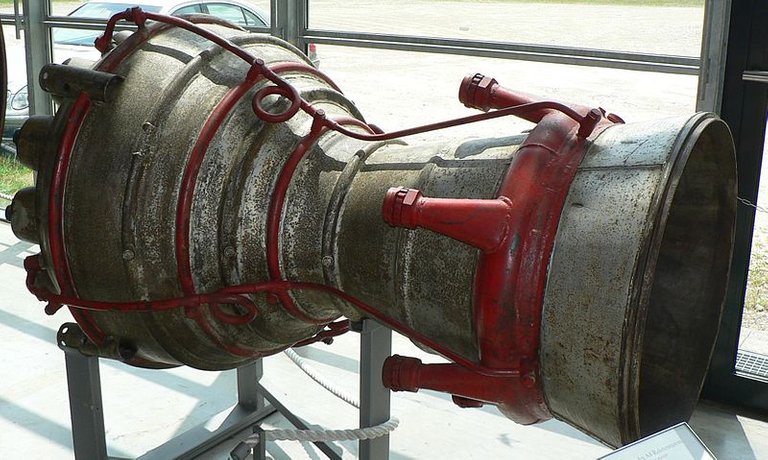
Converging Diverging Nozzle
It is the typical rocket engine nozzle. You can see that it has converging and diverging part. Why so? We will discuss in this post. It will require basic mathematical and theoretical background about fluid laws. But, I will explain without using calculus.
Imagine a cone, and say you decided to cut the pointed part, what do we have now, a nozzle? Yes, a nozzle. Blow air from large opening, you get the push, and the speed of air coming out from smaller side increases. Since, the air passing converges along the length of nozzle, it is called a converging nozzle.
When you blow air from small opening, the case is different. Since, the air passing diverges along the length of the nozzle; it is called a diverging nozzle.
Well, you are now sure that a nozzle is used to change the speed of flow of gas. The thrust force which we experienced above depends on the change of speed of gas flow. Same thrust is used in rocket engine for propulsion.
It is pretty clear that when area of duct decreases, the speed increases. Now, let us formulate a law according to this result.
"The velocity of flow of air is inversely proportional to the area of the duct."
Let us do some calculations based on this. Consider larger opening to be of an area of 5000 m^2 and smaller to be that of 1 mm^2. When initial speed of sound is 1 m/s and calculated speed of sound in 1 mm^2 side.
.png)
This is a speed greater than the speed of light. It is not possible. Oh wait, what if our theory is correct and special theory of relativity is wrong? Let's do an experiment according to above dimensions. The result will be disappointing for us. Pretty bad. Then let us use what we know till now. The rate of flow of mass remains the same in flow.
mass flow rate=
.png)
The problem was, we were missing out density. We do not know how exactly density changes. So, let's take a general case of changing of all quantities. \Delta is the representation for small change. The change can be negative.
.png)
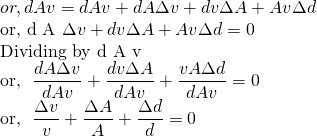
.png)
The fraction .png)
is called the relative change of parameter.
We are interested in relation of relative change in velocity to the change in area.
.png)
Let this be equation (i)
Another equation we know is Bernoulli equation.
.png)
let this be equation (ii)
From the definition of Mach number, it is the ratio of local speed of gas to speed of sound in local condition.
M = v /a
.png)
Substituting this equation in (i)
.png)
i, When M < 1 i.e the speed of gas is less than the speed of sound; when the area decreases there is increase in velocity.
ii. When M > 1 i.e the speed of gas is greater than the speed of sound; when area decreases there is decrease in velocity.
So, for supersonic speed i.e M >1, the converging nozzle alone is not sufficient. We should use converging nozzle up to M = 1 and then use diverging nozzle to further increase the speed of gas flow. Such nozzle is called a converging diverging nozzle.
Sources
All the mathematical expressions are coded in quicklatex.com

Nice detailed update. Upvoted and following u as always. Regards Nainaz
thank you so much.
:D :D
wow...this is spectacular article...seriously article, very useful and its good knowledge for me. thanks for sharing @gauss01. :D
wish my lecturer were like you!