Supersonic Busemann Biplane

This post may be interesting for the readers in the field of aeronautics but for the general readers, this post may be difficult to comprehend. When something explodes, it creates disturbances in the air which finally reached our air. We say we hear the sound. So, people are interested how fast does the sound travel? When lightning occurs, we see the lightning first and hear the sound. So, it is obvious that it travels with a speed lower than that of light. It is found that it travels at the speed given by equation below;
a = √ {γRT}
γ = ratio of specific heat of gas
R = universal gas constant
T = Absolute temperature.
This speed of sound is called sonic speed.
If the speed of the object in the medium is greater than the speed of sound in given medium then the speed of the object is called supersonic speed. This is the first word of the topic.
Adolf Busemann was an aerodynamicist to propose an efficient conceptual design of aeroplane in supersonic speed. May be this will justify the second word of the topic.
And finally, Biplane means a plane which has a pair of wings one below and other above.
From above, it is pretty clear that Adolf Busemann made the conceptual design of Biplane to make supersonic flight efficient. How does it make flight efficient may be the next problem. Before that, let us talk about what makes it inefficient.
In supersonic flow, shock waves are inevitable. These are tiny thin region across which flow parameters change drastically. Due to this drastic change, the drag increases which makes flight inefficient.
Present Context:
In the present context, the cross-section of the wing is diamond shaped.
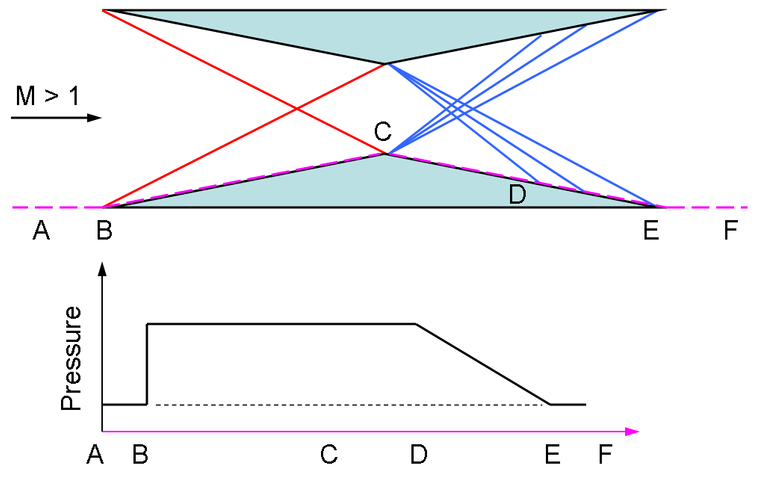
When an object moves at supersonic speed, the shock wave is created emanating from the nose as shown. Due to this, the pressure is increased in the inclined surfaces. Now, due to expansion in the midpoint, the pressure is decreased. Simply, we get the pressure difference and drag is created.
Busemann BIplane:
Busemann biplane consists of two wings which cancel the shock waves created by two wings. The oblique shock is created at front and expansion fan at the middle. The shock waves pass symmetrically and fill the expansion fan to maintain same pressure. So, there is no theoretical wave drag and it makes the plane efficient.
Sources
i. Picture 1: http://www.extremetech.com/extreme/133259-supersonic-biplanes-more-fuel-efficient-quieter-sonic-booms
ii. Picture 2: https://aviation.stackexchange.com/questions/25089/why-is-the-coefficient-of-drag-for-straight-wings-at-supersonic-speeds-lower-tha
iii. Picture 3:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Busemann%27s_Biplane
iv. Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, John D Anderson
v. Busemann, A., Aerodynamic Lift at Supersonic Speeds , Proceeding. Volta Congress, pp.315-347, Italy, 1935.