Many scholars believe that fossil energy will drastically decrease by 2050. Others have questioned these conclusions, saying that Earth has enough resources to quench humanity's thirst for human development over the next centuries. arrived.
Among other sources of energy, shale gas and oil must be abundant and available.
Essential characteristics of shale gas and oil:
Shale gas and oil are unconventional natural resources. They are between 2,500 and 5,000 meters below the surface of the Earth.
They are deeper than the conventional crude that is at 1,500 meters.
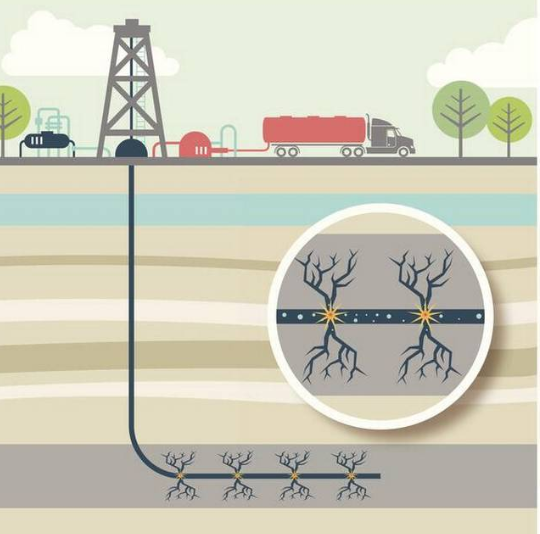
The oil and shale extraction process requires deep vertical drilling followed by horizontal drilling.
The most common method to extract shale gas is "hydraulic fracturing" (hydraulic fracturing). It is simply a matter of sending large amounts of water mixed with certain chemicals to break rocks and release trapped energy minerals.
Context:
In August 2018, the central government approved an ambitious policy allowing private and government stakeholders to explore and exploit unconventional hydrocarbons (including shale gas) in contracted areas primarily for the extraction of hydrocarbons. conventional hydrocarbons.
Unlike conventional hydrocarbons, which can be easily released by permeable rocks, shale gas is trapped in low permeability rocks.
Therefore, a mixture of "pressurized water, chemicals and sand" (shale fluid) is needed to break up the slightly permeable rocks in order to unblock the shale gas reserves.
This process requires about 5 to 9 million liters of water per extraction activity, which represents a huge challenge for India's freshwater resources.
Hydraulic fracturing: the most common way of extracting shale gas:
Hydraulic well fracturing ("fracturing") involves pumping fluid into a well to create sufficient pressure to break or fracture the rock layer.
Fractures are created by pumping large quantities of fluids under high pressure into a well and into the target rock formation.
In general, the liquid contains a "proppant", such as sand, which helps keep the fractures open to allow the production of oil and gas in the well.
Guidelines Issued on Environmental Management:
The Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) has published the guidelines on environmental precautions when extracting shale gas. He stated that "the total volume of fracturing fluid is 5 to 10 times greater than that of conventional methods".
The DGH notification indicates that these problems will be addressed when granting environmental authorizations in accordance with the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process.
However, the EIA process does not differentiate between conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons.
Therefore, it is likely that fracking activities deplete water sources and generate pollution due to the elimination of reflux water.
Negative Consequences by using the Shale Gas:
It requires large amounts of water, on average 15,000 m3 / well.
This also requires a relatively larger area.
This will inevitably affect irrigation and other local needs.
In the USA UU., The experience of 260 chemicals shows that it has been identified that 58 represent a risk to human life and the environment, of which eight are carcinogenic and 17 are toxic to freshwater organisms.
Fracturing can cause tremors in the deepest regions of the earth, causing 25 to 90% of the fluid does not recover and it is possible that cracks will occur in the well, so there will be a risk of contamination in nearby groundwater.
Cases of underground contamination are reported in the United States and Canada.
Fracturing has other impacts, such as increased emissions to air, including greenhouse gases and seismic activity.
Conclusion:
The government implemented an oil shale gas and oil policy in 2013. It allowed national oil companies to practice fracking.
During the first phase, shale gas blocks were identified in Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu.
Environmental groups say they have negative environmental effects. Even well-developed Western countries such as Germany and France and subnational governments like Scotland have banned fracking.
Way to follow:
Indian homes and irrigation thrive thanks to groundwater. The implementation of fracking processes without prior reflection, especially on the "water use policy", can lead to broader problems, which include water stress, groundwater contamination, and health risks. associated with it.
But in the current state of the process, we miss the opportunity to comprehensively regulate the fracturing process for a sustainable exploration of shale gas in India.
As a first step, a sectorial EIA manual on exploration and production of unconventional hydrocarbon resources may be a good idea.