countries that are poor and academically disadvantaged will be at the receiving ends, thereby impinging burdens on the developed countries for emergency aids.
REAL LIFE EVIDENCES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
HEAT WAVES
In July to August of 2003, the summer looked exactly what were experienced 500 years ago, killing at least up to 27, 000 people in Europe, and the associated drought and wildfires coupled with the heat caused the continent’s economies more than 14.7 billion dollars (i.e 13 billion euro) in electric polar, forestry and agriculture sectors.
Also, in July of 1995, a five-day heat waves of temperature 41oC (106oF) in Chicago killed 525 peoples.
3,028 people were caused death by heat waves that struck India in April to June of 1998.
TORRENTIAL RAINFALL AND FLOODING
30,000 death tolls were recorded due to a heavy monthly rainfall with severe land slides and flooding in Venezuelan in December of 1999.
The south – eastern part of the Nigeria had been severally embattled with gully erosion which had destroyed many buildings and farmlands, hence resulting in relocations and poverty.
Between 2012 to 2017 years, there was increasing flood experience that swept houses, farms, farm products, properties and even human beings in both the southern and part of north central in Nigeria.
** DROUGHT, BUSH FIRE AND FOREST PESTS**
Alaska experienced its warmest and 3rd driest summer which coupled with abnormal wildfires that engulfed a larger chunk of Maryland’s forest in 2004.
In the 90s in Russia, the area of the forest burned for at least three times compared with previous 20 years back.
Also, Alaska had its world’s worst records of outbreak of spruce bark beetles in the 1990s.
In 1991, in Yobe and Borno states which encompassed the southern part of Lake Chad, the section of it that was within Nigerian territory, dried up and causing southern migration from the north-east towards the greener plateau and middle belt regions.
ELEVATION SEA LEVEL
Since 1938 about 1/3rd of the marsh at the National Wildlife Refuge’s black water in the Chesapeake Bay in the eastern U.S had started sinking.
28% of the biologically-rich marsh of about four hundred thousand hectares in Louisiana has been lost to the invading sea since 1932.
The Thames Flood Barrier that was used to protect the London city from Atlantic storm surges was used once annually in the 80s has now been utilized more than 6 times annually since 1990s.
Coastal regions of Nigeria were threatened by rising sea level, especially oil-rich Niger-delta, apart from oil pollution, hit by this effect due to its low-lying terrain and crisscross of waterways.
** DISAPPEARING GLACIERS AND RETREATING SNOW PACK**
Six glaciers of Venezuela in 1972 had recently declined to two.
Apart of 82% of the ice on the Mount Kilimanjaro that had been varnished in 1912, 1/3rd of the remaining ice had been disappearing since 1993.
In the western United States, from 1950 to 1997 there has been reduction in Spring snow pack of about three-quarters of the mountainous areas.
** FLAKING POLAR ICE AND THAWING PERMAFROST**
The Larsen B ice shelf, which appeared offshore of the Peninsula and served as a dam for land glaciers, broke down in only 35 days in 2002 and caused an increased in-flow of glacier into the ocean and resultive rise in sea level.
In the spring and summer of 2003 the Ward Hunt Ice Shelf disintegrated into two.
The gaping hole of ice-free water at the North Pole appeared in 2000 and 2001 indicated that Arctic sea ice did no longer serve as extensive and solid as it was.
** ECOLOGICAL IMPACT**
Hawaii experienced its first bleaching event that caused damage to coral reefs in early year of 1996.
13 species have shifted northward and six species have swum into deeper, cooler water but 2 species shifted southward out of 36 species of fishes in the North Sea found between Norway and Great Britain since 1980 in response to warming waters.
Polar bears were listed among the Endangered Species Act as a petition by the environment scientists in the U.S. in 2005.
The golden toads, harlequin frogs and mountain amphibians inhabiting the hilly lands in central and southern America, as well as survival rates of embryos of western toads and cascades frogs in Northwest of United states, had been diminishing markedly.
DAMAGE TO INFRASTRUCTURE
Liquefaction of permafrost (I.e permanently frozen land) has been the cause of sinking and breakdown of buildings and bulging of road in Alaska recently.
People permanently residing in Eskimo village (i.e Shishmaref) that had occurred for 4,000 years on the island of the Alaska’s coast had to relocate due to underlying melting permafrost and invasive sea waves as the sea ice melted and replaced by water.
Increasing desertification had driven thousands of Fulani herdsmen to migrate to the south and middle belt resulting to clashes with indigenous crops farmers ending in destruction of life and properties.
EPIDEMICS OF VECTOR-BORNE DISEASES
Mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti) that transmitted dengue fever and yellow fever which are generally limited to lower altitudes are now found in higher altitudes in Columbia, North of Mexico and some parts of Rwanda.
After 6 years of drought followed by heavy spring rains in south west of United states In 1993, there was an out-burst of deer mouse, which happen to be vectors (i.e carriers) of hantavirus, and are zoonotic to man, hence causing headache, nausea and vomiting.
FUTURE CONSEQUENCES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Considering the future assessment forecast by the groups of the IPPC (the latest report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) that the continuous change in the climate will affect the welfares and health of many people around the globe, but the severity of the impacts will depend on the extent of warming. Therefore, the common probable effects include:
More repeated droughts, heat waves, fires, coastal flooding and storms will elevate the injuries, related diseases and death toll.
Some infectious diseases, including dengue, malaria, fever, yellow fever etc, will extend the more their geographical regions.
There will be an increased concentration of ground-level ozone that will aggravate heart and respiratory conditions.
There will be increased sea levels that will invasively overwhelm the homes and properties of peoples in millions, most specifically on small islands and large deltas of Africa and Asia.
The impoverished nations will feel the most impacts because their adaptive capacities are economically limited and they will seek developed nations for aids.
Although for few decades the global warming’s effects will not be generally bad but with time it will be universally “crazy’’!!!!!!
In conclusion, this poses questions: What can we do? What needs to be done?
This will be found in part III in the next episode of climate change
THANK YOU FOR FOLLOWING THIS SAGA. PLEASE, BE FREE TO MAKE YOUR COMMENT AND UP-VOTE IF YOU FIND IT INFORMATIVE.
COMING REVELATION: THE DRUG: THE SO-CALLED HEAVEN INSPIRATION WATCH OUT TOO
REFERENCES
IMAGES
4 https://www.google.com.ng/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwjm-NeAwIvaAhWQCOwKHUdwC8MQjRx6BAgAEAU&url=https%3A%2 %2Fcommons.wikimedia.org%2Fwiki%2FFile%3AMosquito_bite_from_Flickr.jpg
VIDEO