Consider self-executing applications without anyone's control. Imagine that third party persons or institutions have no influence on transactions. You don't have to imagine anymore… These applications are called Decentralized Applications (dApps). Unlike traditional applications, these software bridges between the user and the provider without intermediaries.
In this article, I want to tell you about Decentralized Applications (dApps). I think decentralized applications will develop further with Web 3.0 and Metaverse...
If you're ready, let's start …
What are Decentralized Applications (dApps) … ? ; A fixed server is a server and applications that do not have anyone to manage and control them. They are built on a blockchain network. Every computer (node) using this network provides the system features required for these applications to run. Thus, it does not run on a fixed server, but is run on tens of thousands of different computers connected to the blockchain network. In this case; A structure that is decentralized and whose control and management is not in the hands of anyone is created.
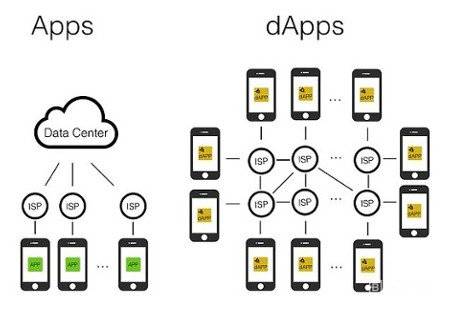
What is the Working Logic of Decentralized Applications (dApps)… ? ; Decentralized applications also work on decentralized blockchain structures. Today, the most basic blockchain network these applications run on is Ethereum. Each dApp has its own smart contract. Smart contracts are created once by the developers of the application and continue to work on their own from that moment on. They can never be changed or updated again. This is exactly what makes all these decentralized structures reliable. If users review and approve the smart contract, which is published in a public, transparent manner, they prefer to use the applications, to exist in it. Although dApps work on the blockchain, the most basic element that determines their importance is their smart contracts.
The same application development methods can be used for dApps as they are used in traditional application development. At this point, the most basic element that distinguishes dApps from others is that the same programming languages can be used on the front, while traditional, central applications use APIs on the back, while dApps use smart contracts.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) Advantages
Zero Downtime; One of the biggest advantages of running applications in distributed processor networks is that when any node leaves the network or a component fails, all remaining units continue to run and take on extra workload. In this way, once the smart contract at the heart of the application is placed on the blockchain, the application will continue to run without interruption as long as the network is alive. Moreover, due to their decentralized nature, dapps are resistant to a wide range of security threats such as DDoS attacks, SQL injections, XML bombs, and cross-site scripting attacks.
Censorship Resistance; Because they run on open and permissionless networks, no institution has the power or authority to prevent users from accessing or deploying decentralized applications.
Security; In general, users can freely interact with decentralized applications simply using their cryptocurrency wallet, without providing or disclosing any personally identifiable information.
Transparency; Since decentralized applications run on public and transparent blockchains, all data, including the dapp's source code, inbound and outbound transactions, is transparent and public. This adds an additional layer of security as all on-chain behavior is fully verifiable and dapps codes can be reviewed and audited by anyone at any time.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) Disadvantages
Difficulty to Install; The immutability of smart contracts makes dapp construction and design particularly difficult. Developers need to plan dapps comprehensively and future-proof right from the creation stage, as it is impossible to make any changes once they are embedded in smart contracts. Moreover, dapps are built using Ethereum's native programming language Solidity. This language is hardly learned, except that developers are particularly interested in building dapps on the platform.
Lower User Experience; In general, decentralized applications provide a greater downstream user experience than their centralized competitors. Especially since technology is in its infancy, it is significantly difficult to navigate, even for tech-savvy people. Worse still, all blockchain transactions are irreversible and final, which leaves no room for error. If the user makes a mistake in the dapp, there is not much that can be done and mistakes can be costly.
Usage Cost; Transacting in a decentralized application requires paying a network transaction fee. This transaction fee is calculated as Gas (Ethereum's native pricing unit) and is placed in ETH and goes directly to the miners running the blockchain network on which the dapp runs. During peak times a simple end-to-end transaction can cost between $2-5, while end-to-contract transactions such as token swaps on decentralized exchanges can cost up to $20.
Slow; Dapps are expensive, but they are also incomparably slower than regular apps. This is because blockchains using the proof-of-work consensus algorithm take time to process transactions and mine new blocks. The average block time on the Ethereum blockchain is 13.3 seconds. The network's workload capacity is approximately 15 transactions per second, which is well below centralized applications. This means that when usage exceeds the network's processing capacity, blockchain becomes denser and transactions take longer and more expensive to process. In such a case, transactions can take hours to process and sometimes even be rejected by the network, unless users pay excessively high gas fees.
Susceptibility to Malfunctions and Hacks; The execution risk of smart contracts is definitely at the top of this list. While the deterministic and autonomous execution of codes and the immutability of blockchains have some security advantages, they can be devastating if implemented incorrectly. In smart contracts, even a minor coding error can cause major disruptions, and many unnoticed design errors can lead to damaging exploits such as congestion to the point of loss or unusability, with funds locked in the contract. Although code audits by reputable audit firms give some confidence to the average DeFi user, uncertainty still remains.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) areas;
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges and token-swap protocols are the most widely used decentralized applications in the cryptocurrency world. Decentralized exchanges eliminate the need for trusted intermediaries to secure funds by using smart contracts. This reduces the risk of the exchange being hacked and protected funds stolen. All transactions on decentralized exchanges are either end-to-end or end-to-contract, and funds go directly to users' wallets. Rather than relying on order books to bid and execute transactions as centralized marketplaces do, decentralized exchanges use Automated Market Makers or AMMs. AMMs are protocols that use smart contracts to extract predetermined algorithms and mathematical formulas for pricing and creating liquidity pools of tokens.
Some of the most popular decentralized marketplaces on the market include; Uniswap, BiSwap, Curve, PancakeSwap …
Lending and Borrowing Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Decentralized lending and receiving applications are the second most used DeFi applications. Dapps in this category allow users to lend or receive money in exchange for crypto collateral without restrictions such as background credit checks or KYC.
The two most popular dapps of this genre are Compound and Aave. Compound is an AMM that automatically matches borrowers with lenders and calculates the interest rate based on the ratio of assets borrowed to assets offered. In addition, Aave allows users to experience concepts such as flash loan, rate change and unsecured borrowing.
Yield-farming Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Yield-farming dapps are essentially automated decentralized mutual funds that use smart contracts instead of human fund managers to raise and allocate capital. The idea in yield-farming dapps is to automate the yield farming process. In simple terms, it is the pooling or locking of capital in various DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards. These dapps offer a hands-free approach to crypto investing and allow users to take advantage by allowing them to pool their gas (transaction) costs.
Users do not need to understand the underlying strategy of a specific yield-farming dapp. They just stake cryptocurrency on the dapp and earn passive interest.
The most popular dapps in this category are Yearn Finance, Harvest Finance …
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized autonomous organizations or DAOs are exactly what their name implies. Rather than relying on humans and typical hierarchical management structures to operate, DAOs use smart contracts to execute decisions autonomously. Although DAOs can have many functions, the most important is that they allow dapp users to participate in the administration in a decentralized way. The world of cryptocurrencies is moving very quickly and innovating, forcing dapps to innovate and change to stay up to date. However, for innovation and evolution, dapps need to make decisions that will not come from a single person or group. Because such decisions are against the core values of decentralized people.
To solve this problem, dapps need to create DAOs that, among other things, allow users to vote and submit protocol changes, create unregulated treasuries to fund future developments, and grant users certain rights or share ownership in the dapp.
My Last Words; The most critical advantage Decentralized Applications (dApps) have over regular apps is their permissionless innovation. Since decentralized applications are completely open and, in most cases, not subject to the control of the parties, they allow developers to create and test freely, making progress in the crypto world in organic and unexpected ways. dapps; Because they are not held by trade secrets, copyrights, brands or patents, the entire crypto world benefits from combinatorial innovations, which are individual advancements built on the efforts of others. The future of decentralized applications is unmistakably bright.
“Keep your eyes on the stars, and your feet on the ground.”
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta