Image credit:wikipedia.org
The principle of this process is the thermal separation produced by a phase change. Its applications include wastewater treatment, obtaining distilled water, desalination of seawater, brackish water, groundwater, among others.

Image credit:pxhere.com
However, it should be noted that commercially available membranes are made of synthetic polymers that have high permeability and selectivity but are expensive and non-degradable.
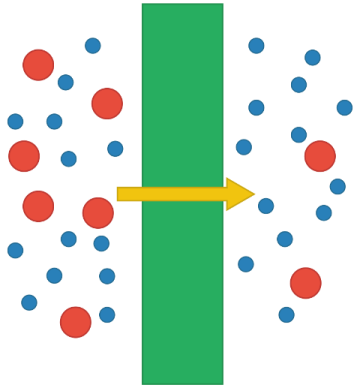
There are several types of membrane distillation whose difference lies in the arrangement of the distillate channel or its operation, one of them is direct contact distillation, which consists of a membrane located between the two fluids at different temperatures.
The membrane used is hydrophobic and the separation occurs due to the difference between the vapor pressure of the saline solution at a higher temperature and the pure water located on the other side of the membrane at a lower temperature, so that the water vapor molecules in the saline solution pass through the hydrophobic and porous membrane. the hydrophobic and porous membrane, condensing on the side of the flow at lower temperature.
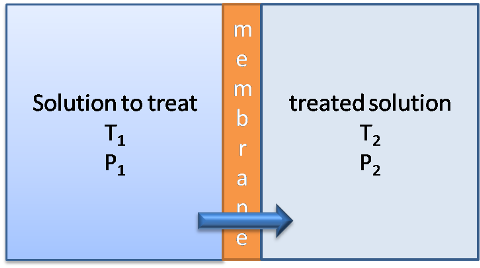
Image credit:@yusvelasquez
In search of alternatives to improve the process, different studies have been carried out to obtain new types of membranes. One study[1] on this subject consisted of obtaining a composite cellulosic membrane system, using pure microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) as a scaffold and its composite as a barrier layer, in which the MFC can be extracted from different lignocellulosic biomass sources.
The preparation of microfibrillated cellulose consisted of homogenization of cellulose microfibrils through carboxymethylation pretreatment of pulp fibers. This pretreatment consisted of approximately 30 g of undried pulp fibers which were exchanged with solvents by washing with ethanol, then impregnated with monochloroacetic acid dissolved in isopropanol and added to a previously prepared reaction solution and during one hour the carboxymethylation reaction was carried out, finally they were subjected to the washing process in three steps.
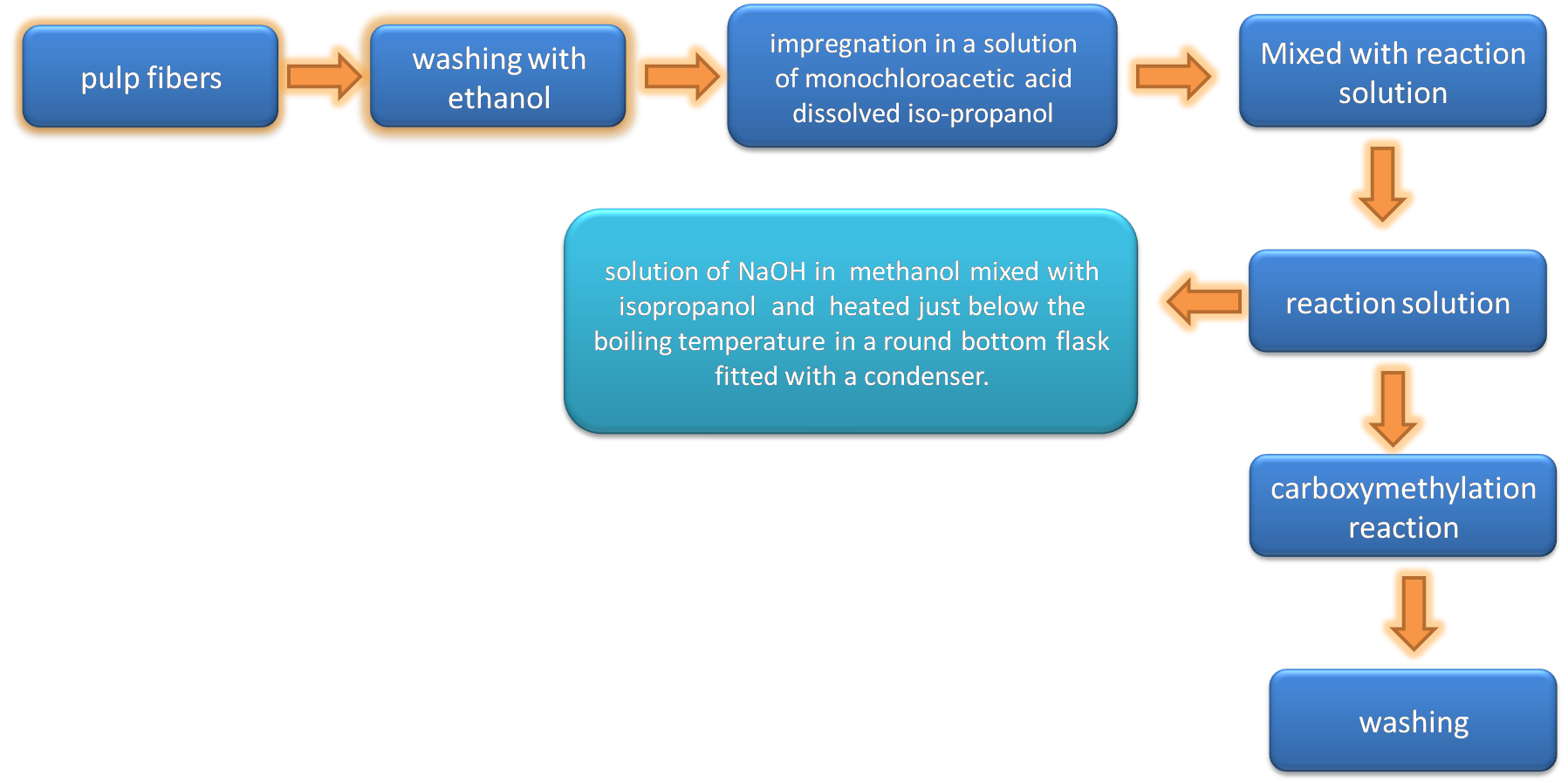
Image credit:@yusvelasquez
Among the most outstanding results of this study were that the membranes showed superhydrophobicity (water contact angle >150°), high porosity and high wet mechanical strength.
It should be taken into account that the efficiency of the membranes depends on certain characteristics such as morphology, water contact angle characteristics such as morphology, pore size, pore distribution, polarity, polymer, and polarity, base polymer, affinity between the membrane material and the solute between the membrane material and the solute to be separated, among others.
On the other hand, the cellulosic membrane that obtained the best performance in the study was tested in a direct contact membrane distillation to achieve the desalination of two types of water: simulated black water and seawater (NaCl solution from 8 g/L to 35 g/L NaCl) obtaining a high water flux and a high proportion of salt rejection, which can be compared with the performance of commercial polytetrafluoroethylene membranes.
Therefore, the importance of the study is reflected in obtaining membranes that have characteristics that allow them to be used in membrane distillation and are degradable contributing to the conservation of the environment to be used in different fields.
So far this post, thanks for reading
References
[1] Joshi, R., Zheng J. and collaborators. (2022). Superhydrophobic Cellulosic Membranes for Membrane Distillation
[2]Distillation Membrane Technology Study(2017)
Every new technology to protect the environment is good

!1UP
You have received a 1UP from @gwajnberg!
@stem-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
I gifted $PIZZA slices here:
@curation-cartel(11/20) tipped @yusvelasquez (x1)
Join us in Discord!