I started a series on cranial nerves, and currently I have been able to explain four cranial nerves which are the olfactory nerve (cranial Nerve 1), The Optic nerve (cranial nerve 2), the oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve 3), and the Trochlear Nerve (Cranial Nerve 4). If you haven't read through these posts, you should do that now, and I am sure you wouldn't have any cause to regret reading through. Well, I guess I had a good start, starting a post can be very stressful, not because I do not know what to write, but because I do not know how to start putting it down, but once I am able to start, I am surely going to keep running like a sport car in a race. In this post, I will be discussing the Cranial Nerve 5 which is the trigeminal nerve
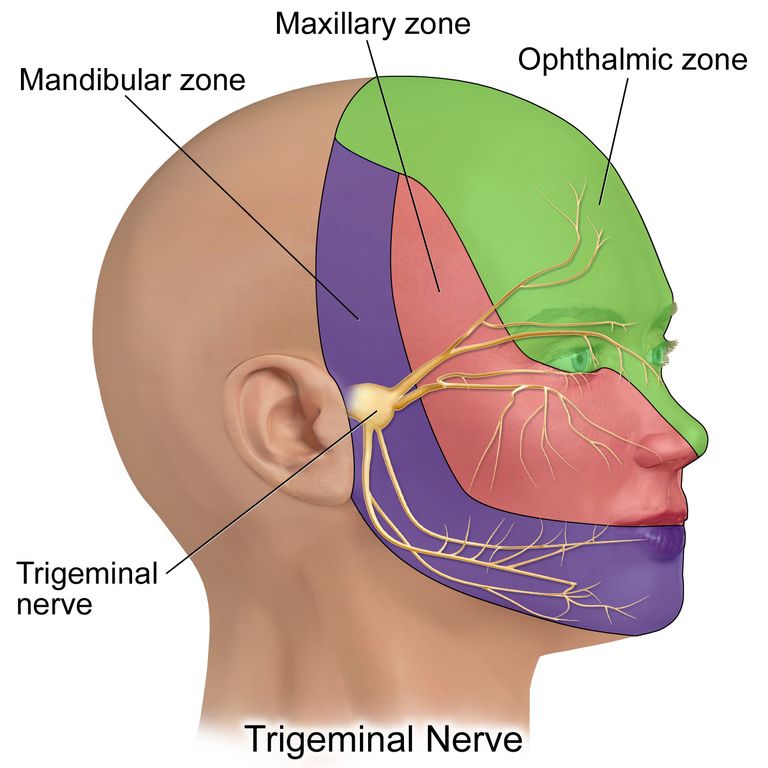
If you remember in my posts on Oculomotor nerve and Trochlear Nerve, I explained that their nucleus and point of origin is in the midbrain, it isn't that simple for the trigeminal nerve. The Trigeminal nerve has nuclei in the peripheral nervous system and in the brain stem. In the peripheral nervous system is the Trigeminal ganglion which is responsible for the peripheral processes. The nerve from the ganglion goes to the brain stem and connects to several nuclei in the brain stem. The Spinal Trigeminal nucleus, located in the lateral medulla of the brain stem, is responsible for touch, temperature, pressure, pain and proprioception (kinesthesia).. Another nucleus where the nerve of the Trigeminal ganglion is the central/principal pontine trigeminal nucleus, found in the pon of the brain stem. It is responsible for touch and proprioception (kinesthesia) of the jaw and the lower face. Another nucleus is the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus found in the midbrain of the brain stem. It is responsible for proprioception (kinesthesia) in the face. The major nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is the trigeminal motor nucleus which supplies the first pharyngeal artery.
It is important that you remember this because I will be touching it s time goes on. Let's focus on the nerves that go from the trigeminal ganglion to their region/organs where they function. From the Trigeminal ganglion, three nerve branches are created. These branches are the ophthalmic branch [V1], maxillary branch [V2], and mandibular branch (V3)..
The nerve branch fibers are known as General Somatic afferent (GSA) which is responsible for identification of temperature, touch, pressure.
The Ophthalmic branch of the cranial nerve V, moves through the lateral wall of the Cavernous Sinus. The cavernous sinus is located between the periosteal layer of the dura mater and the meningeal layer of the dura mater. That being said, the ophthalmic branch (V1) move through the lateral wall of the Cavernous sinus (it is important to know that cranial nerves 3, 4, V1 and V2 passes through the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus while cranial nerve 6 moves withing the cavity of the cavernous sinus). Passing through the lateral wall, the ophthalmic branch [V1] comes out at the end of the Cavernous sinus and goes through the superior orbital fissure to create three nerve branches which are the lacrimal nerve branch, the frontal nerve branch, and the nasociliary nerve branch. . These branches go to different destinations.
The lacrimal nerve will go through the lacrimal gland and touch the Levator palpebrae superioris muscle, as well as supply the conjunctiva in the temporal (lateral) side of the eye., . The Frontal nerve makes two branches, the supratrochlear nerve, and the Supraorbital nerve branch. The supratrochlear nerve one runs above the trochlear, to connect and supply the superior palpebral conjuctiva, the skin of the palpebral, the bridge of the nose, and medial forehead (scalp).. The Supraorbital branch also attaches to the skin of the palpebral conjuctiva, superior fornix, skin of the forehead, and the skin of the vertex of the scalp..
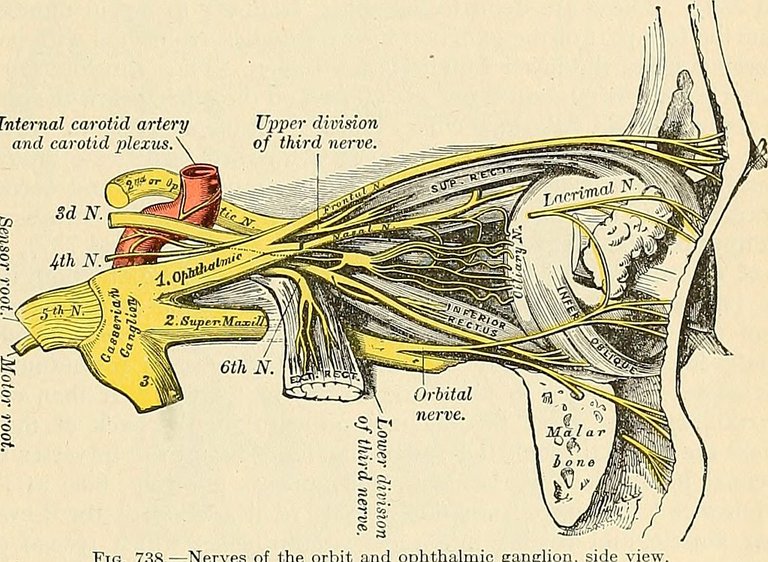
The nasocialiary nerve branch divides to four nerves which are short ciliary nerve, long ciliary nerve, the Ethmoidal nerve, and the Infra trochlear nerve. The short ciliary nerve penetrates the sclera alongside the parasympathetic nerve and the sympathetic nerve, and the short ciliary nerve moves to connect to the cornea while the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve supply the ciliary and iris. The long ciliary nerve combines with the sympathetic nerve to go superiorly, penetrating the sclera and connecting to the cornea., . The Ethmoidal nerve moves towards the ethmoid bone where it branches to two; the Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve, and the Posterior Ethmoidal nerve. The posterior ethmoidal nerve supplies the posterir side of the ethmoid sinus, while the anterior ethmoidal nerve supplies the anterior part of the ethmoid sinus and goes to the nasal cavity. In the Nasal cavity, it divides into medial nasal branch (which supplies the medial part of the nasal cavity), the lateral internal nasal branch (which supplies the lateral part of the nasal cavity), and the external nasal nerve which supplies the skin of the nose, the nasal tip of the nasal cavity, and the external lateral nose.. These nerves are responsible for touch and pain in these areas.
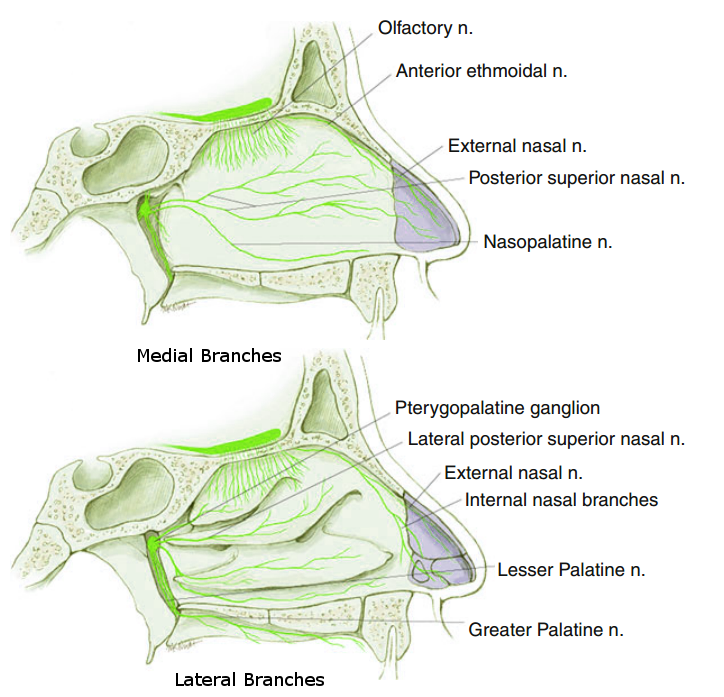
The Infratrochlear nerve runs below the trochlear, but anterior of the medial rectus, to supply the medial upper and lower palpebral, the lacrimal sac, and lacrimal caruncle. The Infratrochlear nerve gives touch, temperature, pressure and pain fiber..
I guess I have been able to explain the ophthalmic branch [V1] of the Trigeminal nerve, I will be moving to the maxillary branch [V2]
The maxillary branch [V2] of the Trigeminal nerve passes through the lateral wall of the Cavernous sinus, similar to the ophthalmic branch [V1], but it doesn't continue to the end of the cavernous sinus, it enters into the Foramen Rotundum. From the Foramen Rotundum, a recurring maxillary branch known as the meningeal/doral branch, attaches and supplies the dora mater for pain sensation. From the Foramen Rotundum, it goes into the pterygopalatine fossa and forms a minor branch into the ptarygopaletine ganglion. In the ptarygopaletine ganglion, several branches of nerves are dispatched. One of the nerve branch known as the nasopharyngeal nerve branch supplies the nasal pharynx, and to the pharyngeal tympanic tubule. Another branch from the ptarygopaletine ganglion known as the orbital nerve branch goes to the orbit, another branch from the ptarygopaletine ganglion known as the lesser palletine nerve, supplies the soft pallet, another branch of the ptarygopaletine ganglion known as the greater palletine nerve branch, supplies the posterior part of the hard pallet. Another branch from the ptarygopaletine ganglion passes through the sphenoid palatine foramen and goes to the posterior area of the nasal cavity. This branch is called the posterior superior nasal nerve branch which supplies the medial wall, lateral wall of the nasal cavity, and the interior hard pallet. If you remember, I said that maxillary nerve branch splits into two, one goes to the ptarygopaletine ganglion, which then branches into the several braches I listed previously, the second branch of the maxillary nerve goes out of the ptarygopaletine fassa to create three branches which are the posterior superior alveolar nerve, the Infraorbital nerve, and the zygomatic nerve.,, .
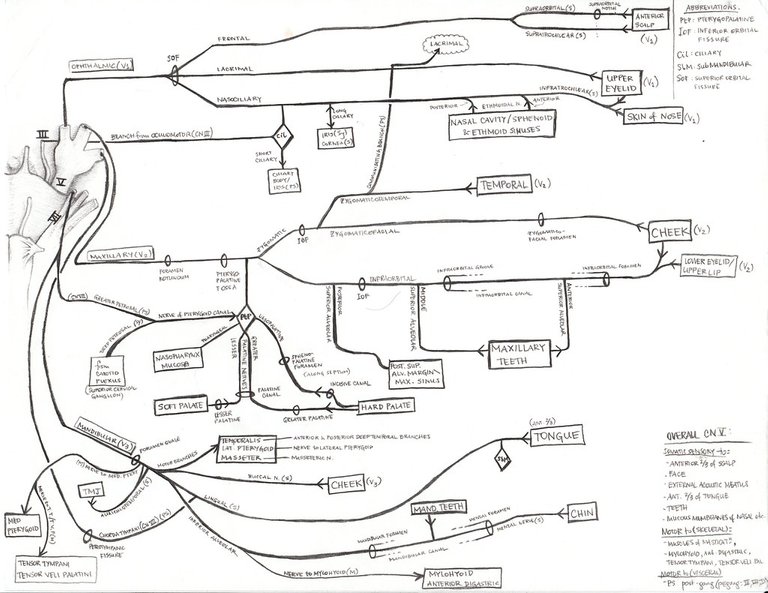
The Infraorbital nerve, and the zygomatic nerve go together into the inferior orbital fissure. The infraorbital nerve splits into three nerve branches, Two aveolar nerves and one infraorbital nerve. the superior alveolar nerves which are the anterior superior alveolar nerve, and the Medial superior alveolar nerve. The branch of the infraorbital nerve moves through the inferior orbital foramen where it splits to become three nerve branches where one of the nerve branch supplies the upper superior labial branch (the lip), another nerve branch supplies the inferior palpebral, and the last branch supples the upper nasal branch (upper nose).,
At the end of the inferior orbital fissure, the zygomatic nerve breaks into two branches which are the zygomaticotemporal nerve branch, and the Zygomaticofacial nerve branch. The zygomatical temporal nerve branch supplies the tempo, while the zygomatical facial nerve branch supplies the facial branch (cheeks).
The posterior superior alveolar nerve supplies the hard pallet, the gingiva, (teeth tissue), and the mollars (teeth). The Medial superior alveolar nerve comes from its branch to supply the nerves of the premolar (teeth), and the gingiva, the anterior superior alveolar nerve will supply the nerves of the canine, biscupid, cuspid, and incisors.,.
The mandibular nerve branch (V3) doesn't go into the Cavernous sinus, it goes through the Foramen Ovale, alongside the nerves from the motor nucleus of the Cranial nerve 5. It gives of a nerve branch which runs with the middle meningeal artery which passed through the foramen ovale to the dura mater. This branch is called the Nervus spinosus. Outside the foramen ovale, the mandibular nerve branch gives another branch called auriculotemporal nerve which supplies the temple, the external part of the tympanic membrane, the posterior temporomandibular joint and the tragus and helix of the ear. The Motor fiber split into several nerve fibers which supplies the tongue, the muscle of mastication, and the teeth. The anterior division of the nerve supplies the muscle of masticulation, and it is called the deep temporal nerve, and the nerve supplies the temporalis.. The anterior division of the nerve breaks into a branch called the lateral pterygoid nerve which reaches and supplies the lateral Pterygoid.. Another branch of the anterior division is the Buccal nerve which innervates and supplies the bucal mucosa, the skin of the anterior part of the cheek, and the inferior buccal gingiva of the molar area.. Another branch of the anterior division of the mandible nerve branch is the masseteric nerve which reaches the masseter muscle..
Another part of the mandibular nerve known as the inferior alveolar nerve, goes through the mandibular foramen and splits to create the inferior dental nerve which creates nerve branches that supplies the teeth. These nerve branches are; mylohyoid nerve, inferior dental nerve, incisive nerve, and mental nerve . The Mental nerves supply the skin of chin, lower lip, and lower gum. The mylohyoid nerve goes to themylohyoid and the digastric and tear belly. The Inferior dental nerve supplies the teeth.. The third nerve of the mandibular nerve is the Lingual nerve which goes anteriorly and medially to reach the tongue..
Conclusion
The trigeminal nerve has its origen in the Brain stem, with Spinal Trigeminal nucleus, central/principal pontine trigeminal nucleus, mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus, and the trigeminal motor nucleus. It supplies a lot of structures including the palpebral, skin of the scalp in the temporal, forehead, the pinna of the ear, the jaw, the teeth, the chin skin, the external part of the nose, the nasal cavity, the oral cavity, and many more areas of the face, and muscles of mastication (chewing) which includes (the Tensor Tympani and the tensoe veli palatini). It has Special visceral efferent fibers (SVE), and General somatic Afferent fibers (GSA). It functions in picking up sensations with respect to pain, touch, pressure, temperation, as well as sensation for mastication in the mastication muscle, since it contains both sensory and motor fiber nerves.
Image Reference
Image 1 || Wikimedia Commons || Trigeminal Nerve
Image 2 || Flickr || The Fifth, Trigeminal, Trifacial Nerve
Image 3 || Wikimedia Commons || Posterior Superior Nasal Nerve
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Yay! 🤗
Your content has been boosted with Ecency Points, by @eni-ola.
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for new Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more
@tipu curate