
We explore the inner workings of the Polygon blockchain and the layers of which the network is comprised.
Polygon is a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain.
This means that Polygon works by selecting validators in proportion to their MATIC stake.
While it is described an Ethereum side chain, the Polygon blockchain is compromised of its own infrastructure including nodes, token (MATIC) and range of native dApps.
The only difference being that transactions are ultimately processed on the Ethereum mainnet.
For this subsection of our LeoFinance Polygon (MATIC) guide, lets dive down a little deeper on the inner workings of the network.
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain.
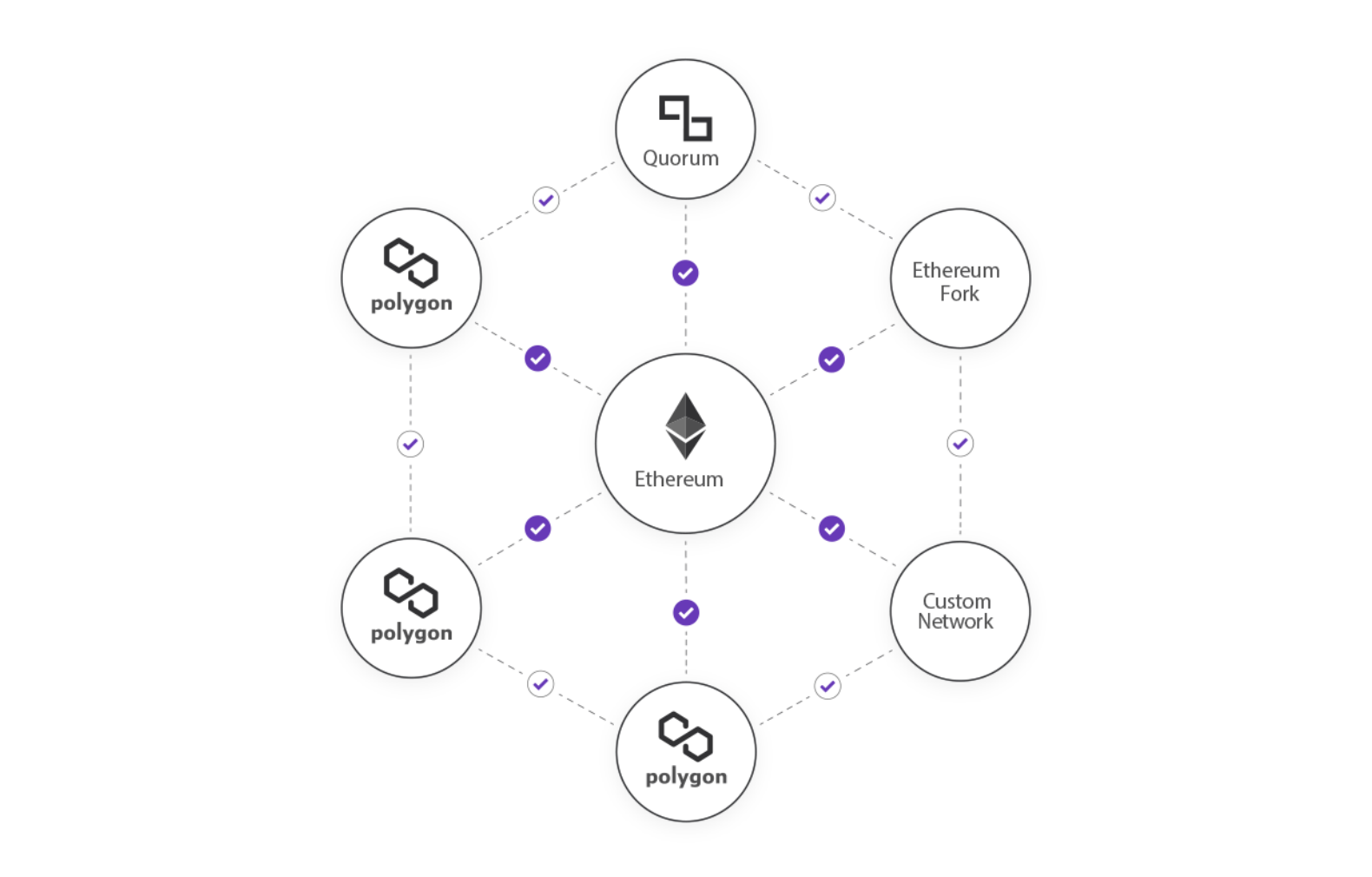
These are sidechains that are built on top of a primary blockchain which is otherwise referred to as layer-1.
In Polygon’s case, this layer-1 blockchain is the Ethereum mainnet.
As a layer-2 scaling solution, Polygon works alongside Ethereum by handling transactions off of the main chain.
Polygon ultimately increases Ethereum’s capabilities by:
- Improving transaction speed.
- Improving the number of transactions per second.
- Lowering gas fees.
4 layers of Polygon
When it comes to network architecture, Polygon is comprised of 4 distinct layers.
Layer 1: Ethereum Layer
Thanks to the use of smart contracts, Polygon chains are able to execute any critical component over the Ethereum network
This means that applications built on Polygon can take advantage of the decentralised security that the Ethreum mainnet can offer.
Layer 2: Security Layer
The second, optional layer provides ‘validators as a service’.
Ultimately the security layer checks all aspects of any Polygon based blockchains and validates transactions if required.
Layer 3: Polygon Networks Layer
Moving onto the third, the mandatory networks layer is utilised by all Polygon based blockchains to allow for interoperability.
It allows Polygon networks to each act independently, while taking advantage of Polygon’s Ethereum layer-2 capabilities.
The network laters is responsible for block production, consensus, and collating transactions.
Layer 4: Execution Layer
The final layer is the mandatory execution layer that interprets and executes transactions included in Polygon’s network chains.
This is achieved by hosting a series of smart contracts that ultimately provide funtionality to all dApps built on the Polygon network
Final word on how Polygon (MATIC) works
Ultimately, the Polygon network is an Ethereum sidechain offering value to the vast Ethereum universe of decentralised applications.
Each Ethereum based dApp can be easily converted to an associated Polygon blockchain version.
By taking non-core functions off the Ethereum network and onto layer-2, users gain the best of both worlds by experiencing faster/cheaper transactions on Polygon and all security/decentralisation aspects of Ethereum.
For more a more technical look at how Polygon (MATIC) works, check out the official light-paper.
Best of probabilities to you.
Direct from the desk of Dane Williams.
Why not leave a comment and share your thoughts on how Polygon (MATIC) works within the comments section below? All comments that add something to the discussion will be upvoted.
This Polygon (MATIC) blog is exclusive to leofinance.io.
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
Please, give me Polygon site link you used or do POS.
Thank for sharing!
!PIZZA
@forexbrokr! I sent you a slice of $PIZZA on behalf of @tin.aung.soe.
Learn more about $PIZZA Token at hive.pizza (2/10)
Sorry Tin, what exactly are you looking for?
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta