Many folks from Africa, Latin America, and Asia practises what is generally known as traditional medicines, whereby they depend on the medicinal properties of plants within their reach to cure one ailment or the other. Even in this age of allopathic medicine when appropriate compounds are adequately measured and mixed together by qualified pharmacist, and prescribed by medical doctors, many in the developing countries of the world still uses plant extracts to treat one ailment or the other whereby same person makes and prescribes the medicine. On this notes, many have endanger their lives by taking plant extracts without adequate or proper measurement. The truth of the matter is that these extracts taken from plants are actually plants own way of defending themselves against herbivores, fungi, insects and plant diseases. Plants synthesize several hundreds of chemical compounds which are known as phytochemicals. The biological activities of some of these phytochemicals have already been established. At times, some folks mixed these plants together under certain conditions to improve the medicinal effect of the concoction. The fact remain that these people uses plants for medicinal purposes, however, they don't know the names of these phytochemicals and in what quantity that they should be consumed. Thanks to rigorous researches in laboratories that have identify and are still identifying some of these actives chemical compounds in plants as well as carrying out the toxicological profile of these medicinal plants to ascertain their safety and efficacy using cell culture experiment, or laboratory animals.

What are phytochemicals
Whenever you consume green leafy vegetables and fruits , what you take in is more than vitamins, fiber or minerals. You also take in what is known as phytochemicals. There isn't much media talk about these phytochemicals that we consume in our vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. This is because researchers in the last three decades just began to identify some of these chemicals in plants and their possible medicinal properties. They were able to established that phytochemicals are effective against diseases such as cancer, strokes, cardiovascular diseases among many other diseases.
Studies has shown that diets with high percentage of fruits and vegetables helps to lower cancer rate and occurence of heart related diseases.
Phytochemicals is the combination of a Greek word Phyto which means plant and chemicals. So they are chemicals produced by plants mainly from primary or secondary metabolism. They are accumulated in several parts of plants such as the seed, leaf, stem, flower and root. They are known to have pharmacological activities in the plant that produced them.
Beta-carotene.png, Public Domain,  )
)
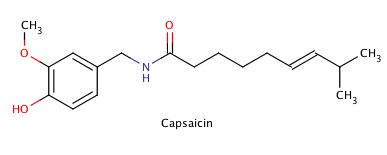
As earlier being stated, they are produced in plants for defence against diseases, competitors or predators. They give plants colour (pigment), smell, taste. For example, the orange colour of carrot is as result of the presence of a phytochemical called Beta-carotene which is a powerful antioxidants scavenging free radicals in human body when consumed. Our red pepper too got that heat sensation as a result of a chemical called Capsaicin
Till recently, more than 4,500 of these phytochemicals have been reported by researchers. They are classified on the basis of their physical and chemical characteristics, their protective function. Out of these 4,500 phytochemicals known, about 350 of them have been well studied by researchers.
You can't find all phytochemicals in a single plant. Their presence depends on the type of plant, climatic conditions, environmental conditions, pre and post harvest conditions, genomic as well as agronomic conditions. These conditions influences the presence and amount of phytochemicals in plants. For instance, according to a report, annual sunshine and altitude affect the amount of flavonoids and rutin content as well as antioxidant activity of Potentilla fruticosa L a plant selected for study by the researchers. The point here is that these factors largely affect the distribution of phytochemicals in plants.
Classification of Phytochemicals
Going through many literature, classification of phytochemicals became hectic because of these plant chemicals have diverse forms and structures. However, they are classified based on their function in plant metabolism. So they are classified as primary and secondary metabolites.
The primary metabolites are the common nutrients we seek for when we consume food such as carbohydrates, protein, vitamins. They are produced when the plants is in growing phase known as the trophophase. Primary metabolism produces the primary metabolites when all the nutrients needed for the plant growth are already in place. This primary metabolism is the bedrock for cell growth, reproduction and development of plants. In other words, it is the primary metabolism that is in charge of all these physiological processes changing genetic code (DNA, RNA) into carbohydrates, amino acids, and protein. Primary metabolites are needed for the survival of the plants, so they are produced in large quantities and can be found in the growing part of the plant.
The Secondary metabolites are the products of secondary metabolism. These metabolites do not take part in the physiological process going on in plants. But plant need them for survival in the environment where it grows. The connection between primary and secondary metabolism is that the latter depends on the products and biosynthetic enzymes of the former. The compounds from secondary metabolism acts in the capacity of being an antagonist against diseases causing agents and herbivores or at times, they could act to attract pollinators. These two actions depend on the type of the secondary metabolite present and the plants. In plants these compounds also help to deal with abiotic stress. In other words, they don't partake in physiological process in plant , but they take charge of protecting the plants.
Considering the secondary metabolites, some will be discussed in details as touching their classification, structures and function.
Phenolic compounds.
Out of all phytochemicals known so far, Phenolic compounds are the most widely distributed in plants. These class of phytochemicals are obtained as products from the Shikimic acid pathway. The shikimic acid pathway or shikimate pathway is present both in higher plants and microorganisms. This pathway takes place in plant chloroplast and is responsible for the production of precursor which then leads to the production of phenolic compounds. There is no much big deal on how these compounds are produced. Understanding the pathway could even be of help to get these compounds synthesized. For instance, in the pathway which involves seven steps. The chart below is just step 1 and 2 of the entire pathway.
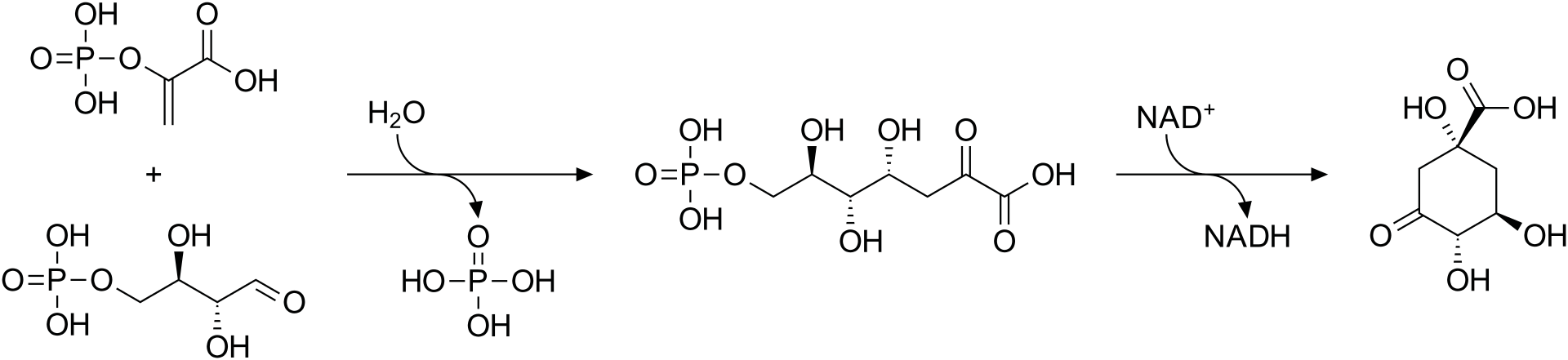

The reaction above is between phosphoenolpyruvate, erythrose-4-phosphate and water. The reaction give rise to 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptuloso-7-phosphate and ortophosphate. The step two begins with 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptuloso-7-phosphate and NAD+ to give (3-dehydroquinate) and NADH. The final product of the seven reaction step is a key compound called Chorismic acid This step is catalyzed by an enzyme called Chorismate synthase
It's of great importance to note here that the shikimic acid pathway is not the only metabolic pathway to obtain phenolic compounds. The other pathway is the Acetic Acid Pathway. The Shikimic acid pathway see to the formation of mainly phenylpropanoids while the Acetic Acid pathways see to the formation of phenols alone. However, most phenolic compounds are formed through Shikimic acid pathway. Flavonoids the most common group of the phenolic compound is the product of both pathways.
Characteristics of Phenolic compounds.
Phenolic compounds are characterized with the presence of minimum of one aromatic ring with hydroxyl group substituent.
They are commonly attached to sugars and protein molecules.
The antioxidant properties are related to the presence of hydroxyl group substituent on the aromatic ring.
Their free form also exist in plants tissues, however less common.
Their free state is toxic and hence protect the plants against insects and animals.
As a vegan you save yourself some trouble of been sick by consuming fruits and vegetable

The presence of Phenolic compounds in fruits and vegetable have been linked to antioxidant ability of vegetables and fruits. If you are a vegan, you could save for yourself a whole lot of money from going for medical trips. This is because fruits and vegetables has high level of chemicals that deals with oxidative stress, in other word, they help to deal with oxygen reactive species (ROS) that could be produced and accumulated in human cells and tissues. These ROS are responsible for various diseases in the body.
Classification of Phenolic compounds
Phenolic compounds are actually divided into phenolic acids and Polyphenols, like earlier stated, they are attached with other molecules, such as monosaccharides and polysaccharides. At times they exist as derivatives of such combination such as methyl esters.
On the basis of chemical structures, Phenolic compounds are divided into subgroups such as ;
- Phenolic Acid
- Flavonoids
- Tannins
- Lignans
- Stilbens
- Coumarins
- Quinones
- Curminoids
From the above listed, Flavonoids, tannins and phenolic acids are the main phenolic compounds of dietary importance. Others need to be strictly control. Generally, phenolic compounds have antioxidant properties and they play play major role in lipid oxidation tissues of plants and animals.
In the next article, each of the subgroups of phenolic compounds will be considered.
Summary
Phytochemicals are plant chemicals. They are distributed in different part of plants such as the root, seed, leaves and flower. They are responsible for scavenging free radicals in the body thereby preventing occurrence of diseases. Phenolic compounds are the most widely distributed out of all the phytochemicals known and they are products of shikimic acid pathway and Acetic Acid Pathway.
References
https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-primary-metabolites-and-secondary-metabolites.html
http://blog.cancernet.co.uk/phytochemicals-types-food-sources/
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/fill-up-on-phytochemicals
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medicinal_plants
Greetings friend excellent publication, very explicit that is what is desired at the time of transmitting a content as complex as that which you share with us, it is important to know that these metabolites is a "form own of the plants to defend itself of the herbivores, fungi, insects and diseases of the plants".
Coincidentally, there are plants such as fodder legumes that have secondary metabolites such as mimosina, which is known as anti-nutritional compounds in cattle farming, since when the cattle consume high quantities, some of these plants, such as Leucaena, could cause hair loss, among other effects.
See you later my friend, have an excellent weekend !
Thanks for coming around @amestyj, plants secondary metabolites really play a major role in protecting the plants. You are absolutely right, antinutrients are also phytochemicals and are highly dangerous to both animal and human if the plants containing them are not properly treated to processed.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Thanks for using the STEMsocial app
and including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which give you stronger support.
Greetings @steepup, thank you for sharing this wonderful entry, congratulations for such a complete manuscript, full of scientific rigor.
As you mentioned, here in South America the use of plant specimens is widely practiced to treat multiple pathological conditions, in fact I have been developing a thematic series entitled phytopharmacology, of descriptive scope, however, it has had some receptivity. Kind regards, we continue reading
Thanks @lupafilotaxia for those encouraging words. These phytochemicals has received so much attention in the world of science in the recent times. We have these leaves some at our backyard which we can just explore though cautions still need to be taken in using them, but they have been found to be a great medical use. I would love to read those series of your when eventually published. Thanks so much