Hello, StemSocial community! This is the very first time I am posting in this community after observing its posts for two days and perceiving that I can also add something to this community via my expertise. As the description of the community says, it is about divulging information about biology, history science, etc, so I as a medical student thought it perfect platform to disseminate health and medical-related information which we very keyful for the readers.
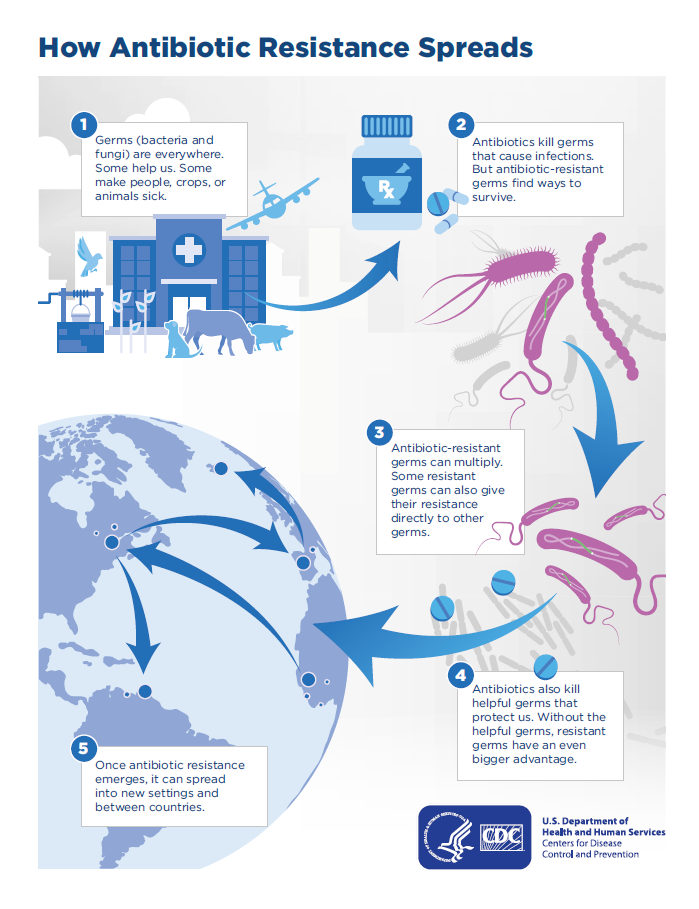
My topic for this post is “Antibiotic Resistance”
Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are any substances that are naturally, semisynthetically, or synthetically derived from microorganisms and used to treat and cure infectious diseases by killing or controlling microbes behind them.
We all are aware of the term antibiotic because we often use it either in complicated infectious diseases or in treating simple fevers. The discovery of antibiotics was a great milestone in the medical field because we found treatments for many infectious diseases but unfortunately, that advantage over infections does not last long due to the vehement development of resistance against antibiotics.
Antibiotics Resistance:
It is the ability of microbes to defeat the drug which was meant to eradicate them. It is a naturally occurring process but is precipitated rapidly by the irrational use of antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance is of major concern for the healthcare system because it has become impossible or nearly impossible to annihilate resistant microbes. Just in 2019, about 2 million people lost their lives due to the development of resistance against antibiotics.
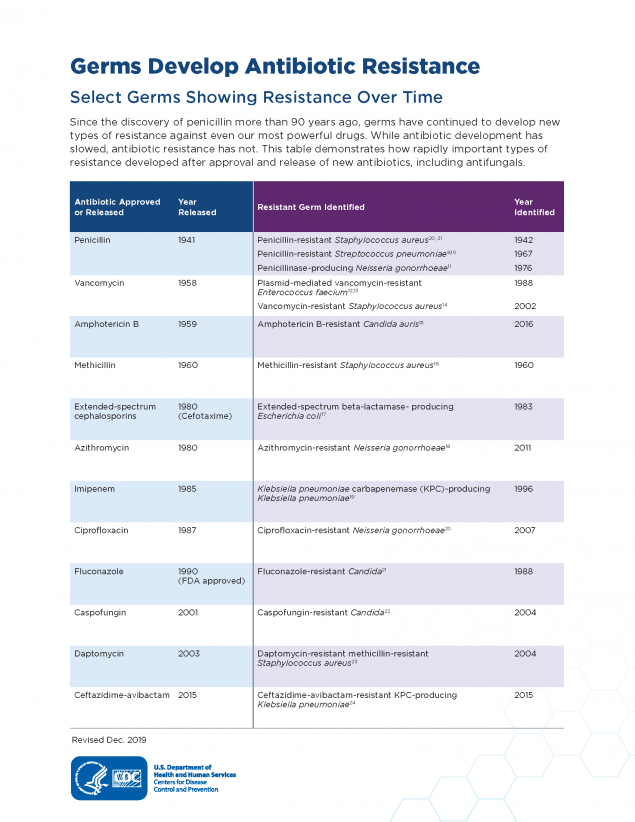
Here below are some examples of antibiotic resistance:
- Resistance against sulphamethoxazole + trimethoprim used to cure UTI caused by E.Coli
- Resistance against chloramphenicol which was the drug of choice against typhoid fever.
- Resistance produced by staphylococcus aureus against penicillin, methicillin, and vancomycin.
- Neisseria gonorrhea has developed resistance against penicillin, methicillin, azithromycin, and ciprofloxacin.
- Development of resistance against 1st and 2nd generation cephalosporin.
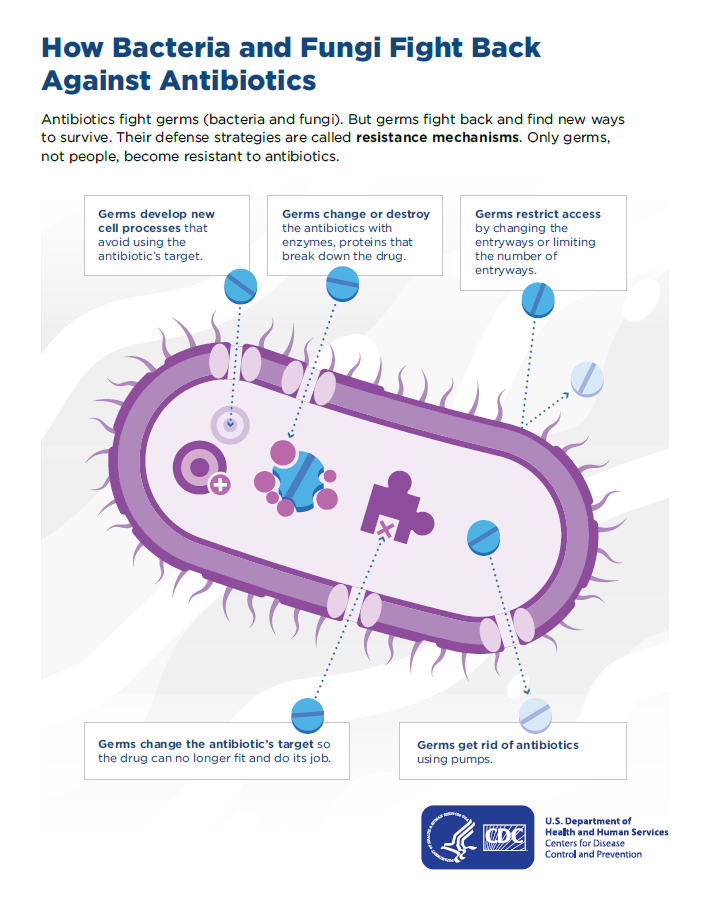
How does resistance develop?
Microbes are the living creature. They possess a machinery that protects them. They develop different methods to nullify the effects of antibiotics. They contrive various resistance methods which are here below:
1)No permeability: This type of resistance is generally shown by gram-negative antibiotics because they have cell membrane over their cell wall which offers greater resistance to the pervasion of antibiotics.
2)Efflux pumps: Microbes also develop efflux pumps which rapidly expel drugs out of bacterial cells before they can cause damage to bacteria.
3)Enzymatic breakdown: This is the case mostly noticed against beta-lactam antibiotics when the beta-lactamase enzyme distorts the beta-lactam ring destroying the biological activity of the drug.
4) Modification of binding sites: Antibiotics bind to binding sites over bacterial cells before making entry into bacteria. Modification in those binding sites will prevent antibiotics entry e.g. against penicillin.
5)Gene transformation: Resistance is also developed from microbe to microbe via the transformation of genetic material.
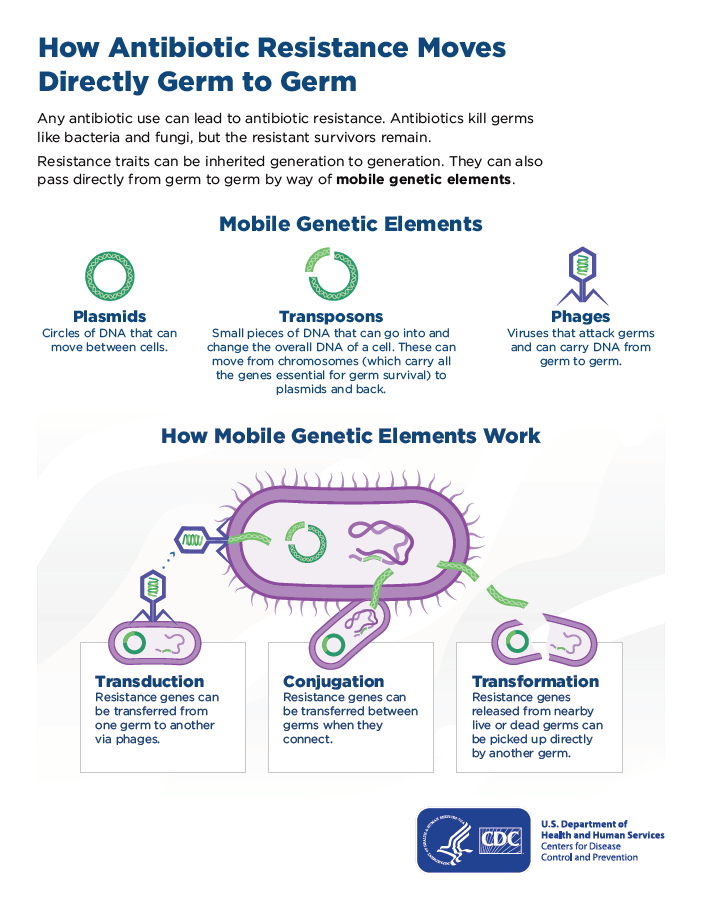
Causes of antibiotic resistance:
Here below are some causes that lead to antimicrobial resistance:
Irrational use of antibiotics: It is the major cause behind the debility of not just antibiotics but the majority of other drugs as well. It can simply be stated as overuse, misuse, use without indication, and use without selectivity. The proper way of using antibiotics is after analyzing them against strains of bacteria which is meant to be killed.
Irrational prescribing: It is due to a lack of knowledge of the prescriber and inappropriate identification of bacteria. Drug of choice and duration of treatment are the key factors behind infectious treatment and prescription lacking them is causing resistance.
Noncompliance of patient: It is a scene in which the patient leaves taking antibiotics just because symptoms are relieved and they think that the infection has ended. Such a type of attitude has also precipitated antimicrobial resistance. e.g in the case of tuberculosis
Single drug use: When only a single drug is used against infectious microbes. It becomes easy for it to develop resistance against it with time. That’s why to treat infection drug regimen is mostly prescribed.
Agricultural use: This has been known very recently that the usage of antibiotics for agricultural purposes is rampantly producing resistance issues.
Impact of drug resistance:
Antibiotic resistance is a major concern for the healthcare system these days as with the speed antibiotics are getting resistant, it will soon become very hard to treat infectious diseases. Public rampant abuse of antibiotics has developed complications in choosing antibiotics while performing surgery. Hundreds of antibiotics have been discovered after a lot of research and investment over them.
The development of resistance is leveling all these efforts and investments. AMR is a problem for all countries at all income levels. Its spread does not recognize country borders and is rapidly increasing the mortality and morbidity ratio.
The 2022 Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) report highlights alarming resistance rates among prevalent bacterial pathogens. Median reported rates in 76 countries of 42% for third-generation cephalosporin-resistant E. coli and 35% for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus are a major concern. For urinary tract infections caused by E. coli, 1 in 5 cases exhibited reduced susceptibility to standard antibiotics like ampicillin, co-trimoxazole, and fluoroquinolones in 2020.
Moreover, failures of antibiotic prophylaxis arising from antibiotic resistance have also been observed. Increasing antibiotic resistance potentially threatens the safety and efficacy of surgical procedures and immunosuppressive chemotherapy. It is estimated that between 38·7% and 50·9% of pathogens causing surgical site infections and 26·8% of pathogens causing infections after chemotherapy are resistant to standard prophylactic antibiotics in the USA.
This is just an awareness post to let the community know about raising concerns about antibiotic resistance.
All the images are taken from this source
**References***
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance
https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about.html
https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about/how-resistance-happens.html