CELL
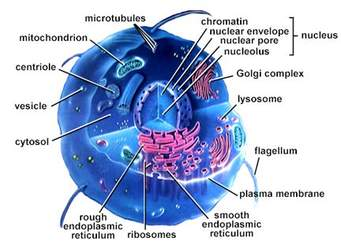
Cell is the smallest, structural and functional unit of life.
Component of a cell.
There are 3 major component of a cell
Component
cell membrane nucleus cytoplasm&it organelles
• Cell membrane
• Cytoplasm and it organelles
• Nucleus
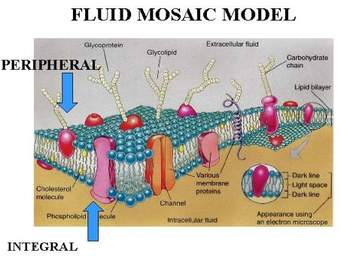
CELL MEMBRANE
The cell membrane is the outer part of a cell, and also called the plasma membrane. It dictates what goes in and out of the cell. The cell membrane has 2 components;
Cell membrane
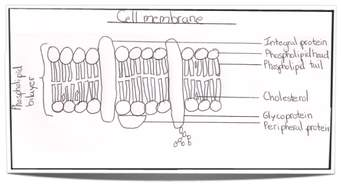
lipid protein
phospholipid glycolipid cholesterol integral peripheral
Membrane lipid
• Phospholipid
• Cholesterol
• Glycolipid
Phospholipids.
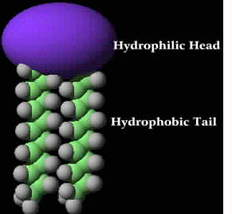
The cell membrane is usually referred to as a lipid bi-layer [bi=2. Lipid=fat]; i.e. it is made up of 2 layers of phospholipids.
The phospholipid has 2 parts;
• Hydrophilic head [hydro=water. Philic=loving] i.e. the head is water loving{found in water}
• Hydrophobic tail [phobic=fearing or hating] i.e. the tail is water hating [found within the cholesterol}.
Cholesterol.
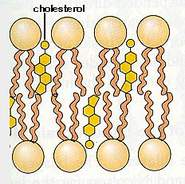
They are found between the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids, where they perform the function of maintaining the cell membrane stability.
Glycolipid
They are sugar [glyco or glycogen=stored sugar] attached with lipid, and are found
on the outer surface of cell membrane.
Membrane protein
There are 2 types of membrane protein
• Integral protein
• Peripheral protein
Integral protein
They are projected all the way through the membrane.
Peripheral protein
They are attached only to the surface of the membrane and do not penetrate.
Nucleus
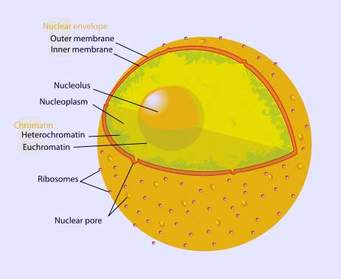
It is the control centre of the cell, because it controls all the activities going on in the cell. It contains both DNA [chromatin] and RNA.
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid [it is responsible for duplication of organelle]
RNA: Ribonucleic acid [it is responsible for the synthesis of protein].
The nucleus is enclosed in a membrane called the Nuclear envelope, which possesses pores called Nuclear pore.Cytoplasm and its organelles.
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like fluid in which the cell organelles are suspended.
CELL ORGANELLES
• Mitochondria
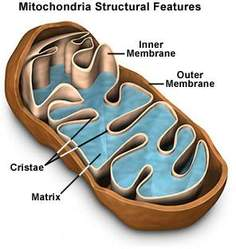
It is also called the power house of the cell, because it provides all the energy required for cell activities. It contains DNA, which accounts for it duplicative characteristic.
• Endoplasmic Reticulum.
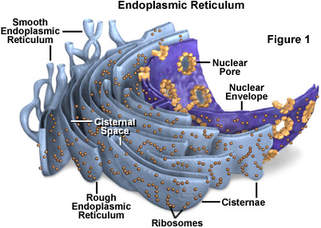
There are 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum;Smooth E.R
Rough E.R
• Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum; It is also called Agranular E.R, and it performs the function of detoxifying drugs or chemical substances, and also synthesis lipid.
• Rough Endoplasmic reticulum; It is also called Granulated E.R, because it is attached to ribosomes, and it function is to synthesis protein.
• Ribosomes
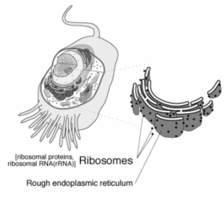
They contain RNA, which enables them to synthesis protein.
• Lysosomes [lys[is]=breakdown]
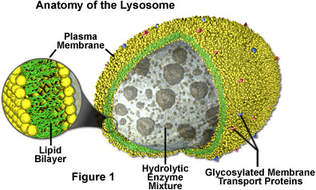
They are also called Suicide bag or packet. They are type of secretory vesicles that breakdown undigested proteins, and also destroy foreign materials.
• Golgi apparatus
They are also called Golgi body, they package and modify materials such as protein into the cell membrane.
• Centrioles
They lie at 90 degree to one another, and they form spindle fibre during cell division.
• Perixosomes
They contain catalase and oxidase, which enabled them to detoxify hydrogen peroxide.
NB; with the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe the cell.
To attempt questions is the problem of some students, so to attempt this question, you should follow the sequence below;
• Draw the diagram
• Definition of a cell
• List the components
• Pick the component one after the other, starting from the cell membrane, following by the nucleus, and finally the cytoplasm and it organelle. While describing the organelles you are expected to talk about[other name, what it contains and it function].
