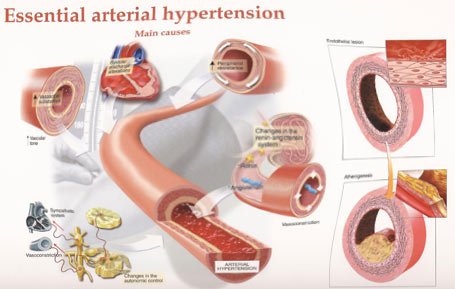
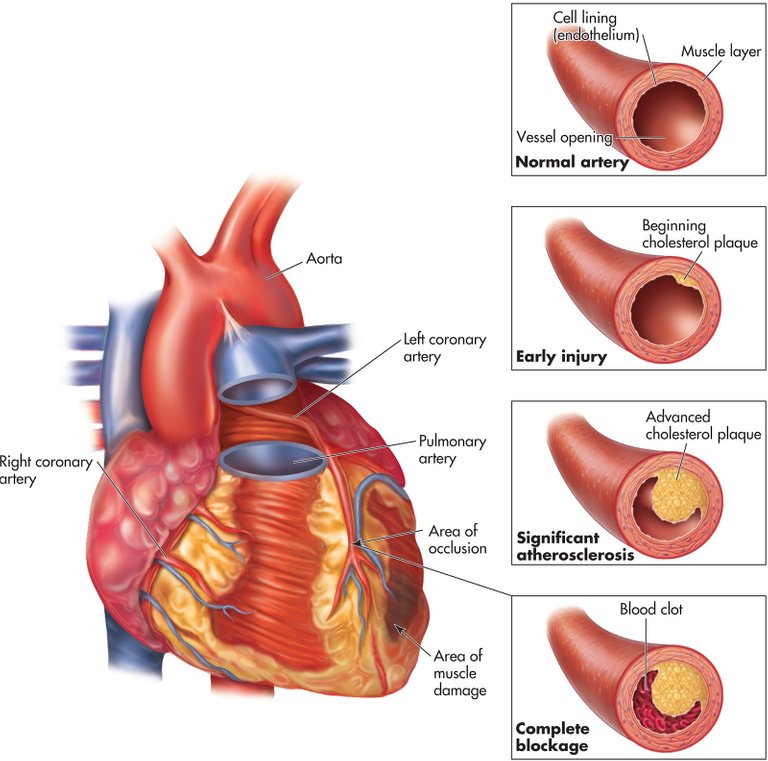
Hello steemit and steemstem friends, today I’m going to talk about a topic that all of you heard about and that have a big importance for the global population, this is going to be a little bit hard to explain, but I’ll treat that this be as understandable as possible. I’m going to talk about arterial hypertension.
The hypertension is a asymptomatic and easy to detect disease, nevertheless, it have a lot of serious and lethal complications if you don’t treat it on time. The chronic hypertension is one of the most important modifiable risk factor to develop cardiovascular and kidney diseases.
About a third part of the adult population of the developed countries or the ones that are in a way to convert itself in a developed country, suffer arterial hypertension; is the main cause of medical consultation on the medical services of primary attention. Talking about numbers, 115/75 of arterial pressure for every increment of 20 mmHg on the systolic pressure or 10 mmHg on the diastolic pressure, the risk of a cardiovascular event doubles.
Let’s start.

What is arterial hypertension?
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP) is a chronic disease which is characterized for a continuous increment of the blood pressure numbers that are above the limits and for the ones the cardiovascular risk increase. Agree with numerous international works , the cardiovascular morbidity and mortality cause have a direct relation with the number increase at systolic pressure sustained above 139 mmHg or a diastolic pressure sustained above 89 mmHg, however, is a risk factor for coronary artery disease and for cerebral vascular accident, heart failure, the peripheral vascular disease and chronic kidney disease.
For a clearer concept, the hypertension is a disorder in which the blood vessels have a high persistent tension that can damage them. Every time that the heart beats pump blood to the vessels that carries the blood to all the body parts. The arterial tension is the force that exerts the blood through the arteries being pumped by the heart. The higher the tension is, the more effort has to perform the heart to pump.
How these start to act on our body?
The arterial hypertension, in a silent way, produce changes on the blood flow in a macro and microvascular level, cause for the dysfunction of the inner layer of the blood vessels and remodeling the wall of the resistance arterioles that are the responsible of keep the peripheral vascular tone. A lot of these changes precede in time to the arterial pressure elevation andproduce specific organic injuries.
In a 90% of the cases, the cause of the HTN is unknown, so it is denominated “Essential arterial hypertension”, with a hereditary influence.
Between the 5 and the 10% of the cases have a cause directly responsible of the tension number elevation. This kind of hypertension is denominated “Secondary arterial hypertension”, that can be treated and disappear forever without a long-time treatment, also, it can be an alert to localize more serious diseases in which arterial hypertension is just a symptom.
The diuretics and the beta-blockers reduce the apparition of adverse events for arterial hypertension related with the cerebrovascular disease. Nevertheless the diuretics are more efficient in the reduction of events related with the coronary artery disease.
How can we classify the hypertension?

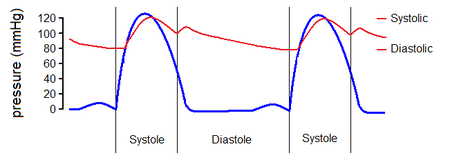
The arterial pressure is express by two measurements, the systolic and diastolic pressure that are the highest and the lowest, respectively. For the majority of the adults, the normal arterial pressure in repose is in the range of 100-130 mmHg systolic and 60-80 mmHg diastolic. For the majority of the adults, the high arterial pressure is presented by a pressure on repose between 130/90 and 140/90 even more. For kids are applied different numbers. The monitoring of the arterial pressure in an ambulatory during a period of 24 hours is more accurate than the arterial pressure measurement in a consulting room.
The systolic arterial (the first number) is the blood pressure on the arteries during the ventricular systole, when the blood is expulsed since the heart to the arteries; the diastolic pressure (the second number) is the pressure in the diastole, when the heart relax the arterial pressure falls off.
It can be classified as hypertensive if a man or a woman arterial pressure is consistent unless with 140 mmHg systolic or 90 mmHg diastolic.
Diagnostic
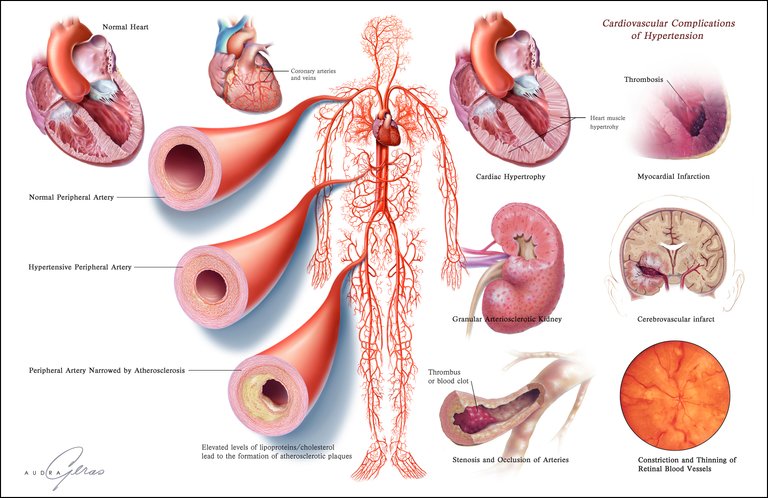
The medical story of a hypertensive patient has to be collected and filled with information provided by the closer relatives, by other doctors or paramedic personnel who have attended him/her on the past. The hypertension is an asymptomatic disease for excellence, it is called the silent assassin, so it’s not a surprise that you can’t collect a lot of its symptoms information on the story or that these are not very specific (headache, dizziness and vision loss, for example). Once that this has been defined and having been documented all the relevant aspects of the present disease, have to make emphasis since the first consultation on these aspects.
Traditional and not traditional cardiovascular risk factor.
- Family background of the disease, especially if there has been deaths for a cardiac cause.
- Socioeconomic, cultural and employment status, family status, access to health systems, level of education, environmental or situational factors that cause stress.
- Comprehensive list of comorbidities (usually interrogating antecedents by systems)
- Hygienic-dietary habits: coffee, tea, carbonated drinks, alcohol, tobacco, sodium, food, physical activity.
- High blood sugar level and high glucose consumption (if the person has diabetes)
- Exposure to drugs that can cause hypertension (ephedrine, methylphenidate, ergotamine,among others)
In this case I just wanted to make reference to the main forms of diagnosis, because there are too many other ways.
Relevant information
Most of the time there is no specific cause triggering of the hypertension, which is why it is called primary hypertension or essential hypertension. 90-95% of hypertensive patients would be from this group. Although there is no specific cause, it is known that there are conditions that increase the probability of developing high blood pressure, such as advanced age and a family history of hypertension. The presence of other diseases such as diabetes, high cholesterol and obesity also predispose to hypertension.
There are a smaller percentage of cases in which arterial hypertension is secondary to some specific circumstance: alcohol consumption (especially in males), some drugs (corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, contraceptives in women), kidney diseases, and other less common disorders.
Recent data from the Framingham Heart Study suggested that these individuals over 65 years of age have a 90% lifetime risk of having high blood pressure. Since the 1980s, the number of undiagnosed patients has increased by 25% to almost 33% in the 1990s, the prevalence of kidney failure has grown less than 100 per million to 250 per million and the prevalence of heart failure congestive doubled.
It is more common in urban than in rural areas, and more frequent in Afro-Americans than in caucasian people. The incidence has been calculated between 0.4 and 2.5% per year. Mortality per death certificate is 8.1 per 100 000. Using other standard it becomes 76 per 100 000. It is calculated between 8 000 to 9 000 annual deaths attributable to HTA. From 66 to 75% of cases of cerebral thrombosis have hypertension. 90% of non-traumatic intracranial hemorrhages correspond to HBP.
News :Study Links Low Levels of Oxygen in Blood to Poor Pulmonary Hypertension Patient Outlook
Low levels of oxygen in the blood of people with idiopathic or heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH or HPAH) are associated with secondary diseases and a poor patient outlook, a study shows.
IPAH and HPAH patients can have hypoxemia, or low levels of oxygen in the blood, either at rest or during physical activities. Secondary diseases can contribute to hypoxemia, studies have shown.
But researchers had never categorized the prevalence of hypoxemia in these patients or its association with a specific patient’s characteristics and outlook.
Closure.
Controlling blood pressure (BP) decreases in 20 to 25% the possibility of having a myocardial infarction, 35 to 40% a cerebrovascular accident and more than 50% heart failure. Blood pressure reduces the risk of cardiovascular events by up to 10% and induces regression of existing left ventricular hypertrophy. The prescription of an aerobic program, a proper and individualized diet, the abandonment of smoking and reduce the consumption of ethanol, have a great benefit in all people, so doctors should worry about informing patients of this change in their lifestyle, before prescribing medications.
The choice of the drug is the crucial element of the prescription, taking into account various factors, particularly the patient's previous experience with antihypertensive drugs, their adherence capacity, the lowest possible number of pills, the cost and the presence of comorbidities.
Ref Information
- Svetkey LP, Moore TJ, DASH collaborative research group y col. <>«Angiotensinogen genotype and blood pressure response in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) study»
- Your guide to lowering your blood pressure with DASH (artículo completo disponible en inglés). National Institutes of Health
- https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/ency/article/000468.htm
- Harrison Principios de Medicina Interna 16a edición (2006). «Capítulo 230. Vasculopatía hipertensiva»
- https://www.webconsultas.com/hipertension/hipertension-351
- https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hipertensi%C3%B3n_arterial
- DiNicolantonio, James J.; Mehta, Varshil; O'Keefe, James H. (August 2017). "Is Salt a Culprit or an Innocent Bystander in Hypertension? A Hypothesis Challenging the Ancient
- http://www.who.int/features/qa/82/es/
- http://www.monografias.com/trabajos93/sobre-hipertension-arterial/sobre-hipertension-arterial.shtml
- Sorof J, Daniels S; Daniels (October 2002). <>"Obesity hypertension in children: a problem of epidemic proportions"<>
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertension
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here.
Thank you for taking the time to read this publication. I hope you have a happy day, see you in the next. Do not forget to leave a comment about what you thought, thank you very much.@juanjdiaz89