Rocket Propulsion - Basic Principles
Rocket propulsion is the process by which a rocket engine produces thrust, which is the force that propels a rocket through space. The basic principle of rocket propulsion is based on Newton's third law of motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
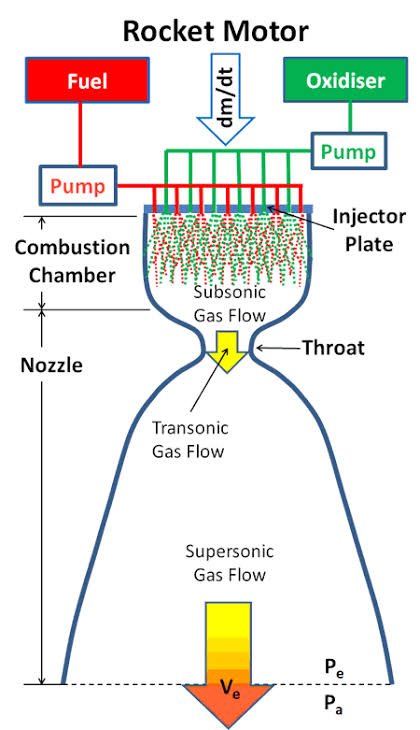
Source★ https://rb.gy/bwkz
The basic components of a rocket engine are the fuel and oxidizer, which are mixed and ignited to produce a high-pressure and high-temperature stream of gases. These gases are then expelled out of the engine nozzle, creating thrust in the opposite direction.
There are two main types of rocket engines: liquid rocket engines and solid rocket engines. Liquid rocket engines use liquid propellants, such as liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, that are stored separately and mixed together in a combustion chamber. Solid rocket engines use solid propellants, which are already mixed and packed into the engine casing.
The amount of thrust generated by a rocket engine is determined by the mass flow rate of the propellant and the velocity of the exhaust gases. This is expressed by the rocket equation, which states that the velocity and direction of the rocket can be calculated by the mass of the rocket and the exhaust velocity.
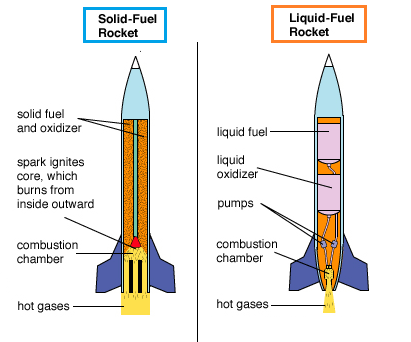
Source★ https://rb.gy/d1zh
Rocket propulsion is a critical technology for space exploration, as it enables spacecraft to travel vast distances and escape the gravitational pull of the Earth. The development of more efficient and powerful rocket engines has been a major focus of space agencies and private companies around the world.