.jpg)
We know that time will only flow forward. We cannot go back to what happened yesterday and wait for our tomorrow, which has never happened yet. One of the biggest mysteries in physics is why the arrow of time points to the front. The arrow of time is a concept proposed by English physicist Arthur Eddington (general relativity verified by the total solar eclipse) in 1927. It is used to describe time as if only time has passed. We can go from the past to the future, but we cannot go back to the past. If space and time together form four dimensions, then time is the only dimension that can only move in one direction.
All equations used by physicists to describe the universe, such as equations describing gravitation and electromagnetism, work perfectly in either direction. These equations are considered symmetric and do not seem to be affected by the direction of the time arrow. However, time does have an arrow. Why is this happening?
Principle of entropy increase
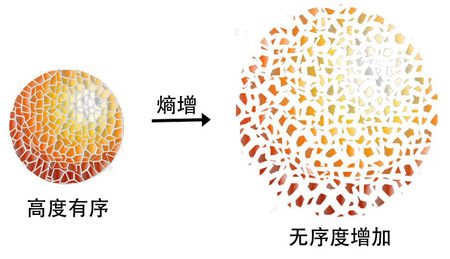
The answer is the second law of thermodynamics, which means that the entropy is always increasing. Entropy means disordered or unusable energy. In a closed system, the degree of disorder always increases spontaneously. This is the principle of entropy increase. Imagine that a pile of molecules spontaneously turns into a messy molecule and does not combine to form a single person.
If the entropy increase principle is applied in real life, this means that if milk is spilled from the jar, the milk will not return to the jar; or if a glass cup is dropped from the hand, it will break. Will not be reassembled and returned to the hands. If we have experienced any of these events, we can know whether the time is moving forward or backward, unlike the symmetry equation mentioned above. Because of this principle of entropy increase, it means that time only goes in one direction.
The irreversibility of the second law of thermodynamics may be related to the origin of the universe itself. The starting point of the universe is very small and dense—the singularity. The universe has been expanding since it was born 13.8 billion years ago. At the time of the Big Bang, the entropy of the universe was very low. Over time, its entropy increased. This is called the arrow of the universe.
The final possible outcome of the universe is to become a completely disordered structure with maximum entropy, which means that all matter and energy will be evenly distributed. The available energy will eventually be sparsely dispersed throughout the universe, so it is cold everywhere. This outcome is called the Cosmic Heat Death. Another outcome is that the universe will stop expanding and enter the opposite state, known as the Great Universe. In the large collapse of the universe, the entropy may decrease, and time may thermodynamically change direction.