Have you recently observed the happenings in different parts of the world today? These are ranging from retreating of the glaciers and polar ice sheets, increase in the levels of the oceans and seas, elevations in extreme weather conditions, change in compositions and extinctions of wildlife distributions, resurgence and upsurge of endemic and rare vector-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue, Ebola etc, relocations of coastal settlers to alpine settlement, socio-ethno crises involving pastoralists and farmers, emergence of new and strange species, persistence of heat waves, drought, wildfires and desertification,
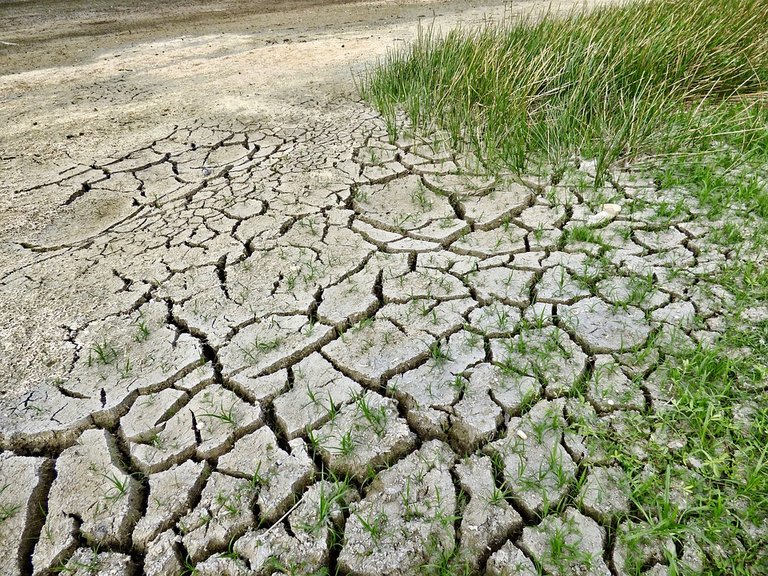

FIGURE 1: DROUGHT AS A SIGN OF CLIMATE CHANGE
frequency and intensity of hurricane, cyclone, typhoon, tornado and tropical storms, to irregular downpours and floods etc which are causing a great loss of finance to many continents per annual. For example, the heat waves, allied drought and wildfires that happened on July and August 2003, in Europe caused their economy more than 13 billion euros due to losses in electric power, agricultural and forestry sectors, although there are many more of events of colossal loss in different parts of the world, which we shall see in this climate saga.

FIGURE 2: AWARENESS CAMPAIGN
However, these ugly occurrences have been linked to the phrase “Earth on the Fire’’, otherwise, the globe is warming which resulted into the aforementioned climate change events. Whether we like it or not, climate change has come to stay, therefore is a future mayhem and will linger for more two hundred (200) years, having tried to stop the global warming that caused it; hence what we need now is to find ways on how to adapt to it and if possible trying to reduce the intensity of these climatic events. There is no way we will talk about climate change without understanding the science of global warming, greenhouse effect and greenhouse gases.
THE SCIENCE OF GLOBAL WARMING, GREENHOUSE EFFECT AND GREENHOUSE GASES
The term “greenhouse’’ emanated from the event that takes place in the glass house in which plants are cultivated. It was noticed that inside the glass house is very hot on sunny day due to entrapped long-wavelength infra-red radiation that cannot pass through the glass house and escape into the space unlike the short wavelength Ultra-Violet radiation that is absorbed by the hard surfaces and plants within the greenhouse. Even, this is what happens when your car is parked outside under the heat of the sun and the inside is very hot due to entrapped infra-red radiation.

**FIGURE 3: THE GREENHOUSE **
Likewise, some gases in the atmosphere block the reflection of solar radiation (i.e infra-red radiation), thereby re-sending them back to earth and the retention of infra-red radiations on the surface of the earth causes it to warm up and increase the earth surface temperature, resulting in the noun phrase called “greenhouse effect’’, and these atmospheric gases are termed “greenhouse gases’’.
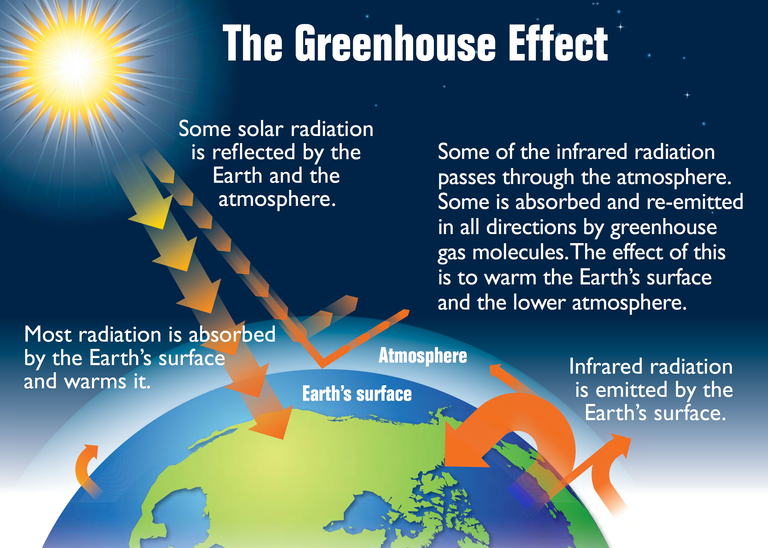
FIGURE 4: THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
** WHAT ARE GREENHOUSE GASES AND HOW ARE THEY FORMED?**
It is not all the solar radiations or solar energy from the sun that are released into the earth through the space, go back into the space; because some are absorbed by climate system such as polar ice sheet, air, land surface and oceans, as well as other hard materials on the land, and this supports the fact that only about 30% of total sunlight that came to earth reflect back into space by the ocean, reflective land surface, atmospheric dusts and cloud. This is the manner the earth surface and the atmosphere are warmed up in a regulated pattern. The solar radiation is reflected back in the form of infra-red radiation and this solar reflection is then reabsorbed and reflected back by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (i.e greenhouse effect), thereby amplifying the infra-red-induced heat and surface temperature of the earth in a regulated manner.
The greenhouse gases include: majorly water vapour and carbondioxide and others like methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, halocarbons (chlorofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbon, hydrofluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride). These gases are further classified into natural greenhouse gases (examples water vapour, methane and carbondioxide) and artificial greenhouse gases are halocarbons from refrigerators, exhausts from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, coals and biomass. Also, some greenhouse gases are classified as short-lived (example Ozone) while other are classified as long-lived greenhouse gases (e.g CO2, N2O, CH4 and CFC). The artificial greenhouse gases can give rise to the natural counterparts.

FIGURE 5: GREENHOUSE GASES AND THEIR SOURCES
Carbon (IV) oxide (CO2), apart being the by-product of biological metabolism in animals it is also raw material for photosynthesis (i.e self-production of food by plants), in that manner causing carbon cycle and stability in the ecosystem. However, incomplete combustion of various organic products such as fossil fuel, coals, woods and petrochemicals (i.e nylon and plastics), deforestation and cement production are increasing activities of human in all aspects of human endeavours; and these activities have been perpetually altering the physiochemical balance of atmospheric composition of CO2 by continuously causing CO2 to be released into the atmosphere, hence increasing greenhouse effect, global warming and eventual climate change.
Methane is the product of biological process in underground waste degradation, in fermentation of foods in grass-eating animals as well as in man (who is lactose intolerant and suffering from flatulence), peat bog, livestock degradation, paddy rice cultivation and manure utilization. This is where its natural gas name stems from since it is produced by natural processes. However, methane can also be released into the atmosphere from oil refinery in form of escaped gases during flaring of oil gases. Nitrous gases are formed from nitrogenous fertilizer (i.e NPK fertilizer). Halocarbons are by-products of refrigerators, air-conditioners and as industrial effluents. All these are caused by human activities and their escapes into atmosphere upset the compositions of atmospheric gases that lead to climate change in eventuality.
The question is what would happen if the sunlight is totally blocked from coming to earth or is completely reflected back into the space?
ARE GREENHOUSE GASES TOTALLY BAD OR WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF THESE GASES?
Apart from the total blackout the sunlight would have caused if being totally shielded, the earth will also become much cooler and existence of life would not have been possible on it. Therefore, the presence of natural greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide, carbon (IV) oxide and methane are strategically suspended in the atmosphere to continuously cause greenhouse effect and warming up the earth in a sustainable manner so that existence of life can be sustained on this planet.
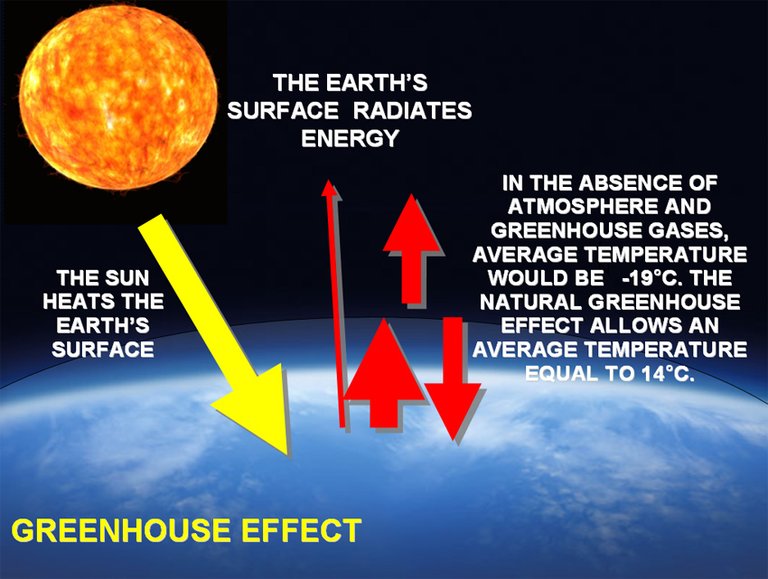
FIGURE 6: BENEFIT OF GREENHOUSE GASES
The concentrations of these natural atmospheric greenhouse gases are in equilibrium with other climate system, hence maintaining the earth surface temperature that supports the ecosystem, otherwise any alteration of this system, as implicated in the unusual global temperature as a result of uncontrollable increase in greenhouse gases by artificial sources due to human activities, will lead into climate change which we are experiencing today and more that we are going to experience in the future.
However, this then leads us to the relationship between the climate and weather; why are they interchangeably used and why cannot they be used interchangeably?
Climate System and Extreme Weather Condition
Weather only describes the state of atmospheric properties such as rainfall, humidity, wind, temperature etc over a space of hours or weeks. Climate system, on the other hand, encompasses the interaction between the weather with the polar ice sheets, oceans and land surface. Climate, then, has a widest meaning as the statistical description of the state of climate system. Therefore, the change in the statistics of the state of climate system that continues over many decades (i.e at least 30 years) refers to what is called climate change which is encompassed an extreme weather condition.
As a result, weather is also embedded within the climate and is looking at a part of the climate system (i.e atmosphere condition) but the climate is describing the state of physical properties of entire ecosystem or the world. Weather is predictable, at least up to a week but climate is unpredictable (except the causes are known and predictable), hence giving climate change a huge presence and future ordeals which we have to be continuously addressed by disseminating awareness of the science, causes, effects and remediation.
The question is: climate change, global warming and green-house effects, how are the linkages?

FIGURE 7: CLIMATE CHANGE AWARENESS
CLIMATE CHANGE, GLOBAL WARMING AND GREEN-HOUSE EFFECTS: WHY ARE THE AMBIGUITIES?
As stated before, the greenhouse effects are the reflections of the infra-red radiation going back into the space by the green gases, whereas global warming is the rise in the global temperature or earth surface temperature over several decades (i.e approximately 100 years) which is caused by increased greenhouse effects as a result of continuous alteration of the partially stable greenhouse gases in the atmosphere by human activities. It is even more appropriate to term the aforesaid definition as human-induced global warming.

FIGURE 8: GLOBAL WARMING OR EARTH ON FIRE
For example, research evidences through sensor of earth-orbiting satellite have showed that between 1906 to 2006 years the surface temperature of the earth has increased by 0.6 to 0.9 degree Celsius and also between 1850 to 2012 years the increased surface temperature is by 0.8 degree Celsius. The increased surface temperature has been stored in the oceans, as well as mountain and land glaciers, Greenland and Antarctic polar ice sheets and Arctic Ocean’s sea ices, thereby melting, shrinking and causing the latter to undergo a gradual disappearance that in turn causing their melted water to add to the levels of the seas and oceans observed recently. This means that more rises in sea level implies more precipitations or downpours, more tropical storms, hurricane, cyclone etc other extreme climate. This episodic climatic extremity is termed climate change.
Is climate change natural or Artificial?

FIGURE 9: MELTED POLAR ICE SHEETS

FIGURE 10: TYPHOON
CLIMATE CHANGE: WHETHER IS NATURAL OR ARTIFICIAL?
Climate change is as old as the existence of the world as proven by many evolution theories in explaining the evolution of life on Earth. It was believed that the earth was formed about 4.5 billion years ago and since then climate change has taken place due to changes (i) in the ocean and continent configurations, (ii) in concentration of atmospheric greenhouse gases, (iii) in solar intensity, and (iv) in Earth’s orbit, as well as (v) volcanic eruptions, (vi) evolution of life and (viii) impacts of the meteorites. Also, as far as many millions ago, there is possibility that there was an increase in global average temperature (i.e in a very few degrees) more than what we have today which caused warm and tropical water to be more distanced from the equators, hence giving rise to varieties of oceans and different atmospheric compositions that are differed from recent ones. This period was then followed by ice-age cycles about one hundred (100) thousand year ago in which the average surface temperature of the earth fell by 5 oC; and this lasted till the coldest era of the last ice age which is about twenty (20) thousand years, that had more water sank up in land polar ice sheets, thereby reducing the sea level to at least 120 metres lesser than present day. Although, there was regional evidence of abrupt rise in temperature by 5 degree Celsius in the North Atlantic region owing to abrupt disintegration of the ice sheets of Northern Hemisphere or ocean current’s change. But, at the last eight thousand (8,000) years ago, climate change was recorded comparatively stable, and this stimulated permanent settlement, agricultural involvements and population bloom occurred at that period. This was evidenced by data from climate archives like ice cores.

FIGURE 11: VOLCANIC ERUPTION AS AN ANTI-GLOBAL WARMING
However, this ice era was later followed by warm periods in which the major greenhouses gases such as CO2 and methane were abundantly given off into the atmosphere, leading to retreating of polar ice sheet. This era was what gave rise to present day 19th and 21st centuries of climate change which was amplified and exacerbated by human activities as explained before, and between 1850 to 2012 years the increased surface temperature is by 0.8 degree Celsius.
Therefore, it is now to come to conclusion that the two factors that cause climate change are (i) natural processes and (ii) human activities. The natural processes further involved the external influence which described how (a) the radiations of the sun and (b) volcanic eruptions influence the climate system such as atmospheric greenhouse gases, polar ice sheets, oceans and land. The volcanic eruptions have been proven to reduce greenhouse effects due to atmospheric dusts and particles they formed that shielded sunlight coming into the earth, thereby reducing the surface temperature. However, high intensity of sunlight causes increased surface temperature since more heat of the sun will be absorbed and reflected back to the earth by greenhouse gases.

FIGURE 12: BLACK SOOTS AS AEROSOLS IN THE ATMOSPHERE
The internal influence entails the exchange of carbon, water and energy between atmosphere, ice, land and ocean. On the hand, the human influence includes (a) change in the concentrations of greenhouse gases, (b) change in concentration of aerosols (such has natural sources: forest fires, dust storms, volcanic eruption and human-induced source: burning of fossil fuels) and (c) alteration of earth surface’s reflectivity by changing the land cover. Only the human-induced atmospheric aerosols that block solar radiations by reflecting them into the space, thereby causing cooling and reduced surface temperature but increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to incomplete combustion of organic matter and increased altered surface reflectivity by changed land cover due to agricultural activity and urban encroachment.
** OZONE LAYER AND OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES: WHAT IS THE RELATIONSHIP?**
Ozone (O3) can be classified as pollution as both pollutant (i.e ground-level type) and greenhouse gases (i.e stratospheric type). As greenhouse gases, stratospheric ozone reflects back solar radiation into space, therefore, reducing the ultimate intensity of sunlight coming into the earth and protecting life on earth from harmful ultra-violet radiation of sunlight. However, in the presence of other greenhouse gases, most especially chlorofluorocarbon, which dissociated in the presence of ultra-violet radiation, hence releasing chlorine atoms that then destructs the ozone layer. The destruction of ozone layer allows more solar radiations to come into the earth which can be amplified by other greenhouse gases through greenhouse effects, resulting to global warming and eventual climate change.
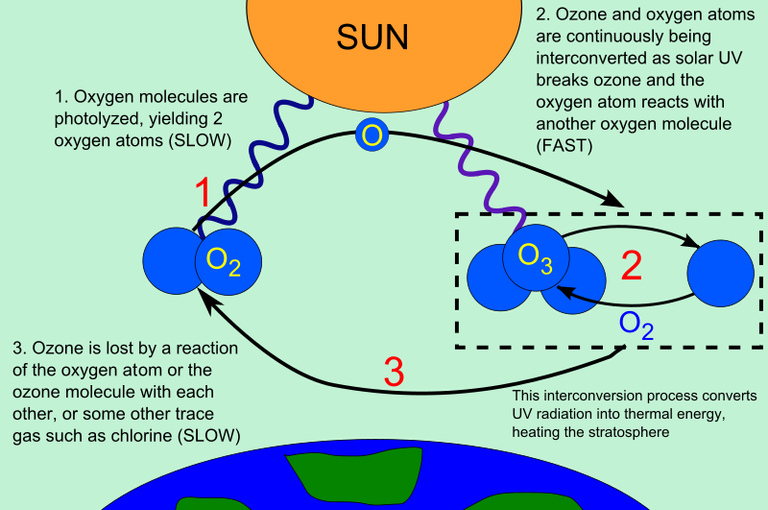
FIGURE 13: MECHANISM OF OZONE LAYER FORMATION AND DEPLETION OF OZONE BY CHLORINE RELEASED FROM CFC
In a nut-shell, having understood the science, meanings and causes of climate change and associated terminologies there is a need to discuss about the effects of climate change with recent related occurrences and future prediction; which you should watch out for in part II of this climate saga.
WATCHOUT FOR THE NEXT CLIMATE SAGA IN THE PART II!!!!!!!!!!
REFERENCES
3. http://saferenvironment.files.wordpress.com/2008/10/greenhouse.
7. https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2016/07/03/16/06/global-warming-1494965_960_720.
8.http://www.berbagiteknologi.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Dampak-Pemanasan-Global.
9. https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2016/09/07/02/34/typhoon-1650677_960_720.
10.https://steemitimages.com/DQmX8cfUo3sYF49BwfDm5uz5HDZDj3MYfD4Ua9kR1VdHvgg/typhoon.
11. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lava_forms.
12. http://www.noaanews.noaa.gov/stories2011/images/controlledburnuscg_300.
Great post👍
thank you sir. i will ensure i put up more interesting and captivating info in part as you keep encouraging me with your up-voting. you are welcome sir.