Hello. It is @hunhani.
Thank you for your interest and support in the previous posts. I will do my best to meet your expectations.
Last time, We have learned about technical challenges we have to overcome for the world of quantum information.
Chapter 6. Current Status of Technology Development for Quantum Computer This time, let's talk about the current status of technology development for the quantum computer.
Simple Review
Hardware development is the first step for the implementation of quantum computers.
- The theoretical work has been quite advanced to this day. Although it is necessary to derive the quantum algorithms for a variety of problems, no matter how good the quantum algorithm is, the quantum computer can be implemented with the hardware to operate it.
- Experimentally, there has been a steady attempt to carry out actual quantum numerical calculations with a very small number of qubits, but there are still many technical steps to overcome.
Quantum mechanical properties and principles
- Duality of particle and wave
- Uncertainty
- Quantum superposition
- Quantum entanglement
- Quantum parallelism
Core technology elements
- Generation of quantum states
- Matintenance of quantum states
- Control of quantum states
- Transmission of quantum states
- Measurement of quantum states
- Quantum algorithm
Related application technologies
- Quantum Processor
- Quantum Communication
- Quantum Repeater
- Quantum Cryptography
- Quantum Memory and Measurement
A quantum computer is the integration of quantum processors.
- It is necessary to induce strong interactions between electrons or photons in the micro world, make them entangled, maintain and control them well in order to operate properly as a qubit.
- Electrons with strong particle properties are relatively easy to transfer, but the errors in computation or measurement are frequent, while photons with strong wave properties are relatively difficult to transfer, but the errors in computation and measurement are infrequent.
- The process of making a lot of entangled qubits and handling them is a very difficult task.
Increase the number of qubits to handle at once!
Last time, we have talked about quantum information processing using qubits. Based on the quantum mechanics of probabilistic representation of the state of matter, we can implement qubits through quantum superposition and quantum entanglement. Unlike the bits that need to have only one unconditional value 0 or 1, the qubit can hold both 0 and 1 at the same time. Two qubits can be represented in four states, such as 00, 01, 10, and 11. In a similar way, three qubits can be represented by eight, and four qubits can be represented by sixteen states. If we have 10 qubits, 1024 states can be represented. Unlike the bit, the efficiency increases exponentially as the number of qubits increases. Of course, we have spent a lot of time to discuss that it is not easy to handle multiple qubits at will.
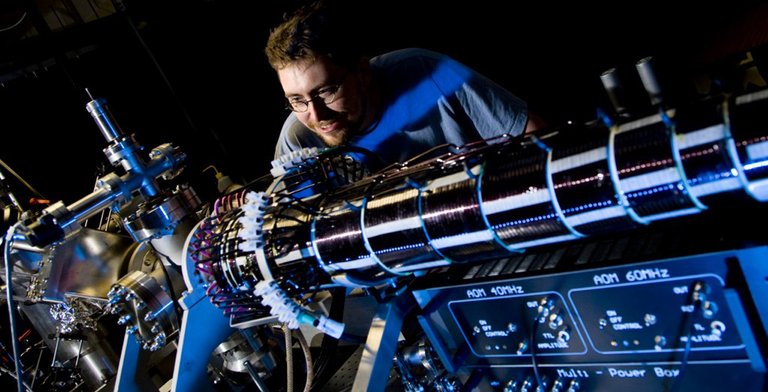
▲ Professor David Kielpinski at the Quantum Mechanics Center in Griffith, Australia, examines the equipment for the quantum computer that can precisely control the state of electrons.
In 2011, Canadian computer developer D-wave systems sold the first commercially available quantum computer D-wave One for a specific purpose to a unit of $ 15 million (about 17.4 billion won). This quantum computer can only perform certain mathematical calculations, but it is hundreds of times faster than conventional computers. The NASA and Lockheed Martin are actually using it. But until 2014, the performance of D-Wave, which was the world's first quantum computer, was not so different from the ordinary computer, which was a little disappointing to the public. It is expected that the performance will improve exponentially as the number of qubits that quantum computers can handle also grows, just as Moore's law of conventional computers doubles the density of integration in 18 months.
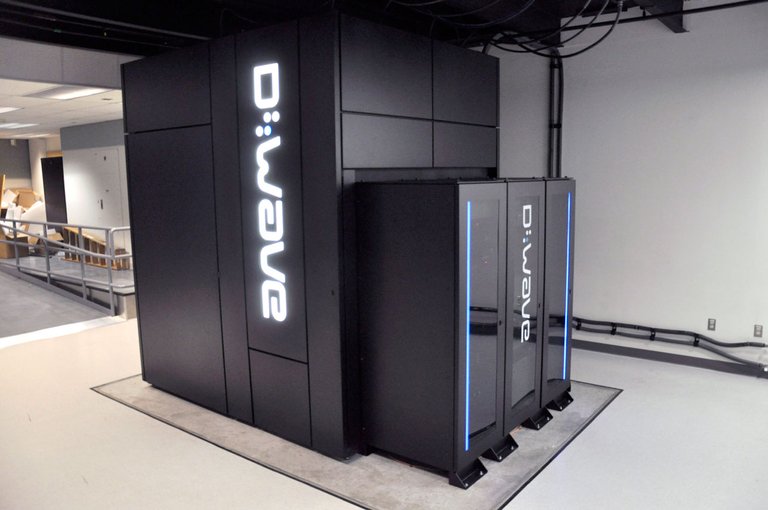

▲ D-wave quantum computer installed at Ames Research Center of NASA.
Global companies compete with quantum computer technology.
In June 2016, Google demonstrated a 9-qubit quantum computer capable of controlling 9 electrons, and IBM developed a 5-qubit quantum computer and released it to the public. IBM's 5-qubit quantum computers are already known to have used more than 40,000 people. IBM has even announced that they plan to develop a quantum computer with a 50-qubit in the near future and start a paid service. Microsoft has also begun to build undiscovered particle-based hardware and cryogenic memory designs for quantum computers. They have hired many quantum mechanics experts to launch commercial quantum computers. Likewise, the most prominent IT companies such as Google, IBM and Microsoft are pouring huge amounts of money into research for the development of quantum computers and are competing for the launch of commercially available quantum computers.
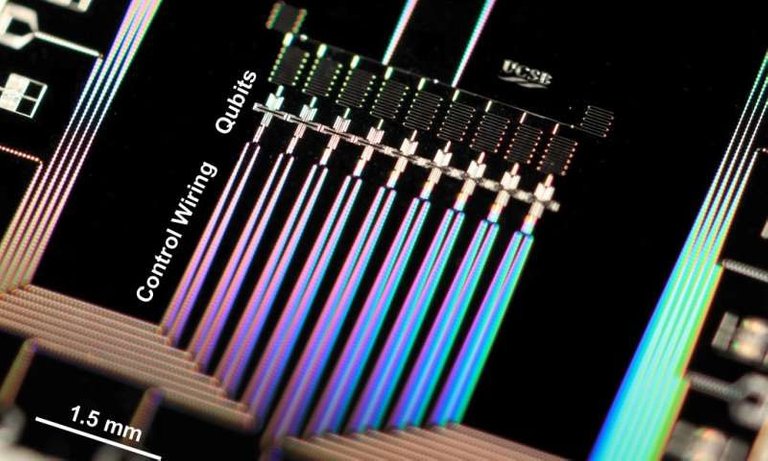
▲ In June 2016, a 9-qubit quantum computer developed by Google using a superconducting circuit.
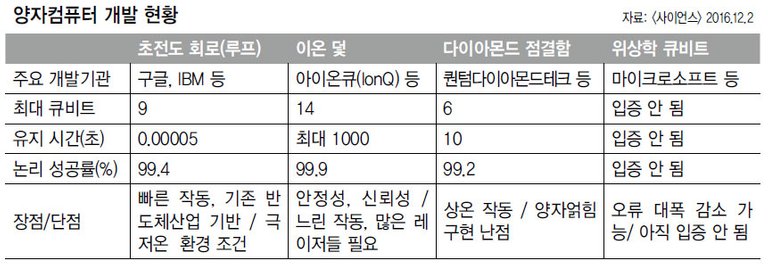
▲ Quantum computer development status
Initiating of quantum computer commercialization.
Google has hired Prof. John Martinis of the University of California to create a quantum processor that directly acts as the brain of quantum computers and is now aiming to create a 50-qubit quantum computer. Although it may be possible to create a quantum computer much better than the existing computer with several thousand qubits or more, it will play a role of driving the investment in the field of quantum computer.
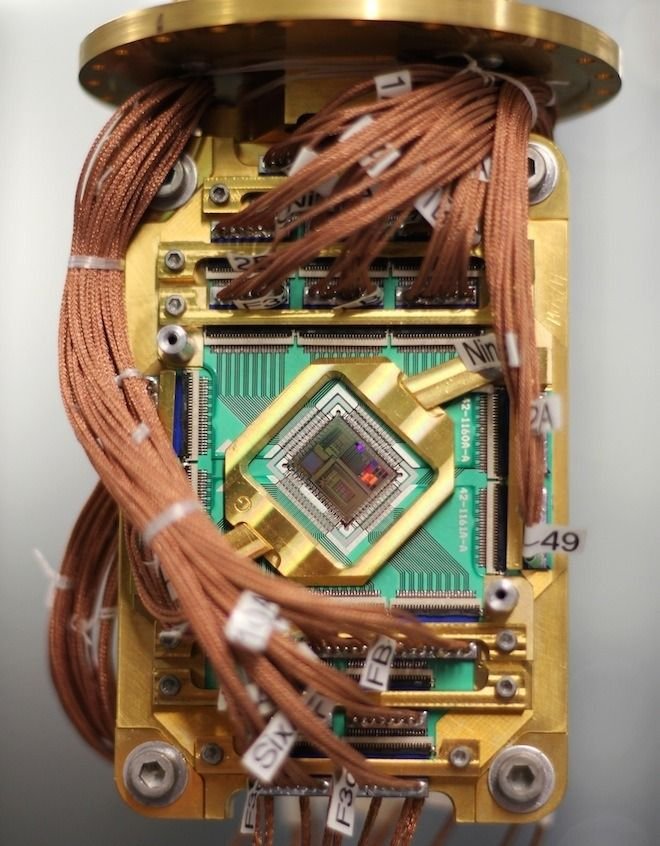
▲ D-wave quantum computer circuit installed at QuAIL (Quantum Artificial Intelligence Laboratory) in collaboration with Google and NASA.
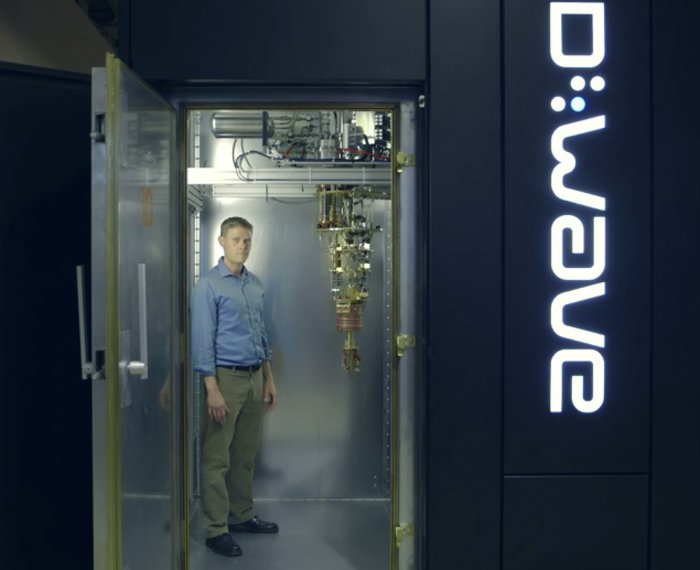

▲ D-wave quantum computer circuit installed at QuAIL (Quantum Artificial Intelligence Laboratory) in collaboration with Google and NASA.
Korea still lags behind quantum computer technology.
According to a survey by the Korea Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, the level of quantum computer technology in Korea is only half of the developed countries. Research is underway to implement a rudimentary level of qubits in Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS), Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), and SK Telecom Quantum Lab, but the technology gap with developed countries is about 7.6 years. However, experts in Korea say that the technology that controls the phenomena necessary for quantum computers is also competitive in the world, so there is a need for domestic large companies to invest with interest.

▲ A graph showing the speed improvements of quantum computers released by Google.
Korea company in the field of quantum cryptography communication.
As we discussed last time, quantum cryptography communication is a perfectly secure communication method against eavesdropping using the non-reproducible nature of quantum mechanics. According to Market Research Media, the global market for quantum telecommunications will grow rapidly from 2021 to 2025 and reach about 26.9 trillion won in 2025. Recently, in June 2017, SK Telecom overcame the distance limit of quantum cryptographic communication and laid a foundation for long distance communication. For the first time in the world, they have succeeded in developing a quantum repeater and transferring the quantum cryptographic key from the Bundang to Yongin and Suwon in the round-trip 112Km test network. SK Telecom's quantum repeater for quantum cryptography is a pure domestic technology that has been developed after the last two years of effort thanks to the support of the national project. They plan to apply it to domestic and overseas commercial networks through cooperation with global companies. It is expected to contribute to industrial revitalization by linking with most industries that need security such as administration and defense.

Arrival of age of quantum information!
The Technology Review published in February 2017 by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) predicted the arrival of the age of quantum computers in the 'Ten Innovative Technologies of the Year'. The road to commercialization of quantum computers is still far away, but the prominent IT companies and the most prestigious research institutes are competing with each other to develop quantum computers. So I think the age of quantum information is approaching faster than we thought.
Next time, we will deal with how valid the following sentence is. “quantum computer will eventually kill the block chain system.”
I want to deliver it as easily as possible, but this topic is very difficult for everyone. If you comment your question, I will reply to you as easily and concisely as I can.
The following chapter is introduced.
Chapter 7. Can Quantum Computers Kill Blockchain?
Please do not take your eyes off!
Previous Story
- [Quantum Computer & Blockchain Security] Chapter 0. Introduction
- [Quantum Computer & Blockchain Security] Chapter 1. Quantum computer! What the hell is different with ordinary computer?
- [Quantum Computer & Blockchain Security] Chapter 2. Magical phenomena of nature, Quantum Superposition & Entanglement.
- [Quantum Computer & Blockchain Security] Chapter 3. Janus-faced quantum computer Quantum Parallelism and Quantum Communication Security
- [Quantum Computer & Blockchain Security] Chapter 4. Quantum Information Processing using Qubits
- [Quantum Computer & Blockchain Security] Chapter 5. Technological Challenges to Overcome for Quantum Information World
- [Next-generation Transportation] Hyperloop! Why is it so special?
- [Review] 18 Stories to See “Interstellar” Movie More Fun with Physics
- Engineer Dream Diodes with a Graphene Interlayer
- All images used in this post are from Google Images.

Please hurry up with the next episode ;). We all believe in the blockchain
Haha, I will upload it soon.
nice
Thanks
Hello FRIEND !! GOOD LUCK !
Quantum computing seems to be the most powerful and secured system. :-)
If the system works well then yes!
great imformation , am interested in quantum theory and ive just made apost about quantum physics , it would be kind of you if you just chech it out and tell your opinion and how to improve my posts
https://steemit.com/science/@mostafa1/where-would-we-be-if-we-had-never-discovered-quantum-physics-would-ourlifes-be-the-same
Ok. I'll check it out.
@hunhani
Great writeup!
Keep sharing great content.
THanks!!
Thanks for the compliment :)
How long until quantum computers start breaking the blockchain technology at will?
Is there a solution? Could we have a quantum-proof next generation blockchain?
First of all, please follow up Chapter 0 ~ Chapter 6. The details about your questions will be discussed in the next Chapter.
Sure, I'm staying tuned for the next chapter as this is the question I'm interested the most in regard to quantum computing.
Thanks. I will upload soon!
Looking forward to it... :)
Check this out!
https://steemit.com/writing/@hunhani/quantum-computer-and-blockchain-security-chapter-7-can-quantum-computers-kill-blockchain#@steemitboard/steemitboard-notify-hunhani-20170729t111436000z
You might want to shorten the link a bit because it points to a random comment under your article, not the article itself. Of course, it still works, but yeah... ;)
what steem