Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, made important statements at the Ethereum Shanghai Summit. The most important one; It is the transition from Proof of Work (PoW), which they have been working on for 7 years, to Proof of Stake (PoS). It was his statement that the transition would be completed by October at the latest. The second most important coin in the cryptocurrency markets will bring a new breath to the markets with this update.
So why is it important to switch from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS)…?
What is Proof of Work (PoW) … ?
What is Proof of Stake (PoS) … ? What are the advantages… ?
If you're ready, let's start …
**Proof of Work (PoW); **Basically, it is a protocol developed for the prevention of attacks aimed at disrupting the operation of a system and the prevention of unwanted messages sent by e-mail called Spam. The Proof of Work protocol originated in a 1993 paper by computer experts Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor. By 1999, it was included in the literature with the efforts of researchers named Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels.
During the development of PoW in the nineties, the most common usage area was to prevent moves to render computer systems inoperable, especially DDoS (Denial of Service) attacks. Likewise, the Proof of Work protocol was used to prevent spam. On October 31, 2008, in the Bitcoin whitepaper published by someone or someone named Satoshi Nakamoto, it appeared in a different form from previous usage areas. The document named "Bitcoin: Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System", which revealed the first cryptocurrency Bitcoin, revealed how a reliable payment system and cryptocurrency can exist thanks to the Proof of Work protocol.
Proof of Work, included in the fourth article of the said document, answers questions about why this mechanism is included in the Bitcoin infrastructure.

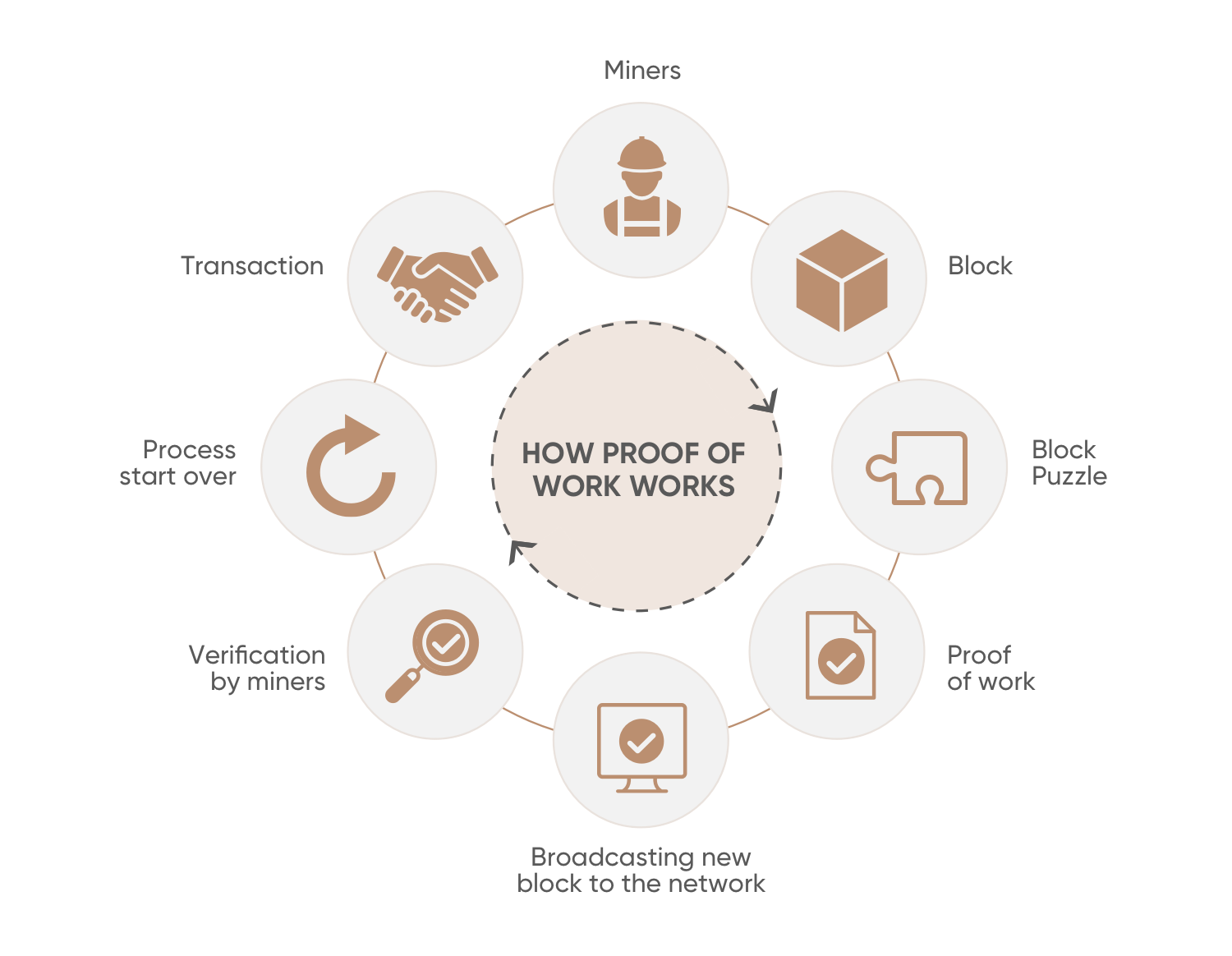
How Proof of Work (PoW) Works ... ?
Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies are blockchain systems protected by networks of decentralized nodes. The main task of these systems is to ensure the sustainability and continuity of the network. There are operators on the network called miners, who are tasked with adding new blocks to the blockchain. Adding these blocks is possible by solving some complex mathematical problems. Since it is very difficult to solve these problems, powerful processors are needed.
The first miner who solves the problem and verifies the transactions in the block broadcasts the transaction to the network, earning the cryptocurrency reward determined in the network and the transaction fees paid for the transactions in the block. Transactions published on the network verified by miners are recorded in a distributed ledger system called a blockchain. All users connected to the network can download a copy of the blockchain and at the same time perform verification of all approved blocks.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the Proof of Work (PoW) Protocol?
Proof of Work, the most common and fundamental protocol in the cryptocurrency industry, offers radical changes in terms of technology and economy by allowing a payment system and currency to work without a central authority. For example, computing power is used as one of the important mechanisms that ensure the security of data in the network. Thanks to the Proof-of-Work protocol, at least 51 percent of the computing power in the network must be captured in order for attacks on the Bitcoin network to be successful. Considering the size of the Bitcoin network and its high computational power (hashrate) today, such an attack is unlikely to succeed. Computing power represents the number of attempts the processors in the network can make in one second and can be thought of as the verification power.
Although the obligation to capture most of the computing power to take over the network is seen as one of the biggest advantages of the PoW protocol due to the security it provides, experts also express the concern that this may lead to monopolization. So this huge advantage becomes one of the biggest disadvantages of the PoW protocol at some point. Because the processors with the largest share can have the highest voting power in the network. The principle of decentralization, which is the most important feature of the Bitcoin network, creates a contradiction with the network principles due to the risk that the strong can easily gain authority.
Because a system based on the PoW protocol requires high processing power, it leads to very intense energy use. This situation can lead to both high costs and the irresponsible use of energy resources.

Emerging as an alternative to Bitcoin's Proof of Work protocol, Proof of Stake (PoS) is a protocol that considers digital asset ownership rather than a system based on computational power. The PoS protocol, presented in an article published by blockchain developers Sunny King and Scott Nadal in 2012, focuses on eliminating the high energy consumption and some other problems required for Bitcoin mining. Peercoin was the first cryptocurrency to use the PoS protocol.
The Proof of Work protocol used in the Bitcoin network is a system where miners, who hold most of the processing power, have more say in the network and therefore earn more returns. Bitcoin mining requires high energy consumption, but the Proof of Stake protocol does not allocate network power based on processor power. In PoS, the generation of the next block can be handled by operators who execute several combinations simultaneously. There are multiple types of Proof of Stake protocol.
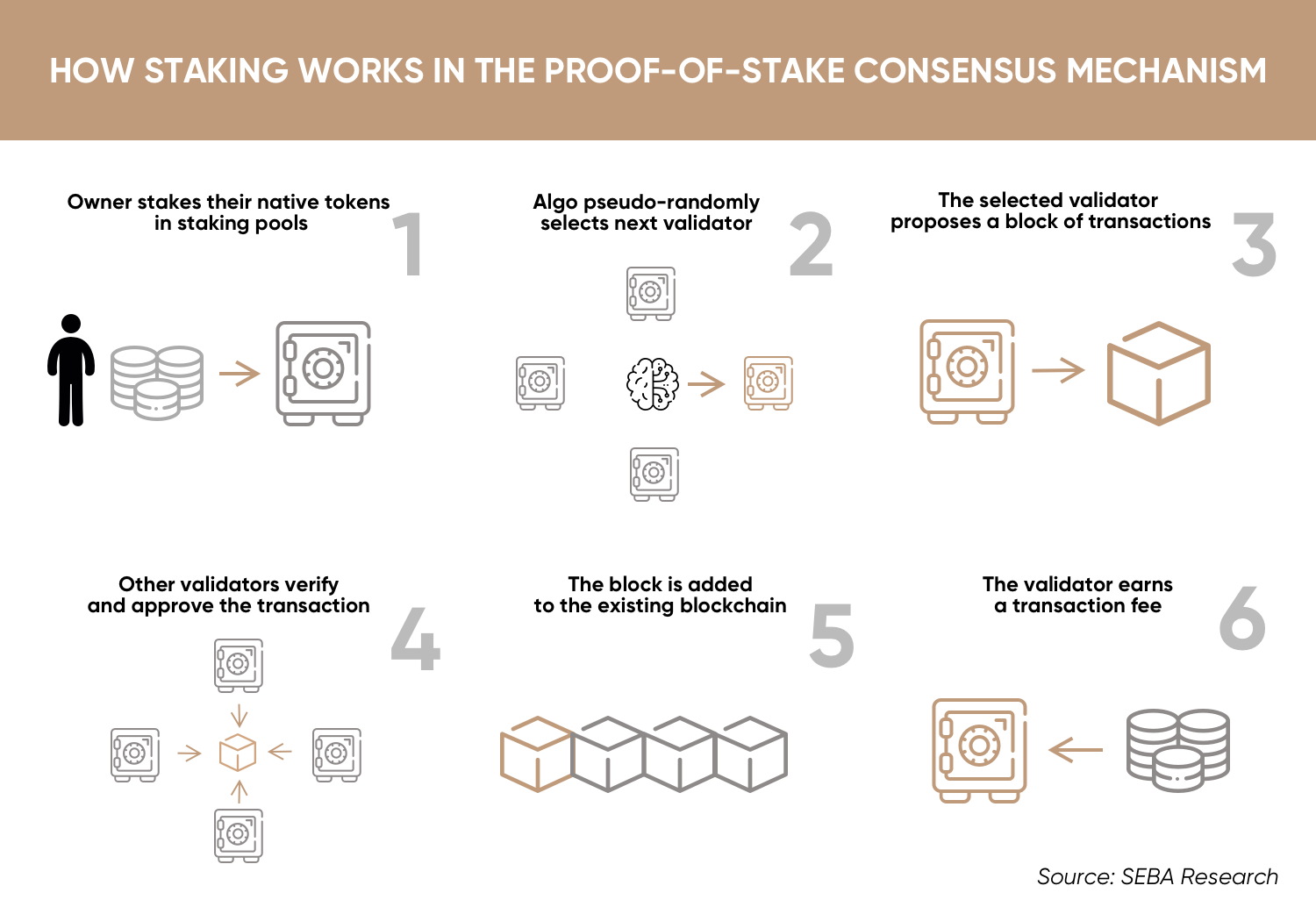
In the Proof of Stake protocol, users who want to be able to verify transactions and get a share of the revenue must lock their cryptocurrency holdings to be used for verification. In this locking process, called "Staking" (taking a share of the revenue), in the wallet, the amount desired to be used for this transaction cannot be withdrawn from the wallet until it is unlocked, and is marked on the network as the user's stake.
In blockchains using proof-of-stake protocol, users share block verification rewards and transfer fees (miner fee) paid by other users in proportion to their shares. We can liken this process to owning the shares of a publicly traded company. Users who allocate more cryptocurrencies for "staking" get a higher share of revenue, just as people who own more shares get a higher share of the profits the company distributes.
Ethereum project. With version 2.0, it will be the largest cryptocurrency project using Proof of Stake.
Features of Proof of Stake (PoS) Protocol
The most prominent feature of Proof of Stake is that it emphasizes capital power over computational power. So instead of starting a trade by running a piece of equipment, it is necessary to have an asset to stack. In the PoS protocol, a user holding more cryptocurrencies can also increase his power in the network. The verification process is based on some rules. Users with more assets in their wallet are more likely to be authenticators. This is where the concept of "staking" comes from. The PoS protocol is based on wallet holders earning by confirming transactions. The user with more assets gets a bigger share of the revenue. However, it should be noted that this does not work the same in all PoS types.
To prevent the wealthiest stakeholder from monopolizing the network, the Proof of Stake protocol uses multiple options for block definitions. The most common PoS selection types are random and cryptocurrency age selection.
In random selection, those who approve transactions are selected among the weakest nodes in terms of computation (hash) value but the richest in terms of share (share) value. In cryptocurrency age selection, users who hold the asset the longest are selected as validators, and after verification, these users are rewarded.
Types of Proof of Stake (PoS)
The Proof of Stake protocol, which emphasizes the asset ownership of the users, has evolved over time and started to be offered with different options. Delegated Proof of Stake (dPoS) and Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS) are the prominent types of PoS.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
In the Proof of Stake protocol based on cryptocurrency ownership, a user has the right to verify transactions and generate blocks by keeping their crypto assets in their wallet connected to the relevant blockchain. dPoS, on the other hand, comes with some additional features and leverages the power of stakeholders to resolve consensus by voting fairly.
It uses a social reputation system to drive consensus across its Delegated Proof-of-Stake (dPoS) blockchain network. Referred to as the least decentralized protocol compared to others, dPoS aims to give cryptocurrency holders a say in the management of the network.
Unlike the Proof-of-Stake system, users delegate their crypto assets in their wallets to another user. Cryptocurrency asset is not transferred from the wallet, but is considered as the asset of the delegated user, increasing the delegated user's voice in the network. The person who receives the right to delegate from other users receives a larger share of the revenues in the network and shares the revenue with the delegates in proportion to their shares.
Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS)
In the Proof of Stake protocol, users are selected according to certain criteria and validate blocks. In other words, they cannot generate income from every block produced. However, in the Proof of Leased Stake (LPoS) protocol, users are allowed to lease a certain percentage of an entire node. This system works exactly like PoS, but it also uses a lease method to provide an incentive to participate for users who hold small amounts of assets. Among the cryptocurrencies using the LPoS protocol, the most well-known is Waves.
Users lease the cryptocurrency in their wallets to other users who approve transactions on the network. In the leasing process, the leased amount does not come out of the user's wallet, but is closed for withdrawal and buying and selling transactions. The leased user gets a larger share of the income while mining and shares his earnings with his stakeholders in proportion to their shares. The user can terminate the lease or lease more cryptocurrencies at any time.
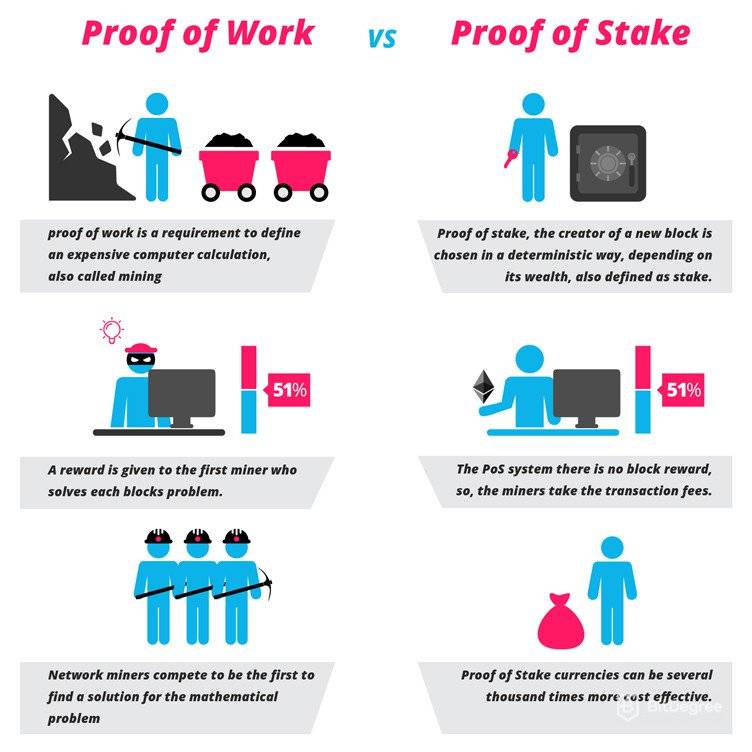
Differences Between Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW)
The PoS consensus algorithm was designed as an alternative to Proof of Work (PoW) and therefore comes with several advantages and disadvantages. In PoW-based blockchains like Bitcoin, validators (miners) can only be rewarded if they find a valid solution to a cryptographic puzzle. In this way, miners can add the blocks they have completed to the Blockchain and move on to the next block.
The Bitcoin network is secure because the mining process is highly competitive and costly (requiring large amounts of computational power). This is also one of the limitations of the PoW model, as the majority of resources used for mining cannot be used for almost anything else.
In contrast, blockchains implementing the PoS model select validators to reach consensus based on a number of factors. The implementation of this selection is constantly changing, but generally takes the size of the stake into account “coin age” (how long the coin will be staked). In most cases, block selection uses a randomization mechanism, which means that validators take turns in the process of generating new blocks.
Unlike PoW, the PoS model requires much less computational power, and validators can secure the network using their own computers rather than specialized mining hardware (ASICs). As a result, PoS systems can provide increased scalability, energy efficiency, security, and a more decentralized system.
In the debate between Proof of Stake and Proof of Work, staking can be more democratic. Users with tokens can join as validators or stakers and benefit from the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ecosystem. More generally, analysts focus on the environmental burden from Proof of Work protocols. Bitcoin, in particular, has developed a large environmental footprint as it gains wider acceptance. Proof of Stake significantly reduces this environmental cost by eliminating advanced cryptographic puzzles.
Proof of Work (PoW) advocates claim that Proof of Stake (PoS) deviates from the original cryptocurrency vision. Bitcoin has differentiated itself from other financial assets because the database or Blockchain record is valuable. While the mining process was energy inefficient, it created a separate and tamper-proof record of all financial transactions. Proof of Stake has some security vulnerabilities in its basic form. For example, the endangered nothing at stake issue focuses on the fact that it encourages malicious behavior when there is no cost to forking or putting bad information into the consensus. The energy cost of Proof of Work inherently limits manipulation, meaning that Proof of Stake needs to use more sophisticated methods to try to stop these security issues.
The discussion of Proof of Stake vs. Proof of Work has largely remained in the technical realm. Proof of Stake has a remarkable lead in Cardano, but the biggest projects have been done with Proof o Work. However, Ethereum's plans to move from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake raise this issue. Ethereum's movement started in earnest in 2020, when Ethereum launched its Proof of Stake Beacon chain. Phase 1 is slated to launch later in 2021 and aims to fully merge with Proof of Stake for Ethereum over the next year.
Besides the traditional PoS model, there are specialized variations such as Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) mechanisms. Apart from this, hybrid consensus systems are also available, such as Hybrid PoW/PoS, which combines features of both PoW and PoS models.
My Last Words; Proof of Stake (PoS) saves a lot compared to Proof of Work (PoW). Electricity consumption cost is almost zero. It also encourages investors to invest more as the reward is wallet balance based. Even if you don't have a computer, you can start generating Proof of Stake (PoS)-powered coins or tokens by purchasing Raspberry Pi devices that are priced at around $50 in the market and running your wallet on this device. Is not it beautiful ... ?
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta