ENGLISH VERSION

Source
Ethereum has the great merit of having made the whole world wake up to the various possibilities that the technology behind cryptocurrencies offers, and not remain simply in the field of finance. Indeed, with the innovation of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) for the simpler implementation of smart contracts within the same base layer, has opened the doors to any type of idea and project that is programmable, to benefit from the features of these new technologies, such as, tokenization, ownership, immutability, among others.
Despite this, it is also a reality that this blockchain has not been able to meet all expectations. We can name two of them. One is scalability, being the first blockchain that presents the proposal of being able to easily program within it, there has been a lot of demand since then, and as the software architecture was not fully prepared for it, it has gone through stages of great user congestion, and although its passage to the consensus mechanism PoS seeks to alleviate this problem there is still a long way to go.
Along with this problem is closely linked the high costs for the gas price used in the various operations that are of various types and there are periods where they enter into a kind of competition, since the one who pays the best commissions will be served faster, there have been cases where it is more what is paid for this commission than what is obtained from a transaction. In this way, the promise that smart contracts can lower the costs of making a traditional contract is not fulfilled.
For this reason, several layer 2 proposals have emerged to address these limitations of ethereum. In this way, we will be able to enjoy the features of this network but solving its particular problems, and even proposing quite interesting alternatives. Not without reason, Vitalik Buterin himself has encouraged the creation of such solutions. In this post, we are going to present in a summarized way and in its most important points the approach of Polygon.
What is Polygon?
It is a solution for Ethereum network scalability that Indian Software engineers Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal and Anurag Arjun had been thinking about and preparing since 2017, as many were alarmed by the congestion of the esteemed network. In 2019 they had a successful launchpad held at Binance, and in 2020 they presented their white paper under the name Matic Network, a name that today is reserved for the project's native cryptocurrency, since in February 2021 it went through a rebranding to take the name Polygon, with which it is known today.
In a first approach and with a few words we can say that Polygon is a layer 2 solution for the Ethereum network that focuses and at the same time enhances scalability so that both developers and users in general feel secure in the use of their dapps, since in the end the most important of our operations such as the registration of transactions is done in Ethereum.
For us Polygon enhances scalability because its vision is not only to offer a solution to this problem, but it goes beyond, since it is open to the construction and connection with various protocols that also aim at scalability. That is why they have at their disposal a framework to make this task easier, we can even find among their resources an academy and a university that take us step by step in the acquisition of the necessary knowledge and skills.
Hence they are right to also present themselves as a blockchain made by developers for developers. In fact, they have recently launched the beta version of Polygon zkEVM, based on the ZK rollups approach, which is a different solution to the Plasma framework with which it was originally launched. Future plans are to continue integrating other alternatives such as Optimistic Rollups, valdium chains, etc.
Polygon is also presented as an agnostic blockchain, because within its scalability solutions other blockchains can make life, this is the reason why it is self-catalyzed as the internet of Ethereum blockchains, in that one of its layers can coexist with various projects and networks that through it have compatibility with Ethereum. Here's how Polygon enhances Ethereum even beyond the scalability it provides, or rather, thanks to it.

How does it work?
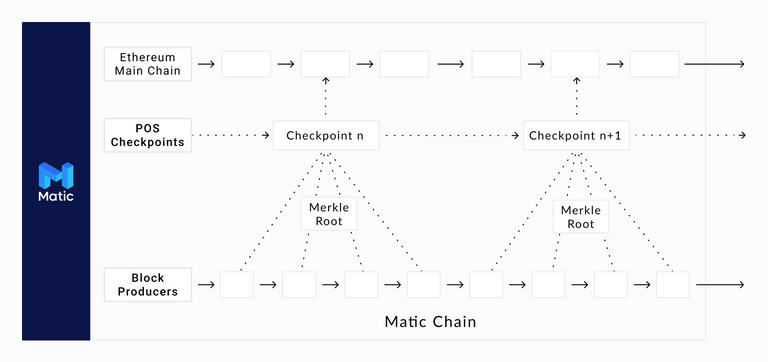
As we have referenced the Polygon network works on the basis of layers, which are four:
The mainnet, which refers to the Ethereum network. Very important because it gives Matic's scalability the security of that one. This is also where some of the various options that the Polygon team is working on come into play: Plasmas, rollups, among others. Each one with its pros and cons, but in a decentralized network this also comes in handy, because each project takes the tool that suits it best.
Then comes, you could say, an additional layer of security, as this is where Polygon's consensus protocol is properly handled. Which is Proof of Stake, which also brings more decentralization to this megaproject. It is important to note that the validators take snapshots of the operations every 5 seconds to pass them to the main layer, which is why it is also called the checkpoint layer.
The third layer is that of block producers, where a smaller number of validators (chosen from the group of layer two) participate, to provide greater capacity to perform operations. Each block is estimated to take only about one second to produce, which further enhances the scalability of both this network and those associated with it.
This last layer is where the various blockhains seeking compatibility with Ethereum through Polygon have their roots, according to the various proposals offered: Matic PoS Chain, Sidechains, Enterprise Chains, etc.
Finally, we highlight within this theme of operation the role played by the cryptocurrency, since, $MATIC currently has a circulation of 9,289,469,069, and has a fixed total of 10,000,000,000 tokens. The functions within the blockchain are as follows: payment of fee (gas), use for staking by validators, development of smart contracts and for voting on governance-related issues (Dao).
Source
Features to highlight
The first thing we notice is the close relationship of Polygon with Ethereum, so that unlike the blockchains called ethereum killers (Polkadot, Cardano, Avalanche, etc.), this is rather an ethereum savior, since it makes known more the benefits it has and strengthens its weaknesses that, as we have already highlighted in the previous paragraphs are: scalability and expenses for commissions on the price of gas. In Polygon we get with a fast blockchain, where you can perform several transactions per second and economic, and at the same time backed by Ethereum in its base layer, with which it benefits from its development but, above all, of the large community it has.
With Polygon it also gives a major boost to dapps, which can now enjoy the best of two worlds. Security and decentralization in one, and scalability and greater accessibility in the other. In this regard, the whole framework offered together with the training to work in the network is phenomenal. In the same way, it is worth highlighting, along the same lines, the interoperability to which the ethereum network opens, together with it, it can be positioned as the way of massive introduction of many people to the web 3.0.
Finally, Polygon's partnerships give more reliability and adoptability to the project. Not only Binance that supported the launch of the token but also renowned projects that make life in it (Mana, Aave, MarkeDAo, etc.), as well as renowned personalities who have made public their admiration for it, it is commonly named in this regard Mark Cuban.

Conclusions
Polygon is a multifaceted project that leverages second-layer solutions to turn ethereum into a multi-chain blockchain or, as they themselves say, the mother blockchain of other blockchains.
The interesting thing about this is that they do not impose anything but have great flexibility, being useful for projects that already have EVM incorporated as well as those that do not, because with their compatibility options they make this possible. In this sense, it is noteworthy that its security layer, where the staking of the $MATICs is done, is optional, so that a sovereign blockchain, with its own protocol, does not have to assume this condition if it is not necessary.
Polygon also presents itself many times as a framework, and as we have seen its development of tools to create blockchains "with a single click" and connect them together has made this possible. That is why its efforts in the architecture of the dapps to offer a pleasant user experience, which seems to us fundamental to facilitate the transition from web 2.0 to 3.0 and avoid to a large extent the existing frictions.
That is why we conclude that Polygon really improves on ethereum in many aspects, plus they have the advantage of being able to take advantage of its capitalization and the community, both of users and developers, that already supports it.


VERSIÓN EN ESPAÑOL

Source
Ethereum tiene el gran mérito de haber hecho que todo el mundo despierte a las diversas posibilidades que desde la tecnología detrás de las criptomonedas tenemos, y no quedarnos simple y llanamente en el ámbito de las finanzas. En efecto, con la innovación de la Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) para la implementación más sencilla de los smart contracts dentro de la misma capa base, ha abierto las puertas a cualquier tipo de idea y proyecto que sea programable, para que se beneficien de las características de estas nuevas tecnologías, tales como, la tokenización, la propiedad, inmutabilidad, entre otros.
A pesar de esto, también es una realidad que esta blockchain no ha podido cubrir con todas las expectativas. Podemos nombrar dos de ellas. Una es la escalabilidad, y es que al ser la primera blockchain que presenta la propuesta de poder programar fácilmente dentro de ella ha sido mucha la demanda desde entonces, y como la arquitectura del software no estaba totalmente preparada para ello, ha pasado por etapas de gran congestión de usuarios, y si bien su paso al mecanismo de consenso PoS busca aliviar este problema todavía falta mucho camino por recorrer.
Junto a este problema está muy unido el de los altos costos por el precio del gas usado en las diversas operaciones que son de diversos tipos y hay periodos donde entran en un tipo de competición, ya que el que mejor comisiones pague será más rápidamente atendido, ha habido casos donde es más lo que se paga por esta comisión que por lo que se obtiene de una transacción. De esta manera, no se cumple con la promesa de que con los smart contract se pueden abaratar los costos de realizar un contrato tradicional.
Por esta razón, han surgido varias propuestas de capa 2 para afrontar estos limitantes de ethereum. De esta manera, podremos gozar de las características de esta red pero resolviendo sus problemas particulares, y hasta planteando alternativas bastante interesantes. No sin razón, el mismo Vitalik Buterin ha animado la creación de este tipo de soluciones. En este post, nosotros vamos a presentar de manera resumida y en sus puntos más importntantes el planteamiento de Polygon.
¿Qué es Polygon?
Es una solución para la escalabilidad de la red de Ethereum en la cual unos ingenieros de Software de la India Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal y Anurag Arjun venían pensando y preparando desde el 2017, ya que como muchos se encontraban alarmados por la congestión de la apreciada red. En el 2019 tuvo un exitoso launchpad realizado en Binance, y en el 2020 presentan su white paper bajo el nombre de Matic Network, nombre que hoy en día se reserva a la criptomoneda nativa del proyecto, puesto que en febrero de 2021 pasó por un rebranding para tomar el nombre de Polygon, con el cual se conoce hoy en día.
En un primer acercamiento y con pocas palabras podemos decir que Polygon es una solución de capa 2 para la red de Ethereum que se enfoca y al mismo tiempo potencia la escalabilidad de manera que tantos desarrolladores como usuarios en general se sientan seguros en el uso de sus dapps, ya que al final lo más importante de nuestras operativas como lo son el registro de las transacciones se realiza en Ethereum.
Para nosotros Polygon potencia la escalabilidad porque precisamente su visión no es solo ofrecer una solución a esta problemática, sino que va más allá, puesto que se abre a la construcción y conexión con varios protocolos que también apunten a la escalabilidad. Es por ello que tienen a disposición un framework para hacer más fácil esta tarea, incluso podemos encontrar entre sus recursos una academia y una universidad que nos llevan paso a paso en la adquisición de los conocimientos y habilidades necesarias.
De allí que tengan razón en presentarse tambén como una blockchain hecha por desarrolladores para desarrolladores. De hecho, hace poco han lanzado la versión beta de Polygon zkEVM, basada en la propuesta de los rollups ZK, que es una solución diversa al framework de Plasma con el cual se había lanzado en un principio. Los planes futuros son seguir integrando otras alternativas tales como los Optimistic Rollups, valdium chains, etc.
Polygon se presenta también como una blockchain agnóstica, porque dentro de sus soluciones de escalabilidad pueden hacer vida otras blockchains, esta es la razón por la cual se autocataloga como el internet de las blockchains de Ethereum, en cuanto que una de sus capas pueden convivir diversos proyectos y redes que a través de ella tengan compatibilidad con Ethereum. He aquí como Polygon mejora Ethereum incluso más allá de la escalabilidad que le brinda o, mejor dicho, gracias a ella.

¿Cómo funciona?
Como hemos hecho referencia la red de Polygon funciona a base de capas, las cuales son cuatro:
La mainnet, que hace referencia a la red de Ethereum. Muy importante porque le da a la escalabilidad de Matic la seguirdad de aquella. Aqui también es donde entran en juego alguna de las diversas opciones en la cual el equipo de Polygon está trabajando: Plasmas, rollups, entre otras. Cada una con sus pros y contras, pero en una red descentralizada esto viene también de maravilla, porque cada proyecto toma la herramienta que más le convenga.
Luego viene, pudiésemos decir, una capa adicional de seguridad, ya que es donde se maneja propiamente el protocolo de consenso de Polygon. El cual es Proof of Stake, lo cual también brinda mayor descentralización a este megaproyecto. De aqui es importante que retengamos que los validadores realizan snapshots de las operaciones cada 5 segundos para pasárcelas a la capa principal, por eso, también se le llama la capa de los puntos de control.
La tercera capa es la de los productores de bloque, donde participan un menor número de validadores (elegidos del grupo de la capa dos), para dar mayor capacidad de realziar operaciones. Cada bloque se estima que ronda apenas el segundo para su producción, lo cual potenia aun ás la escalabilidad tanto de esta red como las que a ella se asocien.
Esta última capa es donde hunden sus raíces las diversas blockhains qeu buscan la compatibilidad con Ethereum a través de Polygon, según las diversas propuestas que se ofrecen: Matic PoS Chain, Sidechains, Enterprise Chains, etc.
Finalmente, resaltamos dentro de este tema del funcionamiento el papel que desempeña la criptomoneda, pues, $MATIC cuenta actualmente con una circulación de 9.289.469.069, y tiene un total fijo de 10.000.000.000 de tokens. Las funciones dentro de la blockchain son las siguientes: el pago de fee (gas), uso para el staking por parte de los validadores, desarrollo de smart contracts y para votar en temas relacionados a la gobernanza (Dao)

Source
Características a resaltar
Lo primero que notamos es la relación estrecha de Polygon con Ethereum, de tal manera que a diferencia de las blockchains llamadas ethereum killers (Polkadot, Cardano, Avalanche, etc.), esta más bien es una ethereum savior, puesto que da a conocer más las bondades que ésta tiene y fortaleces sus debilidades que, como ya hemos resaltado en los párrafos anteriores son: escalabilidad y gastos por comisiones del precio del gas. En Polygon nos conseguimos con una blockchain rápida, donde se pueden realizar varias transacciones por segundo y económica, y al mismo tiempo respaldada por Ethereum en su capa base, con lo cual se beneficia de su desarrollo pero, sobre todo, de la gran comunidad que posee.
Con Polygon también se le da un impulso importante a las dapps, que ahora pueden gozar de lo mejor de dos mundos. La seguridad y descentralización en uno, y escalabilidad y mayor accesibilidad en el otro. Al respecto, todo el framework que ofrece junto a la capacitación para trabajar en la red es fenomenal. De la misma manera es de resaltar, siguiendo esta misma linea, la interoperabilidad a la que abre la red de ethereum, junto con ella se puede posicionar como la via de introducción masiva de muchas personas a la web 3.0.
Finalmente, los partnership de Polygon le dan más confiabilidad y capacidad de adopción al proyecto. No sólo Binance que apoyó el lanzamiento del token sino proyectos de renombre que en él hacen vida (Mana, Aave, MarkeDAo, etc.), así también como personalidades de renombre que han hecho pública su admiración por el mismo, es comúnmente nombrado al respecto Mark Cuban.

Conclusiones
Polygon es un proyecto multifacético que se apalanca de las soluciones de segunda capa para convertir a ethereum en una blockchain multicadena o, como ellos mismo dicen, la blockchain madre de otras blockchains.
Lo interesante de esto es que no imponen nada sino que tienen una gran flexibilidad, siendo útil para proyectos que ya tienen incorporada la EVM como a los que no, pues con sus opciones de compatibilidad hacen esto posible. En este sentido, es de resaltar que su capa de seguridad, donde se hace el staking de los $MATIC es opcional, de tal manera que una blockchain soberana, con su propio protocolo, no tiene que asumir esta condición si no es necesario.
Polygon también se presenta muchas veces como un framework, y como hemos visto su desarrollo de herramientas para crear blockchains "con un solo click" y conectarlas entre sí lo ha hecho posible. Por eso, su empeño en la arquitectura de las dapps por ofrecer una experiencia de usuario agradable, lo cual nos parece fundamental para facilitar el paso de la web 2.0 a la 3.0 y evitar en gran medida las fricciones existentes.
Por eso concluímos que Polygon realmente mejora a ethereum en muchos aspectos, además tienen la ventaja de poder aprovechar de éste su capitalización y la comunidad, tanto de usuarios como de desarrolladores, que ya le respalda.




