#216 Tomorrow's picture: January 21, 1996
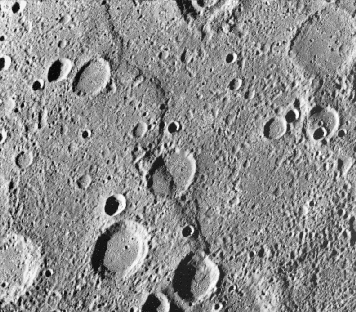
“The surface of the planet Mercury is not without fault. In this case, however, "fault" refers to unusual surface features that are the topic of much speculation. The above fault line is called Santa Maria Rupes, and runs through many prominent craters. The meandering feature is thought to be the result of huge forces of compression on Mercury's surface. Such rupes probably originate from large impacts and a general shrinking of Mercury's crust, which in turn causes parts of the crust to push above other parts."
Copyright: Public domain
#217 Tomorrow's picture: January 22, 1996
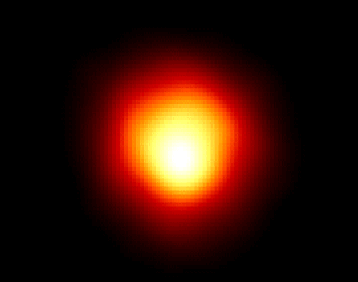
“Betelgeuse (sounds a lot like "beetle juice"), a red supergiant star about 600 lightyears distant, is shown here in this Hubble Space Telescope image which represents the first direct picture of the surface of a star other than the Sun. While Betelgeuse is cooler than the Sun, it is more massive and over 1000 times larger - if placed at the center of our Solar System, it would extend past the orbit of Jupiter. This image reveals a bright, as yet unexplained hotspot on its surface. Betelgeuse is also known as Alpha Orionis, one of the brightest stars in the familar constellation of Orion, the Hunter. Like many star names, Betelgeuse is Arabic in origin. It is derived from a phrase which refers to the hunter's shoulder or armpit, the general area occupied by this star in drawings of the figure in the constellation. As a massive red supergiant, it is nearing the end of its life and will soon become a supernova."
Copyright: Public domain
#218 Tomorrow's picture: January 23, 1996
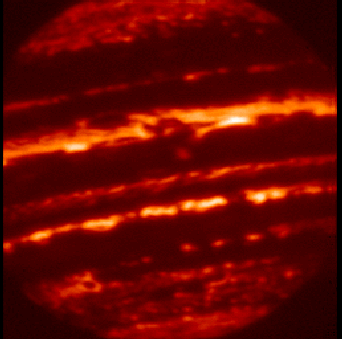
“This near-infrared image of Jupiter was made using instrumentation at NASA's Infrared Telescope Facility, located on the summit of Mauna Kea, Hawaii, in support of the Galileo mission to Jupiter."
Copyright: Public domain
#219 Tomorrow's picture: January 24, 1996

“The image above is part of the Hubble Deep Field and represents humanity's most distant yet optical view of the Universe. Galaxies like colorful pieces of candy fill the field, some as faint as 30th magnitude (about four billion times fainter than stars visible to the unaided eye). The dimmest objects are the most distant galaxies and reveal what the Universe looked like in the extremely distant past, perhaps less than one billion years after the Big Bang. To make the Deep Field image, astronomers selected an uncluttered area of the sky in the constellation Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) and pointed the Hubble Space Telescope at a single spot for 10 days accumulating and combining many separate exposures. With each additional exposure, fainter objects were revealed. The final result can be used to explore the mysteries of galaxy evolution and the infant Universe."
Copyright: Public domain
#220 Tomorrow's picture: January 25, 1996

“This carrot shaped track is actually little more than 5 hundredths of an inch long. It is the trail of a meteroid through a gel exposed to space in low earth orbit by the shuttle launched EURECA (European Recoverable Carrier) spacecraft. The meteoroid itself, about a thousandth of an inch in diameter, is visible where it came to rest, just beyond the tip of the carrot (far right). Chemical analyses of interplanetary dust particles similar to this one suggest that some of them may be bits of comets and represent samples of material from the early stages of the formation of the Solar System. NASA's Stardust mission, planned for launch in 1999, will attempt to directly collect dust from the tail of a comet and return it to Earth."
Copyright: Public domain
#221 Tomorrow's picture: January 26, 1996

“Meteor showers are caused by streams of solid particles, dust size and larger, moving as a group through space. In many cases, the orbits of these meteor streams can be identified with the dust tails of comets. When the Earth passes through the streams, the particles leave brilliant trails through the night sky as they burn up in the atmosphere. Above is an image of a meteor shower known as the Quadrantids. It was made in January 1995 using MOVIE, a new system for making video meteor observations. To make the image, frames from a video tape were computer processed and superposed to show the relative paths of many meteors in the shower. The meteor paths are all parallel to each other, but the effect of perspective causes the trails to appear to originate from a distant radiant point in the sky. In contrast to the elongated meteor trails, the brighter stars of the familiar constellation Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) are visible as points in the lower half of the image."
Copyright: Public domain
#222 Tomorrow's picture: January 27, 1996
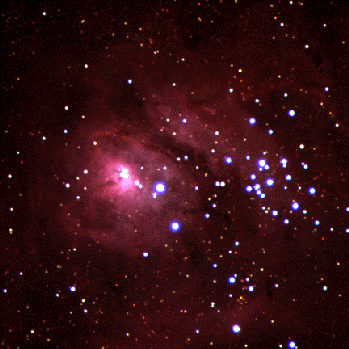
“The large majestic Lagoon Nebula is home for many young stars and hot gas. The Lagoon Nebulae is so large and bright it can be seen without a telescope. Formed only several million years ago in the nebula is the open cluster known as NGC 6530, whose young stars show their high temperature by their blue glow. The nebula, also known as M8 and NGC 6523, is named "Lagoon" for the band of dust seen to the left of the open cluster's center. A bright knot of gas and dust in the nebula's center is known as the Hourglass Nebula. Star formation continues in the the Lagoon Nebula as witnessed by the many globules that exist there."
Copyright: Public domain
#223 Tomorrow's picture: January 28, 1996
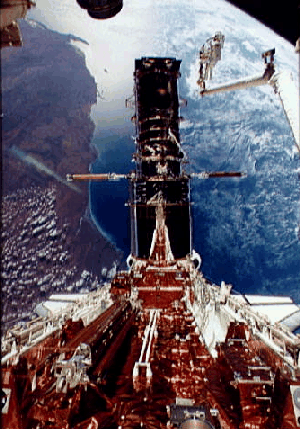
“In December of 1993 astronauts Story Musgrave and Jeffrey Hoffman performed the orbiting repairmans' ballet 400 miles above the Earth. They are seen in this photo perched at the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's robotic arm making final repairs to the four story tall Hubble Space Telescope. The coast line of western Australia is visible below. The complex and highly successful repair mission allowed HST to see into the Universe with unprecedented clarity."
Copyright: Public domain
Upvote! Resteem! Comment! As you like it! Thank you for attention!
Congratulations @george-zagraid! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP