Functional Foods, Regulations and Impact on Lifestyle:
Green Tea and its Nutritional Beneficiaries Regarding Diseases
by Frank- Nutritional Science
Abstract:
Green tea has been identified as one of the most consumed beverages throughout the years. It has grown in popularity and has been incorporated into the American diet for its numerous beneficiary health outcomes. Research and different experiments have been made to test the powerful chemical contents that Green Tea withholds, especially the constituents that are held within the tea leaves itself which are soluble components of minerals, vitamins, and amino acids. Green tea has been known for its potential antioxidant catechins and flavonoids alongside polyphenols and EGCG being the most powerful catechin. The purpose of this paper is to identify the entities that are found within the Green tea, and how the consumer can nutritionally benefit from consuming this beverage, to reduce the chances of developing diseases such as cancer, diabetes, reduces cardiovascular disease, ischemic heart disease and reduction of uric acid in the body. Not only can the consumer adhere nutritional value from Green Tea, but also the consumer can benefit the body to develop an improved lifestyle, and enhance the equilibrium and homeostasis of the body.
Keywords: Catechins, antioxidants, polyphenols, EGCG, cardiovascular disease, Camellia Sinensis, disease fighting compounds, flavonoids, tumorigenesis, carcinogenesis, ischemic heart disease, diabetes, pre-diabetic, cardiovascular disease, black tea.
Introduction:
The effects of green tea have been under research over the years for the numerous benefits it contains. Green tea has been recorded to be consumed worldwide for thousands of years, originating from China for more than 3,000 years ago. Initially green tea leaves were consumed by eating and chewing the leaves, later it was added to boiling water and made as a staple beverage in China, it is widely used all around the world. Green tea is derived from the Chinese plant called Camellia Sinensis, its leaves are cut down and used for the extraction of the tea, which is also known to be used for traditional Chinese medicine. Green tea is proven to encompass constituents of antioxidants within their leaves. Catechins within the tea are found to be antioxidant, there are 4 different categories of catechins composed of polyphenol structure, epicatechin (EC), epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC), and the most abundant one is epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Catechins contain 80-90% of total flavonoids. The substance of catechins within the green tea, oolong tea and black tea can be effected by factors such as fermentation degree, drying condition, preparation of brew, and decaffeination. Green tea has provided available prevention benefits for many diseases including link to reducing cardiovascular disease, reduction in uric acid, reduced risk of ischemic heart disease, effectives in diabetes and significance benefits for weight loss and overall health lifestyle.

Catechins
Illustration 1. Reproduced from: “Cancer Preventive Activities of Tea Catechins”, by Chung S. Yand and Hong Wang (Yand & Wang, 2016).
- Chemical Component of Catechins within Green Tea
Catechins are held within green tea, as shown in Illustration 1, the most potent catechin from these four is epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). In the research article titled: Cancer Preventive Activities of Tea Catechins, by Chung S. Yand and Hong Wang, the article aims at identified the chemical properties of catechins within green tea, their redox activities and their effect on cancer preventive. Discussion on whether the chemical components of catechins (EGCG) in green tea truly serve a purpose on reducing the carcinogenesis or tumor growth is the issue that is faced. EGCG has shown to reduce reactive oxygen species including those such as superoxide radical, peroxide radical and nitric oxide known as ROS or reactive oxygen species. These hydroxyl radicals such as ROS are very reactive and can be damaging to macromolecules such as lipids, DNA, and proteins within the body (Yand & Wang, 2016). These hydroxyl radicals need to be eliminated from the body so no damage can occur. EGCG acts as a defense mechanist against the ROS, which prevents their oxidation and formation. As shown from the chemical structure in catechins they include a benzene ring and many hydroxyl groups, some may include dihydroxyl and trihydroxy which provides the strong properties of antioxidant activity (Yand & Wang, 2016). The chemical structure also contributes to the proneness of air oxidation. Under cell circumstances auto-oxidation can occur wherein cellular changes occurs and the impact of EGCG eliminating ROS, the effect can produce cell death. EGCG and other catechins are acknowledge for their potential detoxifying instruments. Two major enzymes held within the small intestine and liver help induce the reaction of Catechins, sulfotransferases and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. These catechins undergo further degradation in the intestines which can be secreted and seen on the urine and feces. Passive diffusion allows EGCG and catechin to enter the cell, alongside the addition of transporters as organic anion-transporting peptides (OATP) 1A2 and 1B3(Yand & Wang, 2016). The metabolism of EGCG controls the flow of EGCG from the enterocytes into the intestinal lumen or from the liver to the bile and finally defecated in feces and very little in the urine. Passive diffusion allows molecules to more from an area that consist of high concentration to an area of lower concentration, this allow EGCG (catechin) to move freely from the cell membrane, no energy is required from passive diffusion.
- Polyphenolic Structure of Green Tea Polyphenols
Polyphenols, from illustration 2, are made up of flavonoids which are great hydrogen donors, allowing hydrogen to be available. The hydrogen bonding to the EGCG allows the EGCG to create a hydration shell. The bioavailability or active effect of the polyphenols in the body is determined by factors such as polarity, molecular size, and apparent size. The bioavailability of EC contains more molecular weight of 290 containing five polyphenols, EGCG molecular weight is 458 and contains eight polyphenols in the structure, which makes EGCG more effective and vigorous antioxidant. In comparison; when taking two cups of decaffeinated green tea this will allow a consumption peak plasma of EGCG to increase magnificently. (Yand & Wang, 2016).
- Carcinogenesis Inhibition by Catechins in Green Tea
Conferring to the research article: Cancer Preventive Activities of Tea Catechins, by Chung S. Yand and Hong Wang, catechins that are found inside of the Green Tea leaves are proven to inhibit tumorigenesis decrease cancerous cells in the body, as well as functioning to inhibit many other diseases. Study has been conducted on animals where there was a significance difference in decreasing the risk for developing cancer in the stomach, liver, pancreas, bladder, small intestine, lung, mammary glands and skin. (Yand & Wang, 2016). This study was proven to have accessed a certain amount of green tea in the drinking water for the animals. As stated by Yand & Wang: “The epithelial cells in the digestive tract have the opportunity of being directly exposed to orally ingested catechin” (Yand & Wang, 2016). Administration of EGCG at 0.02%–0.32% in drinking water for the animals showed a dependency-inhibition of small intestine tumorigenesis, and increased levels of E-cadherin (tumor suppressors), were seen on the plasma membrane. Green tea extracts were also given in the drinking water, which consisted of 0.6%, and suggested proven to inhibit azoxymethane (AOM)-induced aberrant crypt foci (ACF) in CF-1 mice on a high-fat diet (Yand & Wang, 2016). The consumption of 65% EGCG and other tea catechins for a diet of 8 weeks, resulted from decreasing ACF in the colon of AOM treated rats (Yand & Wang, 2016). The potent of catechins were under study to achieve the purpose of being more effective than EGCG within tea, due to more than one entity that induced their potent. The study was also observed in mice by comparing the activities of PPE, EGCG, and ECG administered in drinking fluid. The following observation were assessed: a decrease of tumor multiplication of about 50%, by both PPE (0.12%) and the corresponding amount of dietary EGCG (0.08%) (Yand & Wang, 2016). This experiment was positive in increasing apoptosis and cell production, correlation between catechins and EGCG can be synergistic among both to inhibit tumorigenesis.
- Effect of Tea Catechin on Lung Tumorigenesis
Studies in this article have been examined to provide the inhibition on lung tumorigenesis, as effective in the correlation between providing EGCG and EGC in green tea, which is more effective than caffeine. Yand and Wang showed this potential of green tea constraining cancer and lung tumorigenesis by running a test through rodents and rats which consumed a certain amount of green tea as compared to caffeine. The experiment consisted of 20 rodents under monitored, which was administered orally of 0.5% PPE (polyphenol E), and 0.044% of caffeine, which was placed in the drinking water. This oral administration of caffeine and amounts of EGCG were given to rodents, mice and rats who had lung tumors (Yand & Wang, 2016) After adequately supervising the effect from 20 to 34 weeks, an analysis could take place in the effects of catechins in association with tumorigenesis (Yand & Wang, 2016). The analysis from this experiment, showed that levels of PPE and caffeine in the body (blood-barrier), helped to reduce cell production and decrease the spread of carcinogen cells, as well as enhance apoptosis for cancer. No significant benefit from reducing tumor cancer cell appeared, but can be identified with further study required to explain the function of PPE (polyphenol E), in the body. As stated by Yand and Wang, could prove the effectiveness of EGCG and caffeine levels to produce tumorigenesis, and that the most effective form for this is EGCG.
- Tea Catechins: Cancer Prevention and other Possible Mechanisms
Conferring to Illustration 2, the actions of catechins are mainly responsible for redox activities such as binding and having effects on eliminating ROS (reactive oxygen species) which as stated before include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical and other free radicals. These reactive oxygen species become alarming to the body due to altering the functions of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids wherein the result may lead to a variety of diseases. Based on research and the experiments done on rats/ mice and providing the amount of tea treatment with EGCG, the ROS oxidative stress within the rates was proven to have some impact and decrease of cancer progression as well as reducing and preventing diseases.
Illustration 2: Reproduced from: “Cancer Preventive Activities of Tea Catechins”, by Chung S. Yand and Hong Wang (Yand & Wang, 2016).Catechin (EGCG) is known to have entities of antioxidant mechanism to reduce diseases. Different actions can be derived from EGCG in tea which induces preventions of illness that is produced in the body. A) of illustration 2, shows cellular events occurring and B) shows direct and indirect binding targets.
- The Correlation of Green Tea Effects on Diabetes
Introduction
According to some epidemiological studies, Green Tea ingesting has been confirmed to alleviate diabetes as well as reducing ALT levels by examining the parameters which include waist-hip ratio, arterial pressure, glucose level, the antioxidant status within the body, and lipids. These factors were taken into consideration and was examined to prove that the intake of Green tea which is rich in antioxidants can provide an improved metabolic system in the body and reduce the risk of individuals to adhere to diabetes. (Toolsee, et al., 2013). In the research article: “Effectiveness of Green Tea in a Randomized Human Cohort: Relevance to Diabetes and Its Complications” by Toolsee, et al., examines the effect of green tea in correlation to the disease diabetes and its potetial effects to the individua who has this diease. Diabetes has been known as a chronic disorder that affects the metabolism in regards to insulin deficiency that can lead to glycemia. The common known types of diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, in which Type 1 it affects the anutoimmune β-cells of the pancreas, this in turns is the body’s defense mechanism, and Type 2 refers to the metabolic disorder of insulin resistance and its deficiency (Toolsee, et al., 2013). This study examined the Mauritian Green tea and its constituents of antioxidants within the Green Tea to reduce diabetes. The emtities of green tea are composed of polyphenol-rich compounds that may alleviate the metabolic syndrome that occurs due to the this disorder.
Methods and Materials
In order to observe the effect of the antioxidant potent on individuals who were pre-diabetics, beverage of green tea rich in polyphenol constituents was administered. The methods of experiment consisted of a controlled group and an experimental group. The experimental group ingested 3 cups of of green tea daily for 14 weeks, and then followed by a 2-week washout period (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The control group ingested a water regimen. High levels of polyphenol related to antioxidant was shown to overpower waist hip ratio of women and also decreased the amount of mean arterial pressure for both men and women (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The ATL levels decreased in women by (13.0%), and increasing the antioxidant potent by 2.7% in men and 5.1% in women. The functional antioxidant component in the green tea beverage plays a key role on the biochemical pathways of diabetes. As stated by Toolsee, et al., : “These green tea polyphenols showed antioxidant activities in vitro by scavenging reactive radical species and function indirectly as antioxidants through inhibition of redox-sensitive transcription factors; inhibition of “prooxidant”enzymes; and induction of antioxidant enzymes”. In regards to the method in which this experiment was conducted both the control and experimental group were given te bags that contained 2 grams of green tea with high quantities of polyphenols, flavonoids, and catechins. The sample preparation was prepared by one green tea infused with 100ml of hot water for 6 minutes, and then brewed under cool water and centrifudged at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes at 25℃ (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The green tea extracted a high level of catechins including EGCG. A standard calibrated graph was assessed for plotting the peaks and their quantities.
Subjects and Regimen.
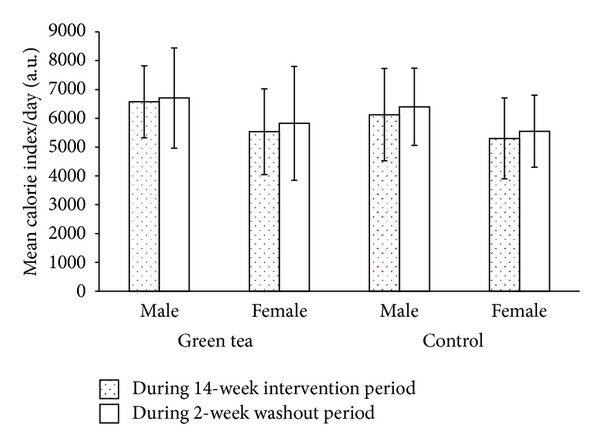
Figure 1. Reproduced from: “Effectiveness of Green Tea in a Randomized Human Cohort: Relevance to Diabetes and Its Complications” (Toolsee, et al., 2013). Flow diagram shows the trial outline and study method & procedure.The subjects of the study included 300 predibetic Mauritians which participated in the survey in 2009, which was organized by the Non-Communicable Diseases Unit of the Ministry of Health and Quality of Life (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The participants were selected randomized, these individuals were at risk of diabetes, their plasma glucose ranged from 110 to 126 mg/dl, their glucose level was measured by the hexokinase method. Ages ranged from 35 to 65 years old, this study excluded smokers who had stoppped smoking 6 months prior to the experiement and restricted alcohol consumption of only two drinks per person. The Clinical trial occurred over a period from November 2010 to March 2011 at the Cardian Center of the Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam National Hospital. A period over 16 weeks was overlooked, and the experiment group (n=65), ingested 1 cup pf green tea without the adding of milk or sugar, three times daily before their meals, which included breakfest, lunch and dinner. This same procedure was followed for 14 weeks and then was followed by a 2-week wash-out period as shown by figure 1. As for the controlled (n=58), also followed the procedure as the experimental group (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The recordings were taken by a random generator which disregarded the influence of gender between the groups. No dietary change pattern was reccommended to the individuals, they were encouraged to keep their normal diets (Toolsee, et al., 2013). Anthropometric and blood pressure was taken into account and recorded among the participants. Height, weight, and BMI were also taken into consider as well as waist girth which was measured in the individuals at midpoint between the iliac crest and lower margin og thr ribs, to see the effects of the green tea on body structure. The measurements were taken at 1 minutes intervals, as well as the blood pressure. Blood collection of 20 ml from each participant was adhered after at least 12 hours. The blood samples were mediated with EDTA-K3 tubes and plasma from sodium flouride (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The human plasma blood removed from the participants was tested for glucose levels. The assay tubes were also tested for the levels of total cholesterol, lipoproteins of HDL and LDL, as well as triglycerides, urea, albumin, creatine, ferritin, and antioxidants that originate from the green tea, and AST/ ALT levels (Toolsee, et al., 2013).
Results and Discussion
In regards to the experiment given over the 16 week period, significant difference were held among the groups. Correlations between variables, daile mean calorie index, and dailr fat/ lipid ratio was evaluated. The mauritian green tea was proven to be infused with high contents of antioxidants inculding procyanidin B2 , epigallocatechin gallate, epigallocatechin, epicatechin gallate, epicatechin catechin and gallic acid. As stated by Toolsee, et al.,: “Procyanidin B2 wasfound to be the most important compound with 496.92mg per cup (200 mL) while gallic acid was least prominent(1.66mg per cup)”. Figure 3. The management of Type 2 diabetes, is known to be treated with conventional therapies, diatery and nutriotional changes, exercise and the combination of pharmaceuticals. Alongside these conventional therapies and other recommended therapies, the ingestion of green tea can also be aquired into the diet to support healthiness and longetivity. There is evidence that provides the main role of green tea towards the health of those with disorders such as diabetes. The contents of green tea, polyphenols are proven to increase the metabolic syndrome and risks of diabetes. This study proved the elevated levels of total phenols, flavonoids and proanthocyanidins contributed to the antioxidant properties in reducing the free-radicals in the body (Toolsee, et al., 2013). According to the study there was a significant increase in serum antioxidants against oxidative stress and radicals, which could improve the conditions of thus said diabetes. The catechins within the digestive tract appered to form complexes and in correlation to lipids and lipolytic enzymes, that interfered with emulsification process withi the lumen, and hydrolysis occurred (Toolsee, et al., 2013). Upon the anthropometric measurements data, shows that green tea consumption during the 14 week period decreased the elevated waist- hip ratio among women in the experimental group (Toolsee, et al., 2013). With the recommended green tea drinking 3 times daily, significant results were obtained which suppressed arterial pressure and promoted good blood flow, and prevented ischemic reperfusion for injury of organs. The effects of catechins have also been studied in laboratories involving rats. EGCG significantly reduces systolic blood flow (200 mg/kg for 3 weeks), which improved endothial function and insulin insentivity. Upon the sudy for rats in the article: “Effectiveness of Green Tea in a Randomized Human Cohort: Relevance to Diabetes and Its Complications” , Toolsee, et al., state that: “It has also been shown that epicatechin derivatives from green tea leaves can relax rat mesenteric arteries, probably by inhibiting Ca2+ influx and increasing nitric oxide release which has a vasodilatory effect” (Toolsee, et al., 2013). The green tea routine followed, prevented glucose impaiement which proved a higher results in the experimental group than the controlled. Green tea was concluded as being a glycemic regulator for indivuduals who have diabetes. The phytochemicals that green tea obtains might ameliorate insulin resistance by acting as peroxisome proliferator to activate receptor lifands with dual alpha/ gamma agonistic effect (Toolsee, et al., 2013). As stated by Toolsee, et al., : “The phytochemicals also in green tea have an effect on preventing intestinal glucose uptake by inhibiting the sodium-dependent glucose transporters of the intestinal epithelial cells” (Toolsee, et al., 2013). In regards to kiney disease the findings based on this research showed that green tea consumption also decreased eGFR concentration. This research article established the findings that the ingested 3 cups daily of green tea into the diet can form part of a healthy lifestyle which can also provide health benefits for those who are prediabetic or have diabetes.
Impact of Camellia Sinensis

(Green Tea) on Liver Regulation Figure 9: The components of green tea, Camellia Sinensis also has beneficary impacts on health especially proven to impact components in the liver (figure 9), green tea has been poven to possess several hepatoprotective properties. The properties that been proven to benefit the liver is due to the compoenets of the antioxidant held within the green tea as well as polyphenols, and catechins. As stated in the articles, : “Chocolate Shake and Blueberry Pie...... or why Your Liver Would Love it by (Gressner, 2012)”, Pure green tea (+)-catechin, commercially known as Catergen, has been extensively studied in the human and, temporarily, also used to treat viral hepatitis. Alongside the effects of the antioxidants, green tea holds redox mediated activities which can help balance the metabolism of glucose. The redox balance through the maintenance of intracellular protein thiol levels, influences the protein tertiary configuration. (Bahorun , et al., 2009).
Effects of Black Tea and its correlation to Cardiovascular Disease
Introduction
Green tea has been tested and proven to provide a numerous beneficial health changes in regarding to disease. Other research that has been done with the consumption of black tea and its effects on uric acid and C-reactive protein for those who have cardiovascular diseases. In the research article titled: “ Black tes reduces uric acid and C-reactive protein levels in humans susceptible to cardiovascular diseases”, by Bahorun , et al., talks about the effect of black tea and association in redusng uric acid and c-protein levels in corrrelation to cardiovascular disease. The constituents of black tea has the same antioxidant properties as those as green twas if not even more potent and stronger due to the color fermentation being longer to make it into black tea. An experiment took place where individuals consumed 9 grams of black tea ( 3 cups) daily for 12 weeks without any additives then followed a 3 week wash out period. Women and men were used for this study and there was a decline in the high levels of uric acid baseline groups >6 mg/dL by 8.5%; p < 0.05 (Bahorun , et al., 2009). The purpose of this research was to prove that the utilization of black tes can decrease the plasma in uric acid levels as well as c-protein levels, which can benefit individuals who are at risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Methods and Findings
The methods of this study included two hundred and sixty three male and female volnteers in a controlled trial who consumed 70% of the time black tea which included 200 ml of tea infused with antioxidants contents. 80 subjects were selected from a waiting list who were at risk of hypeuricemia including hypertension and cardiovascular disease. In regards to potential treatments the use of statin drugs could incorporate in reducing the CRP levels with great benefits. Based on the findings a significant positive correlation was found between diet change and dietary intake if black tea was incorporated, as well as UA (uric acid) values also decreased in consumers. According to the findings done from this experiment, positive outlooks were recorded due to the consumption of tea. Black tea was shown to decreased uric acid levels by 9.4% (p> 0.01), after a 12 week period and 7.1% (p>0.001) in both males and females groups. A daily intake of 9 grams of black tea was equivalent to 738 mg of polyphenols a day. There is a high significance in decreasing plasma levels of uric acid with the impact different teas have to increase the antioxidant effectiveness for patients with coronary heart disease (Bahorun , et al., 2009). In finalizing this experiment of black tea impact to decrease uric acid and c-protein levels, this study indicated that black tea decreased CRP levels and UA levels in both males and females, due to the catechin, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory entities of the black tea. For individuals who have consumed green tea and a variety of green tea, there are most susceptibility and advantages to their overall health and longetivity. Many of the components of teas have been known to not only improve the body as a whole in regards to relaxation, and memory improvements due to the neurological advantages as well as improved immune system but also it has been known to prevent the risk of developing ischemic heart disease. Based on the article: “Tea consumption and risk of Ischemic Heart Disease”, they consucted an experiement which included China Kadoorie participants at 10 different areas in which consumed tea over the several months. The findings help to emphasize the beneficial impact of tea in correlation to ischemic heart disease. During the 7.2 years they documented 24.655 cases, and concluded that tea consumption proved to reduce the risk of IHD. When more than 90% consumed tea, a 97% proved a positive reduction due to the polyohenol-catechins in the tea. Limitations included some possible missclassification, but results varied from person to person based on other factors such as height, weight, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, blood pressure levels, regions, occupation and income status. More positive results came about those who consumed tea for a longer period of time. In conclusion the numerous effects of green tea and other teas in the consumers diet for any patient who might be undergoing ischemic heart disease, diabetes, tumors,uric acid and cardiovascular disease could benefit from ingesting tea. Based on the reaserch done so far and many more that are underway of the health beneficiaries and longetivity that green tea includes to the health of a person, there is enough evidence to conclude that people should incorporate green tea intake into their nutritional meals to adhere to the numerous health outcomes it brings. For those who undergo stages in their lifes of certain diseases and other who do not have disease can also benefit from consuming at least of a cup a day of green tea. Teas are available in many flavors and varieties all over the world and have become popular as a functional food due to its antioxidant properties it contains. Many researchers and others have proven the benefits of tea regarding towards health and promoting the reactions and metabolisms in the body towards many diseases. Based on the constituents held within green teas it has been proven to reduce the risk of many diseases and disorders. I would highly recommend the consumption of green tea.
References
Bahorun , T., Ramma , A. L., Gunness , T. K., Sookar , D., Bhoyroo , S., Jugessur , R., . . . Arouma, O. I. (2009, November 30 ). Black tea reduces uric acid and C-reactive protein levels in humans susceptible to cardiovascular diseases. Toxicology , pp. 1-8.Gressner, O. A. (2012, October 21). Chocolate Shake and Blueberry Pie....Or why Your liver Would love it. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Research, pp. 1-12.Li, X., Yu, C., Guo, Y., Bian , Z., Si, J., Yang , L., . . . Li, L. (2016, December 16). Tea Consumption and risk of ischemic heart disease. British Cardiovascular Society, pp. 1-7 .Toolsee, N. A., Aruoma, O. I., Gunness, T. K., kowlessur, S., Dambala, V., Murad, F., . . . Bahorun, T. (2013, August 7). Effectiveness of Green Tea in a Randomized Human Cohort: Relevance to Diabetes and Its Complication . Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International , pp. 1-12.Yand, C. S., & Wang, H. (2016, December 9). Cancer Preventive Activities of Tea Catechins. Molecules , pp. 1-19.

I'm a big fan of green tea, which is filled to the brim with antioxidants for warding off chronic diseases and cancer. So folks should completely drop soda and instead stick to drinking tons of water and some green tea!
Definitely, agreed with you. Not only does green tea contains antioxidant properties but it's also helpful for digestion and has been proven to have Medicinal benefits for many health problems. Unlike soda green tea can provide long-term benefits to one's health. Thank you for your comment:)
You're welcome @frank-solutions and thank you very much for informing the Steemit community about green tea. I love reading about healthy food choices, so I look forward to your next salubrious post!
Absolutely, I'll try my best to keep up with the Steemit community and posts.
Awesome, continue raising health awareness and keep STEEMing!