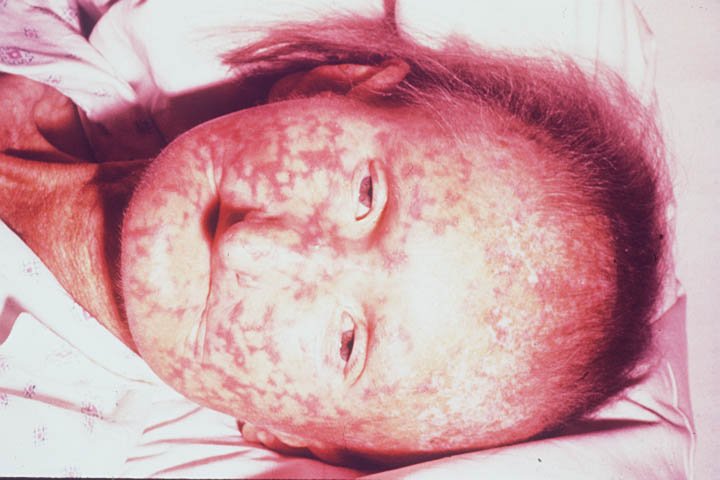
INTRODUCTION
This article was inspired by a post I stumbled on some days back of a lady that had finally surrendered after years of struggle with the disease “scleroderma”, an excruciatingly painful disease which affects the body leading to hardening of connective tissues. Seeing the picture of the young lady and the adverse effect of what the disease had made of her was so appalling.
That was actually the first time I heard of the disease, I guess it’s isn’t a common disease you hear about on a regular because according to statistic fewer than 500,000 but around 300,000 people in the United States have scleroderma making it suitable to be referred to as “uncommon”.
In a befuddled state, staring at the picture and trying to comprehend how disastrous this disease was and had the ability to inflict such a grotesque effect on the human skin, It was expedient of me to emancipate myself from the ignorance of this deadly disease. This led to an execution of a little research in further enlightenment of this disorder which I deemed necessary to share.
WHAT IS SCLERODERMA
Scleroderma is an autoimmune, rheumatic, and chronic disease that affects the body by hardening of connective tissues characterized by skin thickening, spontaneous scarring, blood vessel disease and varying degrees of inflammation, which occurs as a result of overproduction and accumulation of collagen in body tissues including the skin. It involves a situation whereby the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissues. Connective tissues are made up of proteins of which collagen skin is among. The word Scleroderma literally means hard skin.
TYPES OF SCLERODERMA
There are basically two (2) types of scleroderma which are;

Localized Scleroderma
- morphea
- linear
Systemic Scleroderma
- systemic
- diffuse
-Localized Scleroderma:
The skin changes that occur here are usually localized in an isolated area, it’s usually found in
some areas of the skin or muscles and spreading is limited, the internal organs are usually not affected and the people with localized scleroderma rarely develop abnormalities commonly seen in systematic scleroderma. Localized scleroderma are usually in either morphea patches or linear scleroderma. Morphea is usually localized in nature with waxy patchy area of the skin with different sizes and shapes that becomes hardened and pigmented while linear scleroderma usually develops in children and involves hardened waxy skin on the arm or leg which involves deeper layers of skin and could affect the motion of joints.
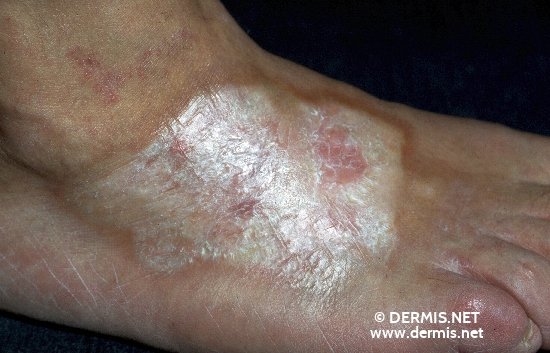
-Systemic Scleroderma:
This type of scleroderma is usually widespread and involves internal organs such as esophagus gastrointestinal tract (stomach and bowels), lungs, kidney, heart and other internal organs in addition to the skin. This type could either be limited or diffuse, limited involves less skin movement and skin thickening which is normally restricted to fingers, hand and face which develop over time while diffuse scleroderma occurs rapidly and covers more skin area compared to limited scleroderma. People with diffuse scleroderma are vulnerable to having sclerosis or fibrous hardening of the internal organs.

SYMPTOMS OF SCLERODERMA
The symptoms could depend on the part/area of the body involved. However, major symptoms of this deadly disease could include fingers becoming sensitive to cold and it’s color changing, as well as it becoming stiff or puffy. Thickened skin usually on the face or hands which looks shiny and smooth, painful or swollen joints, muscle weakness, sores on the finger tips, weight loss, heartburn, red spots on the face and chest as a result of opened blood vessels called telangiectasias.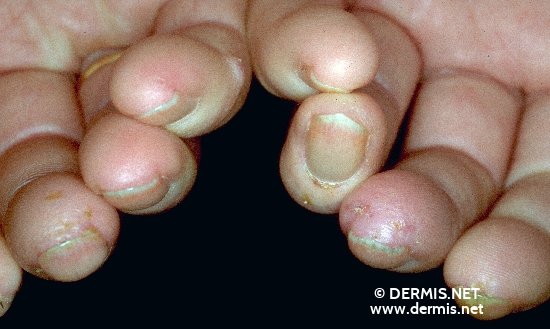
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of scleroderma usually involves blood tests, taking of skin sample (biopsy) and numerous tests depending on the organ affected be it the lungs, heart or esophagus. The diagnostic process might however be carried out by arthritis specialists (rheumatologists) or dermatologists (skin specialists).
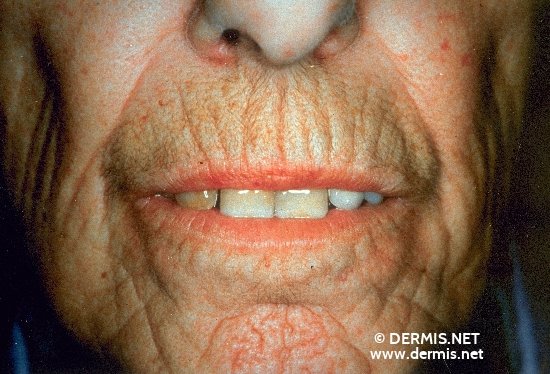
WHAT CAUSES SCLERODERMA
The scary thing is the major cause of scleroderma is unknown, as doctors haven’t been able to able figure out what triggers the process that results in scleroderma which is the over production and accumulation of collagen tissues. However researchers have ascertained some proof that certain genes are important hereditary factors.
The fact that genes are susceptible in developing the disease implies that scleroderma could be hereditary to an extent. In some people who are genetically vulnerable the symptoms may be initiated by exposure to certain types of pesticides, epoxy resins or solvents.
FACTS ABOUT SCLERODERMA
You should be aware that the disease is not contagious, infectious, cancerous or malignant.
It symptoms varies differently for each person depending on the seriousness of effect it has on the parts of the body, where was affected and the extent to which it has been affected.
Early and proper diagnosis as well as treatment by qualified physicians may minimize the symptoms and reduce the possibility of having irreversible damage.
There are two types of scleroderma, Localized scleroderma which is common in children while the other systemic scleroderma is common in adults.
Females are more prone to the disease compared to males with a ratio of 4:1.
Scleroderma is chronic and doesn’t go away but there are treatments that can effectively prevent or limit the damage caused just like diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease.
Factors other than gender such as race and ethnic background may influence the risk of developing scleroderma.
The Choctaw Native Americans are the group with the highest reported prevalence of the disease.
TREATMENT
Based on the information I got from surfing the net, I discovered there are a number of ways that could be employed in approaching scleroderma which can be divided into the use of medications, therapy and surgery.
USE OF MEDICATIONS: The use of medications doesn’t imply that there are drugs that could be used in curing, but rather slowing down and controlling excess production of collagen which is the causative of the disease to prevent further complications. Drugs that are used are those that can
Dilate blood vessels
Suppress the immune system
Reduce stomach acids
Prevent infections
Relieve pain
Therapy: Therapy could be administered to help manage pain, improve strength and mobility.
SURGERY: Surgeries could also be performed in extreme cases which might involve amputation or transplant as the case may be depending on the complexity of the situation.

Thanks for reading, I hope this post was enlightening and meets the required standard that makes it worthy for a favourable consideration in the @steemSTEM competition :).
Images:
http://www.dermis.net/dermisroot/en/33894/image.htm
http://www.dermis.net/dermisroot/en/39094/image.htm
http://escholarship.org/uc/item/1368x3wx
http://thehealthdigest.org/2834/new-scleroderma-drug-designated-as-a-breakthrough-therapy/
http://www.orthop.washington.edu/?q=patient-care/articles/arthritis/scleroderma.html
https://www.disabled-world.com/health/dermatology/skin/scleroderma.php
http://www.dermis.net/dermisroot/en/39079/image.htm
Sources:
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health_info/scleroderma/scleroderma_ff.asp
https://www.scleroderma.org/site/pageNavigator/patients_whatis.html
https://www.medicinenet.com/scleroderma/page2htm
https://www.mayoclinic.org/disease-conditions/symptoms-causes/dxc-20206020
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/scleroderma
Very informative. I definitely learned something new. Thank you!
I am glad you did, Thanks :)