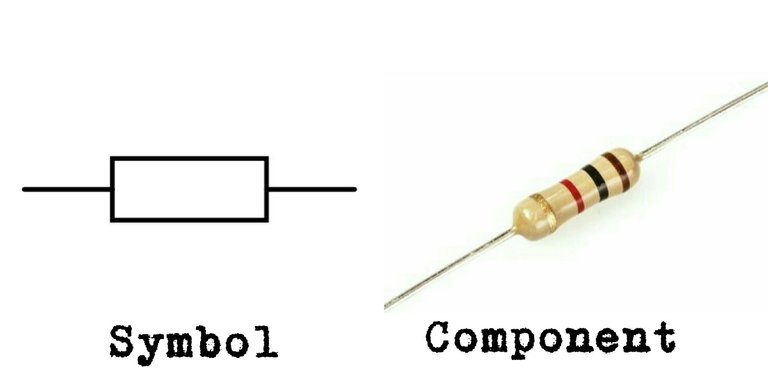
Hello steemians, I will be briefly discussing with you guys what a Resistor is all about. Yesterday I listed and discussed about the sixteen(16) Basic Electronic Components. Today I will be picking one of them and explaining it briefly. Let's begin with today's topic "The resistor"
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. The components which resist the flow of electric current ate called resistor. Resistor are used to control the flow of current in an electric circuit. The two man characteristics of a resistor are its resistance in ohms and wattage rating. Resistors are available in a very wide range of values, from a fraction of an ohm to mega ohms. The power rating may be as high a several hundred watts or as low as 1/10W. The power rating of a resistor is very important because it specifies the maximum wattage the resistor can dissipate without excessive heat. Since the resultant heat is not used, too much heat can cause the resistor brush open.
Types Of Resistors
source
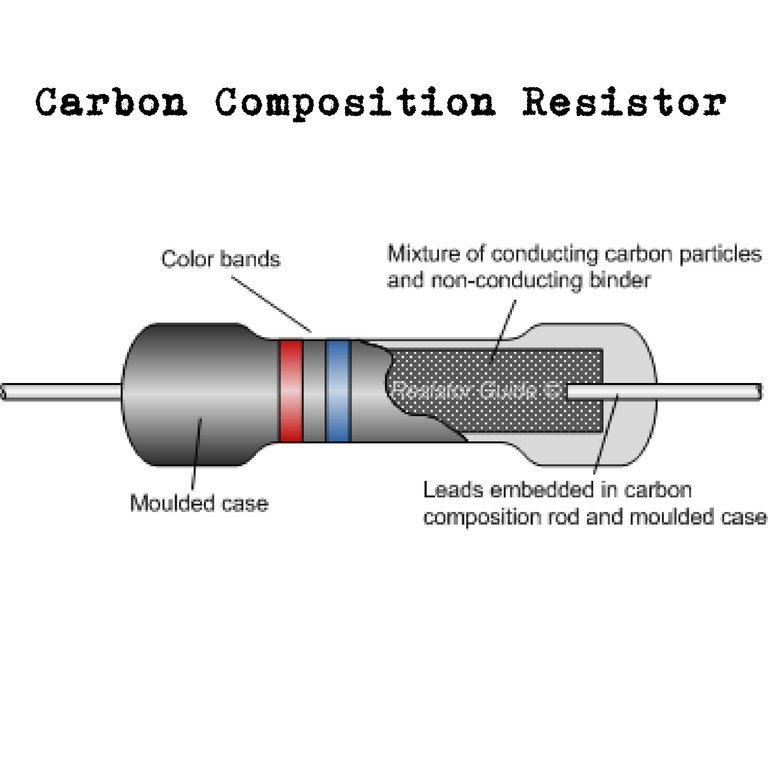
1. Carbon Composition Resistor
This is made of finely divided carbon or graphite mixed with a powdered insulating material in the proportion needed for the desired resistance value. The resistor element is enclosed in a plastic case to prevent, for insulation and mechanical strength. Attached to two ends of the carbon resistive element are metal caps with leads tinned copper wire for soldering the resistor into a circuit. They are available in power ratings of ⅛, ¼, ½, 1 and 2W. They have low failure rates when properly used and are mist commonly used in electronic equipment.
source
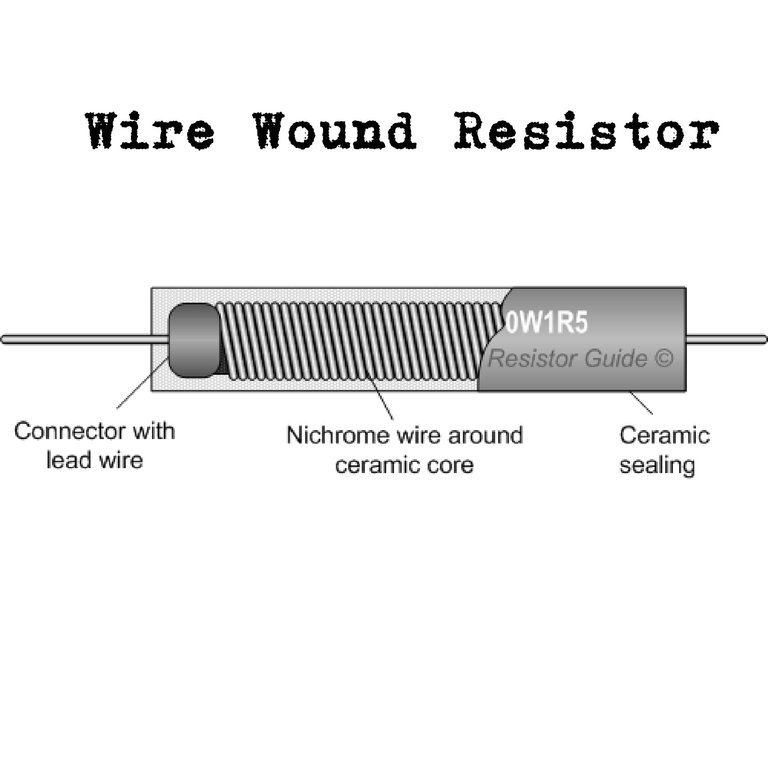
2. Wire Wound Resistor
This consist of a ceramic core wound with a drawn wire having accurately controlled characteristics. These resistors have the highest stability and highest power rating and they are not suitable for low cost or high density, limited space applications. They are available in power rating form 5W to several hundred watts. They are used where accurate, stable resistance values are required.
source
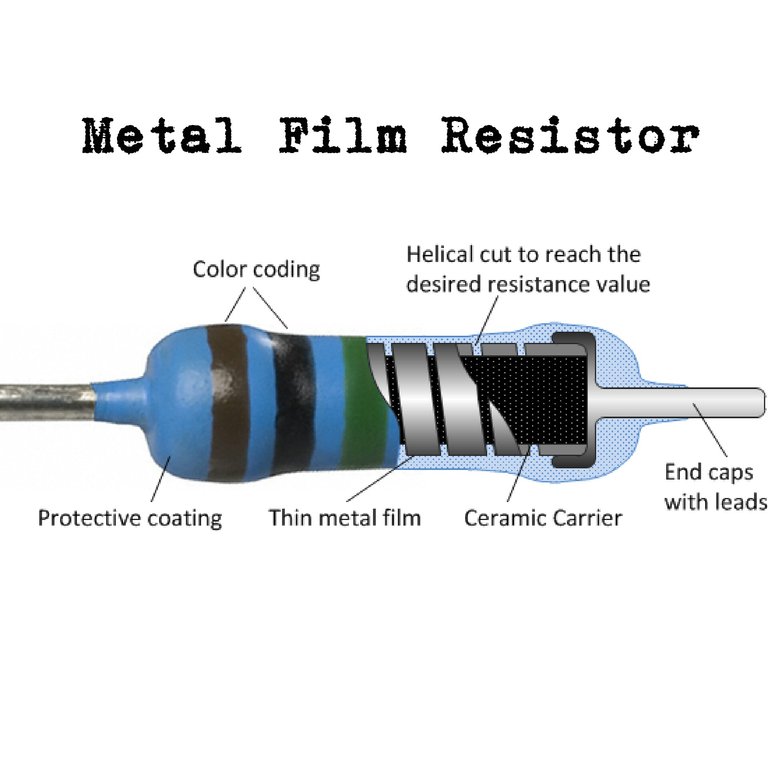
3. Metal Film Resistor
They are made by depositing vaporized metal in vacuum on a ceramic core rod. They have excellent tolerance temperature coefficient and are extremely reliable. They are very suitable for high grade application such as low level stages of certain instrument.

source
4. High Voltage Ink Film Resistor
These resistors consist of a ceramic base in which a special resistive ink laid down on a helical band. They af withstanding high voltages and are used in cathode ray circuits, in radar and I'm medical electronics.

source
5. Metal Glaze Resistor
This consist of a metal glass mixture which is applied as a thick film to a ceramic in a ceramic substrate and then fired to form a firm. The value of their r depends on the amount of metal in the mixture.

source
6. Cement or Ceramic Metal Resistor
Thy are made by firing certain meal blended with ceramics on a ceramic substrate. The value of their resistance depends on the type of mix and its thickness. They are very accurate resistance values and show high stability even under extreme temperature.
Resistors Color Codes
Color codes are used to recognise the value of a particular resistor. The coloured band on the resistor refer to the digit or numbers of the resistor value.
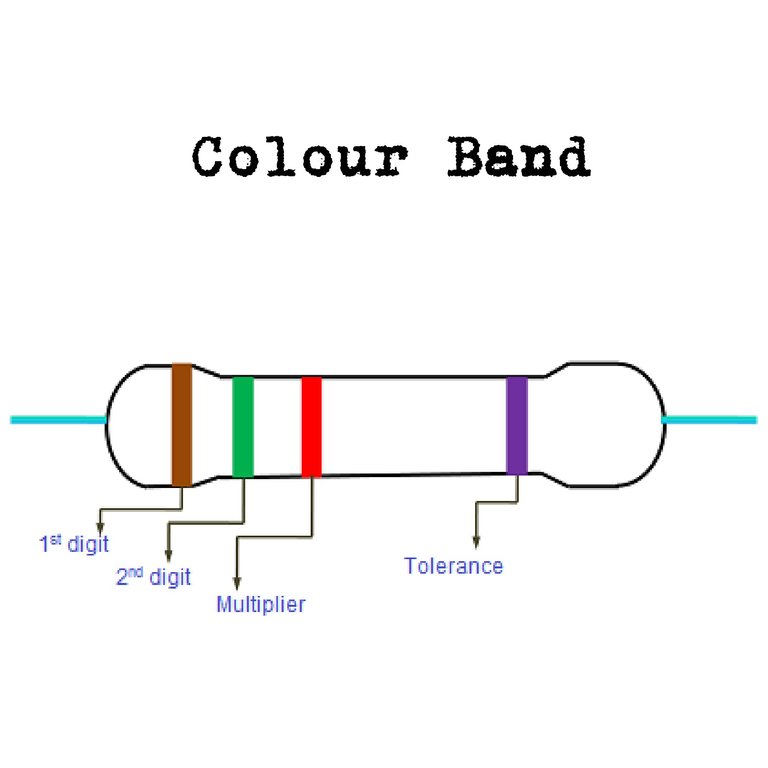
Source
The first colour band indicates the first digit or number of the resistor value. The second coloured band indicates the second digit or number of the resistor value. The third coloured band indicates the number of zeros in the resistor value. The fourth coloured band is usually gold of silver and it indicates that tolerance of the resistor, i.e how accurate the resistor is with respect of its desired value.
Example: determine the value of the resistor with the colour code;
• green, blue, orange, silver
Answers:
• 1st colour band - green - 5
2nd colour band - blue - 6
3rd colour band - orange - three zeros
4th colour band - silver - ±10%
:- Resistor values = 56000Ω±10%
That was a brief detail about the resistor.

Keep these posts going, iv got a little knowledge but a fair amount of interest so I'll be following along.
Wow!, I'm glad. Thanks!.
Great information, I’ll be following and upvoting your page. Regards
Thanks a lot! I'm glad.