
The Gartner 2017 mentioned blockchain as an Artificial Intelligence (AI), transparent immersive experience and digital platforms technology that will bring revolutionary impact within 10 years.
What is a blockchain?
1. Origin
Blockchain was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto (a person or group that remains anonymous) in 2008 as public transaction ledger for cryptocurrency bitcoin. The invention of the blockchain solves the double spending problem without the need of a trusted authority or central server. The bitcoin design has been the inspiration for other applications.
In the process of bitcoin formation, the blocks are one-by-one storage units and record all the exchange information of each block node within a certain period of time. The chain is realized by random hash algorithm between each block. The latter block contains the hash value of the previous block. With the expansion of information exchange, one block is successively connected to another, which is why it’s called blockchain.
Blockchain technology is considered to be the most disruptive technological innovation since the invention of the Internet. It relies on clever decentralized algorithms of cryptography and mathematics. It can be used on the Internet where trust cannot be established without the intervention of any third-party center. Participants reached consensus and solved the reliable transmission of trust and value at a very low cost.
2. Features
A. Decentralization: Blockchain technology does not rely on additional third-party management agencies or hardware facilities, and there is no central control. Apart from the self-contained blockchain itself, each node implements self-validation, transmission, and management of information through decentralized accounting and storage. Decentralization is the most prominent and essential feature of the blockchain.
B. Openness: The blockchain technology is based on open source. In addition to the private information of the parties to the transaction being encrypted, the data of the blockchain is open to anyone. Anybody can query the blockchain data and develop related applications through the open interface, so the whole System information is highly transparent.
C. Independence: Based on agreed-upon specifications and protocols (similar to various mathematical algorithms such as hash algorithms used by Bitcoin), the entire blockchain system does not depend on other third parties, and all nodes can automatically and securely verify and exchange data within the system. Requires no human intervention.
D. Security: As long as you can't control more than half of the data nodes, you cannot manipulate and modify the network data. This makes the blockchain itself relatively safe and avoids subjective human-made data changes.
E. Anonymity: Unless there are laws and regulations, technically speaking, the identity information of each block node does not need to be disclosed or verified, and information transmission can be conducted anonymously.
3. Advantages
A. Intermediary Credit: The most important part of the blockchain is to solve the problem of intermediary credit. In the past, it was difficult for two people who did not know each other and trust to achieve collaboration. It was necessary to rely on third-party justice units. Blockchain technology can without any intermediaries participating, the parties can complete mutual trust.
B. Efficiency and Cost: The disappearance of the intermediary, the rapid and transparent transaction, and the ability to trace the source of each transaction also reduce the agency fees
4. Problems and Challenges
A. Technical level
(a). Processing efficiency: Since each block will contain transaction information for all previous blocks, the longer the data, the longer the synchronization time of each node
(b). Transaction information is not easy to change: Blockchain's The feature is that the transaction record cannot be tampered with. If the transfer data is incorrect or the key is lost, it will result in loss
(c). The data has been tampered with: Any organization that has sufficient hash calculation ability may rewrite the record content.
B. Regulatory system: The characteristics of blockchain decentralization and collective maintenance have subverted people's current mode of operation, weakened the concept of the state, supervision, and impacted the existing laws and regulations.
5. Bitcoin Operation
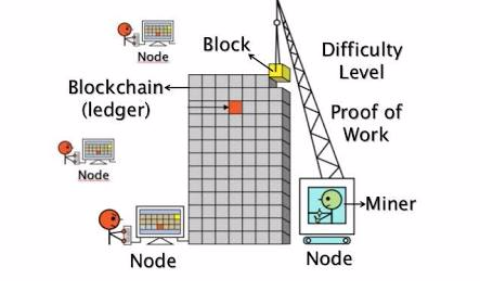
The credit of a payment system must be solved to prevent "repeated payments", that is, no counterfeit money can be created. The centralized credit system relies on state machines to prevent counterfeiting. Bitcoins “timestamp” each transaction. Every ten minutes a block (equivalent to the Internet book), this ten minutes of the entire network transaction is properly time stamped. The question is who will cover it? Let the so-called "Miner" people compete for the ten-minute billing right. The rule of competition is to correctly solve the SHA256 accounting problem. Who can prove that your computer is the fastest? The so-called PROOF OF WORK mechanism is to solve the problem first for bitcoin reward. This is the so-called "mining" process. The actual is to establish a decentralized credit process for the entire network general ledger - blockchain, so the more essential function of the miners is to allow Bitcoin nodes to reach a secure, tamper-resistant consensus. Mining is also the mechanism used to introduce more Bitcoins into the system.
The process of establishing a credit system:
Step 1: Each transaction must be broadcast to every node in order for the entire network to acknowledge its validity (node: miner)
Step 2: Each miner node must correctly time-stamp each transaction for the ten minutes and write it into that block.
Step 3: Each miner node has to compete for the legal bookkeeping right of the ten-minute block by solving the SHA256 puzzle, and strives to obtain twenty-five Bitcoin rewards (the first four years are fifty bitcoins per ten minutes but decreasing by half every four years)
Step 4: If a miner node solves the 10-minute SHA256 problem, all cover timestamp transactions recorded by the 10 minute block will be announced to the entire network and checked by other miner nodes throughout the network.
Step 5: All other miner nodes in the entire network check the correctness of the accounting of the block (because they are also covering time stamped accounts, but they are not competing to legal block account rights, so there is no reward) and they will have no errors. After the legal block, the next block is completed, thus forming a legally-accounted block single-chain, that is, the general account of the Bitcoin payment system, the block chain.
In general, each transaction must be confirmed by six blocks, that is, six-10 minutes billing in order to be finally recognized as legitimate transactions on the blockchain.



Thank yourshare ?