Key Takeaways:
- Even though NFTs are considered pfp/music/art, collections should be regarded as companies and the roadmap as a pitch for investors.
- Nonprofit organizations could consider NFTs as a new way of fundraising, and it gives donors transparency on transactions and social recognition through the holding of their NFTs.
- Fundraising through NFTs lets the investors have immediate liquidity since the markets operate 24/7.
NFTs have been considered empowerment to the community by ownership of art, avatars, PFPs, and music. But it also has to be considered as a way for founders to fundraise their projects.
In the same vein as Venture Capital, NFT holders and minters are investors in an early stage of the project. Holders invest in what they believe could be the next big thing, in other words, in promises that the founders will accomplish what they promised through a roadmap.
So, if VCs and NFT minters invest in an early stage of a startup/NFT collection, which stage might it be? If we take the venture capital median time between fundraising as a metric, minters would be similar to Angel investors or Seed investors. Since the median time of its fundraising is less than 2.5 years.
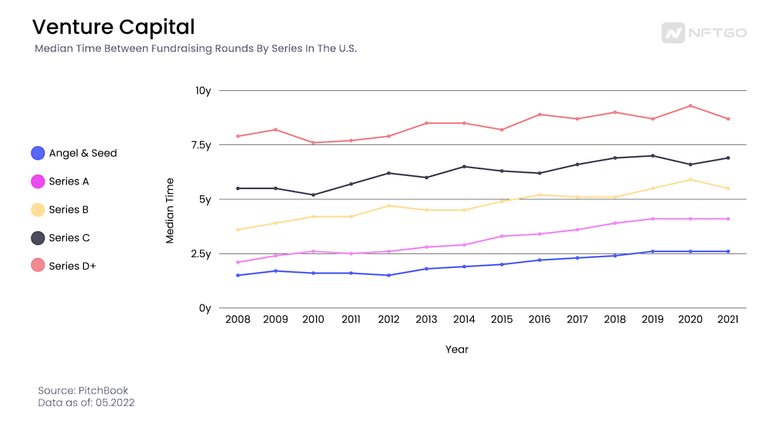
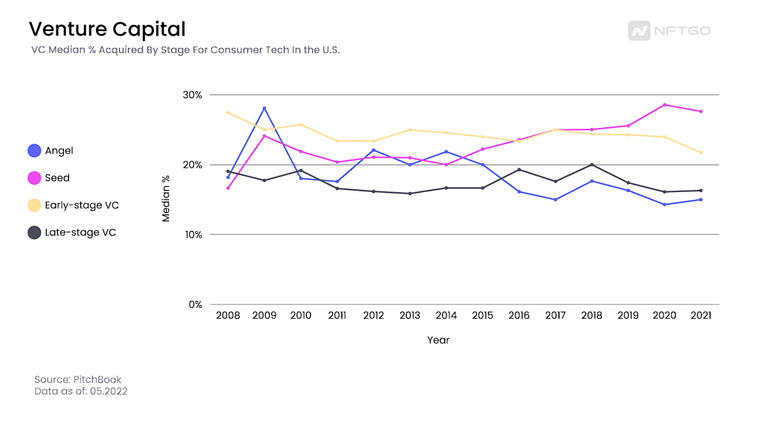
Non-Fungible Tokens should be seen as a consumer tech because ordinary people trade this technology as an asset class. When NFT collections do their fundraising through minting, the community owns around 99.9% of the collection; the remaining pieces (0.01% or 100/10,000) go to a wallet for marketing campaigns, public relationships, giveaways, or collaborations with other projects. The minting phase is where the NFT collection gets its first capital fundraising. The percentage owned by the holders is relatively high compared with the VC median acquisition in the angel fundraising stage, which in the last couple of years has been less than 20%.
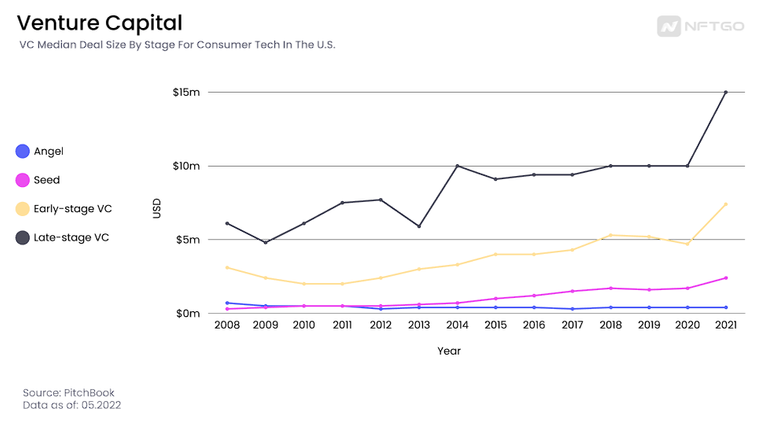
The highest among the money raised from VCs companies is the late-stage VC. In 2021, the median deal size for this stage was 15 million U.S. dollars.
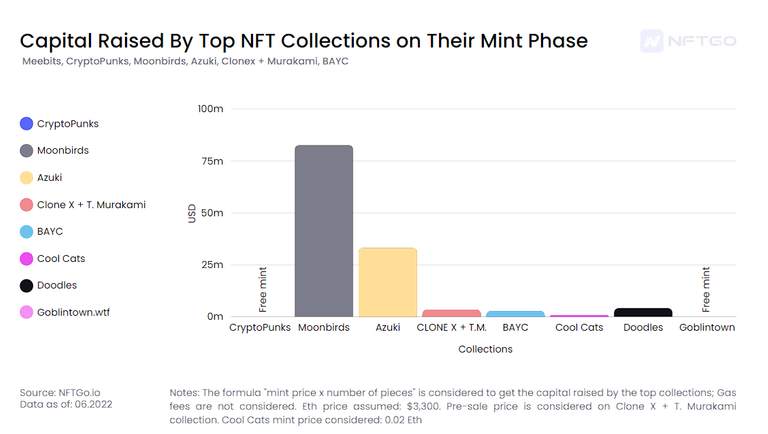
Fundraising using NFTs
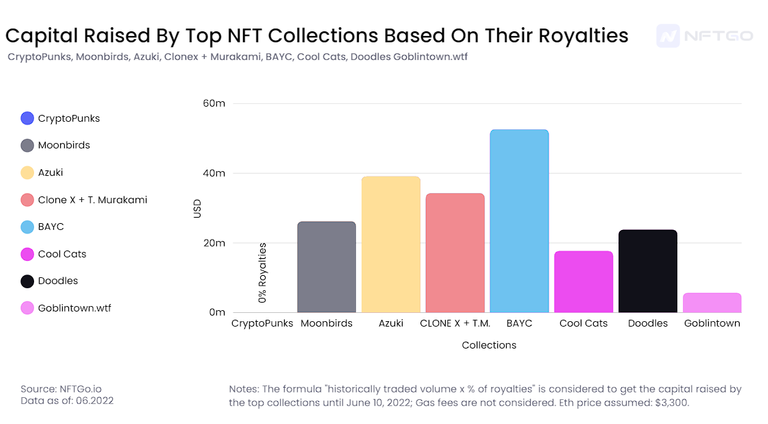
Comparing Angel and Seed stages with some of the most significant NFT collections, we see a correlation between the capital raised by the collections from the community, especially on the Angel & Seed stage.
However, the big difference between Web2 and Web3 is that the capital fundraised from Web3 doesn't stop in the mint phase (VC fundraising depends on the fundraising series, but once the growth company is fundraised, it stops getting money from VCs). Instead, projects keep fundraising from the market because of the ability of creators to earn royalties from each piece traded in the market.
Successful Fundraising NFT Case
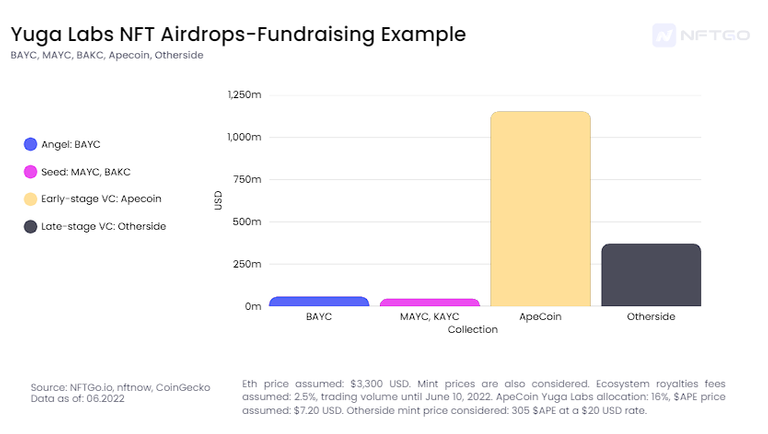
The success of Yuga Labs is because of its heavy marketing campaigns and the strong community behind it. YL, on the other hand, represents the success of an NFT project as a whole. Taking its first NFT drop was considered the seed fundraising stage until taking its latest release as a later-stage VC.
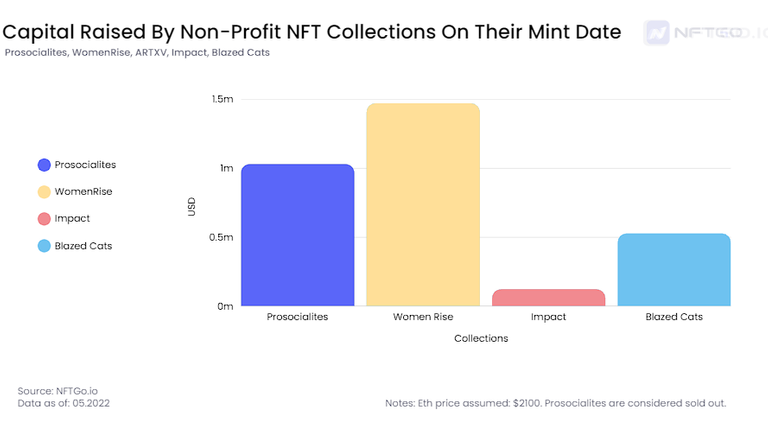
Simultaneously, NFTs open new ways to fundraise companies with profitable schemes and non-profit organizations.
The good thing about web3 is that it enables founders to communicate directly with their community. NFTs allow a more democratic and sustainable way to help organizations solve social problems such as climate change, disease, animal extinction, etc. At the same time, it gives the donors social recognition through the emission and hold of the NFT.
DAOs
On the other hand, others Web3’s fundraising mechanisms are starting to be attractive for NFT collections. DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) are becoming a top priority for Game-Fi NFT sector, PFP, and De-Fi; because of their ability to give full democracy and autonomy on the project’s road of success to their community, users and investors.
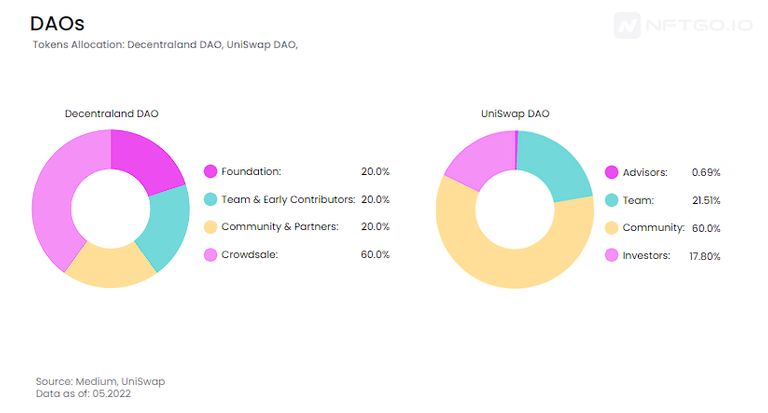
Most of the DAOs’ tokens allocation are for the communities through DEXs, CEXs, and some drops.
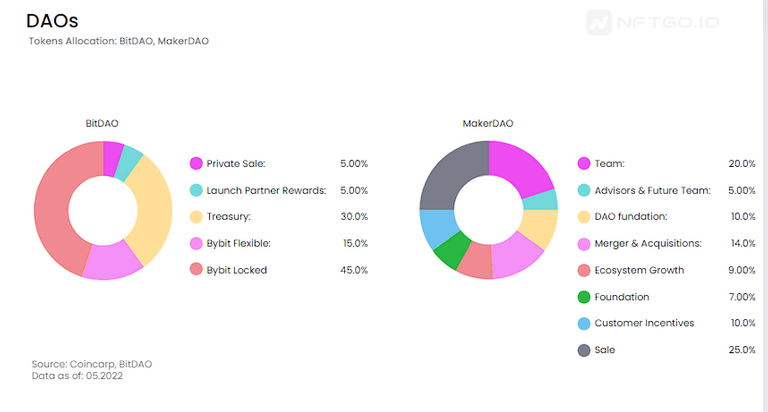
Based on the formula:
Team’s tokens allocation (%) * Current Circulating Supply * Token’s Price
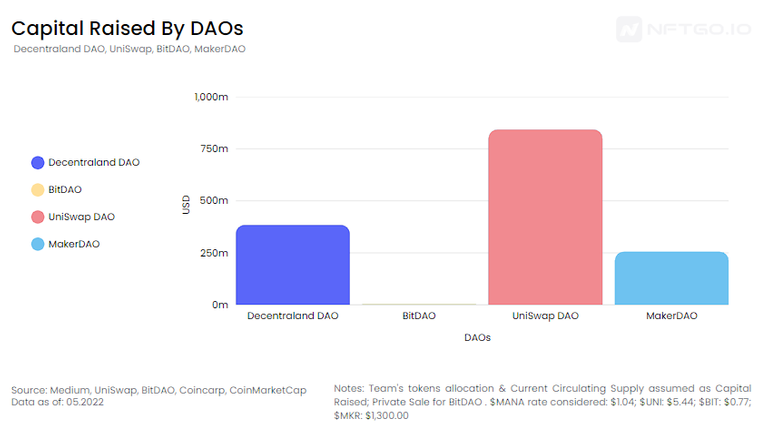
We are able to subtract the capital raised by DAOs which similar in amount of capital raised as the top PFP NFT collections.
Conclusion
NFTs open a new way to fundraise without the need for traditional finances. It allows projects/companies to fundraise through people that believe in them. The significant downside is that NFTs work like the stock market. Bad results lead to a considerable decrease in the asset’s value.
Still, NFTs have a higher upside than other traditional mechanisms for fundraising. This new fundraising method allows investors to have immediate liquidity from the market if they want to sell their “shares” (in this case, NFTs).
The good thing is that using NFTs as a way of ownership adds a transparency layer where you can see through transaction web scanners where the investor's funds are being designated.
The NFTs roadmap should be considered a pitch from founders to the community. It’s crucial to consider how much money projects are extracting from people and if they have a track record of success. Having this in mind might prevent investors from scams.
If you want to know more about NFTs, please visit us at NFTGo.io