DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. This is the molecule which is located inside the nucleus of the cell. Its main job is to store and code the genetic information in the body. Before replication, the DNA is located in the nucleus of the cell like a coil model. But during the time the cell replicates, DNA arrange in a form of structure known as Chromosomes and these Chromosomes help keep the DNA stable during the time of cell replication.
Made by me with CorelDraw X7
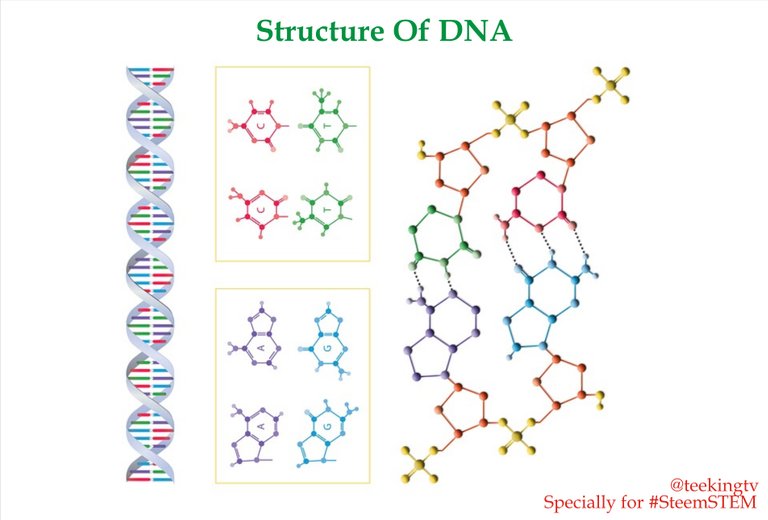
Most of us are familiar with the Double Helix model of the DNA. The Double Helix model demonstrates that DNA is polymer. To understand the structure of DNA, you have to understand the meaning of Polymer.
Polymer is basically mocules which is consisting of many repeating units which are known as monomers.
Take for example, a simpler polymer called Startch. In this case, the monomeric units are known as Glucose. These glucose moecules are joined together by Glycocenic bond and they form the polymer which is known as Startch. In a similar way, DNA is also a polymer and in this case, the monomeric units which form the DNA are known as Nucleotides. And below is the basic structure of a Nucleotides:
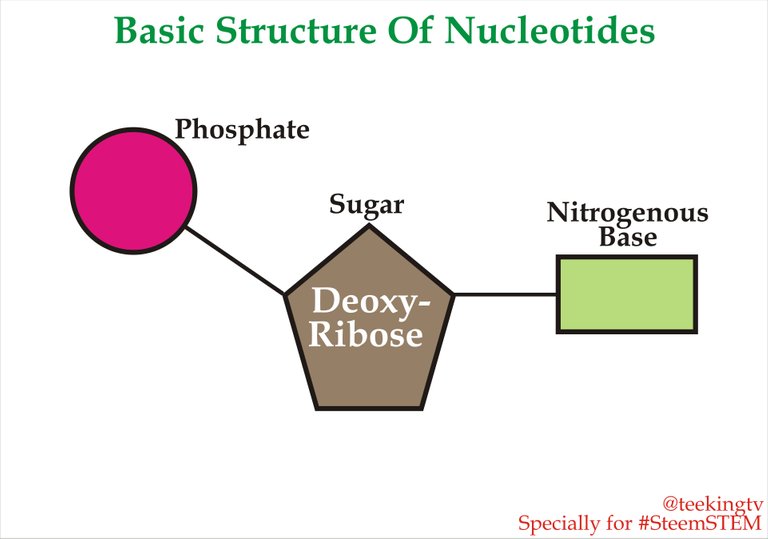
Basic Structure of Nucleotides - Made by me with CorelDraw X7
You can see that it is made up of three important groups; the Phosphate, the Sugar and the Nitrogeous Base. The sugar present in Nucleotides is called Deoxyribose, a five carbon sugar belonging to Penthosys. The Phosphate group consist of Phosphorus ion and then we have the important Nitrogeous Bases which are organic molecules which contain Nitrogen in the form of ring structures.
There are four types of Bases that can be present inside the DNA molecule. These are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine. Since we can have four different types of Nitrogenous Bases, we can have four different types of Nucleotides that are present inside the structure of DNA.
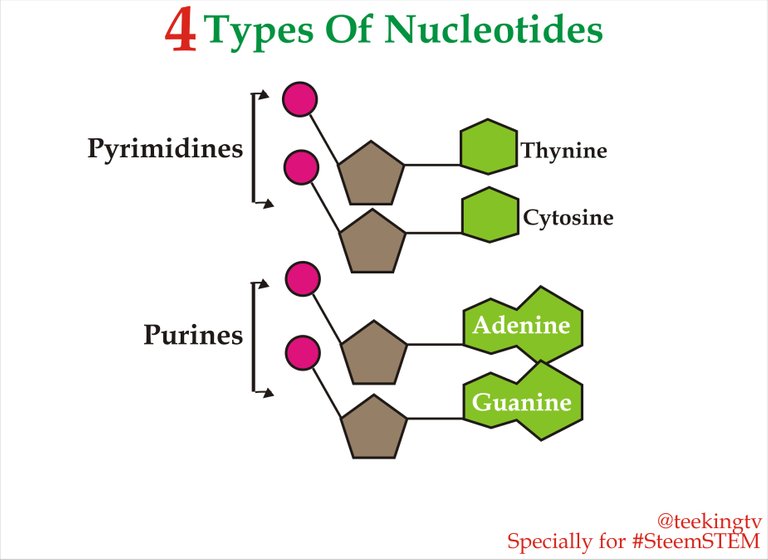
The four types of Nucleotides - Made by me with CorelDraw X7
As you can see, these four Nucleotides are arranged in two groups. The first group is known as Pyrimidines and this consist of Nitrogeous Base, Thymine and Cytocine which are both single ring bases. The second group contains Nucleotides which are known as Purines and this have Adenine and Guanine as the Nitrogeous bases which have double ring structures.
Startch
In a case of Startch, the structure is very simple. This only consists of long linear genes of glucose which are joined together by Glycocenic bond. Below is the chemical structure of Startch and you can see the different types of glucose change.
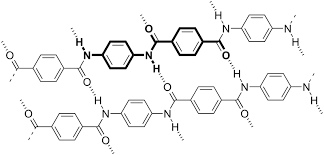
Chemical structure of Startch - Wikimedia image - (Author: Hbf878 - CCO Licensed)
Step-Ladder Model of DNA
In the case of DNA, the four types of Nucleotides join together in a very complex way to form a Double Helix structure. Now, if you zoom in to the structure of this Double Helix model of DNA, you can clearly see that it basically consists of these two blue lines which are crossing around each other. It also consists of these orange lines at the center, connecting those blues lines together. If you untwist the Double Helix, you will get something which is known as Step-Ladder Model of DNA. This also has similar structure and it consists of this blue vertical lines and the orange horizontal lines. These two blue vertical lines basically represent the Sugar Phosphate Backbone of the DNA. And the center lines which are orange in color represents the Base Pairs of the DNA. See the sketch below.
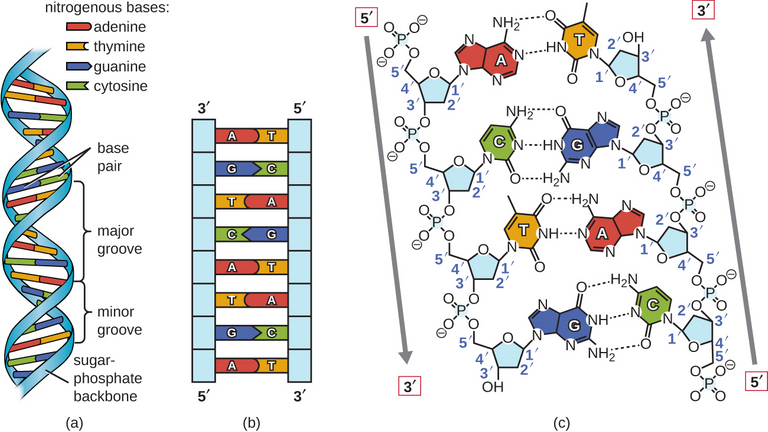
DNA structure - Wikimedia image (Author: CNX OpenStax - CCO Licensed)
How Two Neuclotides Are Joined Together
The Carbon atoms present in the Deoxyribose of the DNA are numbered from one to five in a clockwise direction and you have to remember this numbering of the Carbon atoms because it will help you to understand the concept of Directionality of DNA. What happens here is that the third Carbon in every Deoxyribose forms the bond of this Phosphate group of another Neuclotides that is present below it and this point may extend in both directions. Now if you zoom into this structure, you can basically see that each Phosphate is connected to two Glucose. One bond from the third Carbon of the sugar above and the the other bond with the fifth Carbon of the sugar below.
And now again, if you zoom out, you will clearly see that due to the bond formation between sugar and Phosphate, it creates a Sugar-phosphate Backbone on one side and we have all the Nitrogeous Bases which projects out of the Sugar-phosphate Backbone on one side. What this basically represents is a similar strand of DNA.
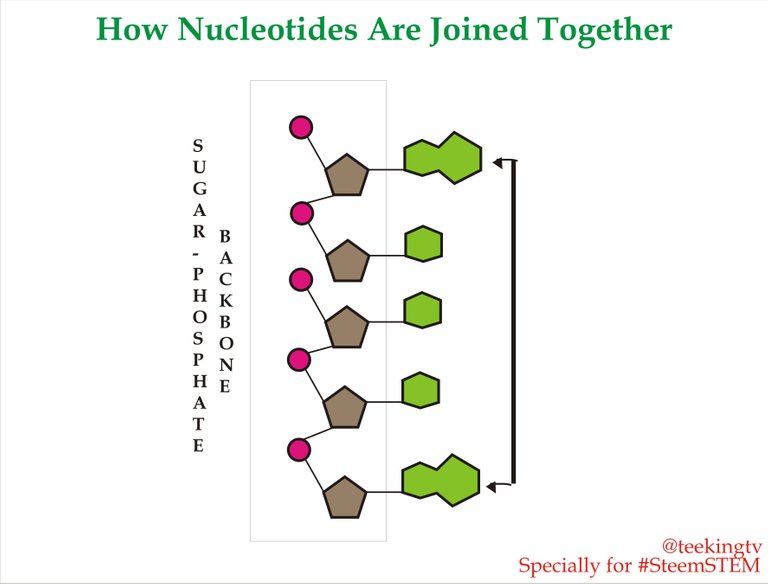
How Nucleotides are joined together - Made by me with CorelDraw X7
Now if you go back to the Step-Ladder model of DNA, you will clearly understand how the Nucleotides in the strand of DNA are joined toghether before the Sugar-Phosphate Backbone which was represented by these blue vertical lines. And at the center, we have these orange lines which which connected these two vertical blue lines which has the Base Pairs at one side.
At the opposite side, we have the other strand of DNA which is quite similar to this original strand but has certain key important differences for you to understand. And to understand these key differences, you have to understand what we call Directionality and Complimentary Base Pairing.
Directionality
What Directionality means is that:
It is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of Nucleic acid.
In this example, you will see the single strand of Nucleic acid where the direction of DNA is expresses in two phases. One is five prime end to three prime end while the other is three prime end to five prime end.
If you look closely at ths structure, you can basically see that it has a five prime end to which the Phosphate group is attached and also three prime end below to which Hydroxyl group is attached. If you come back to the DNA Step-Ladder model, you can see that the strand we made there goes in five prime to three prime direction. And in similar way, if you look at the opposite strand, you will notice that there is one important key difference that runs in completely opposite direction. Its three prime end at the upper direction and its five prime end at the lower direction. Hence, it is said to be from three prime direction to five prime end direction which makes the two strands of the DNA Anti-parallel.
Complimentary Base Pairing
Another important thing we need to understand is the Complimentary Base Pairing which:
describes the manner inwhich the Nitrogeneous bases of DNA molecules align with each other.
So, it basically means that the Base Adenine is always with the Base Thymine and the Base Guanine always forms Hydrogen bond with the Base Cytosyne. You can see this rule in action in the DNA Step-Ladder model and you see that the Base A always pair with Base T, Base C always pairs with the Base G. These Bases are essentially forming the Hydrogen bond in the center which holds these two strands of DNA together.
The Complementary Base pairing is very important as it maintains a proper distance between the two strands of the DNA which is very important for the stability of the two strands of DNA. Now if you look at the Double Helix model of the DNA, you will undertand what these two Helixal lines mean and what it is made up of.
References
Previous Posts
- Is Supersonic Flight Realistic Or Just Some Concept Plane?
- Nope, We Can't Invent A Perfect Engine
- Nah Nah I'm Not Dying Now... Immune Systems Are Natural Killers!
- Isn't The Devil In The Details And Not The Ocean? The Legend Of Bermuda Triangle
- Are We Even Intelligent Enough To Understand What Intelligence Is?
- Are We Really Humans Or Just A Bunch Of Bacteria? Too Many Misconceptions Here
- Who Says You Cannot Build Your Own Airplane? Series #11: Yo! You Don't Mess With Flight Instruments

Hey! Do you write posts that are related to Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM)?
Then join #steemstem on on discord. Click here.
Check this blog post by @steemstem to understand the guidelines on how to become a member of @steemstem.
Also check on this post by @steemstem to understand the use of images so as to avoid copyright infringement.
And in case you are writing from Nigeria, you can include #stemng tag in your posts. Details on @stemng blog.
Thinking of delegating SP to @steemstem to support this great initiative? All you have to do is to use the links below:
50 SP | 100SP | 500SP | 1,000SP | 5,000SP | 10,000SP | 50,000SP
However, ensure you have at least 50 SP left in your wallet.

I am @teekingtv, the no.1 Global Meetup analyst

Nice content. Remembered this from college biology.
Thank you for checking by @wstanley226
Now, this is a well detailed recall of the chemical structure of our DNA. The mention of codes made me see humans as a bag of written programs for specific functionalities with the code for a special skill been commented out in all but one person. So, we have that one character that differentiates us from our neighbour.
Good one @teekingtv
The DNA master is here 😂. Glad to see you here bro. What is your thought on the newly discovered human DNA; i-motifs that has already started outshining the former Viez Diesel; Step-Ladder double Helix? Seems the dude has got some stuffs to benefit us on his sleeve