FUENTE
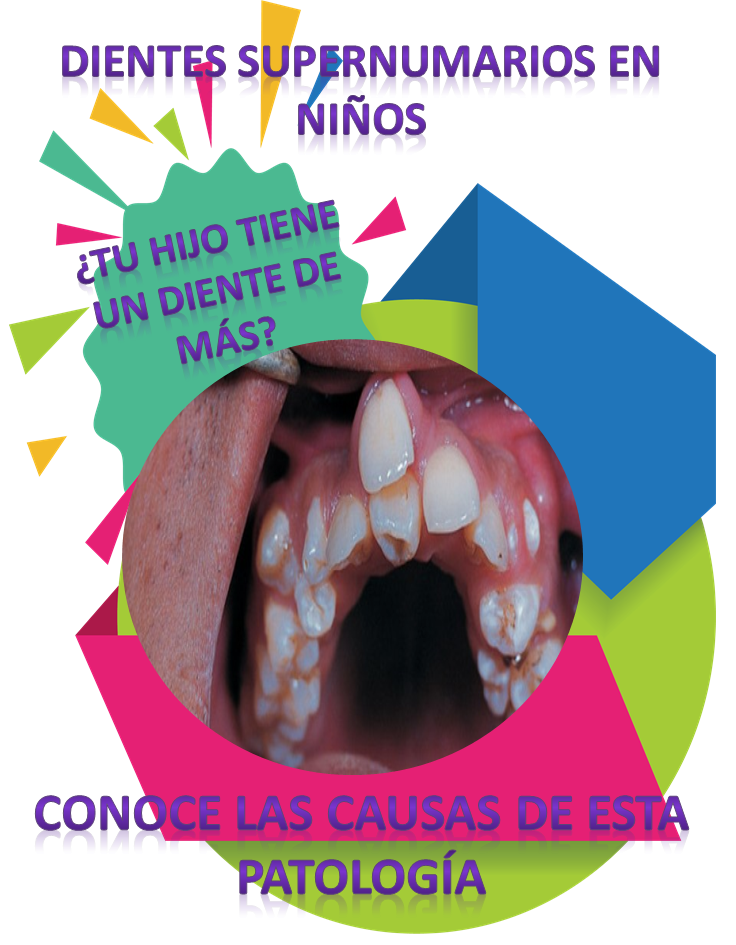
Between the sixth and eighth week of gestation, milk teeth begin to develop, while bone teeth begin to develop from week 20. When the baby is born, the teeth are ready to break the gum and come out little by little until complete the first teething. But what happens if an extra tooth is born?
FUENTE
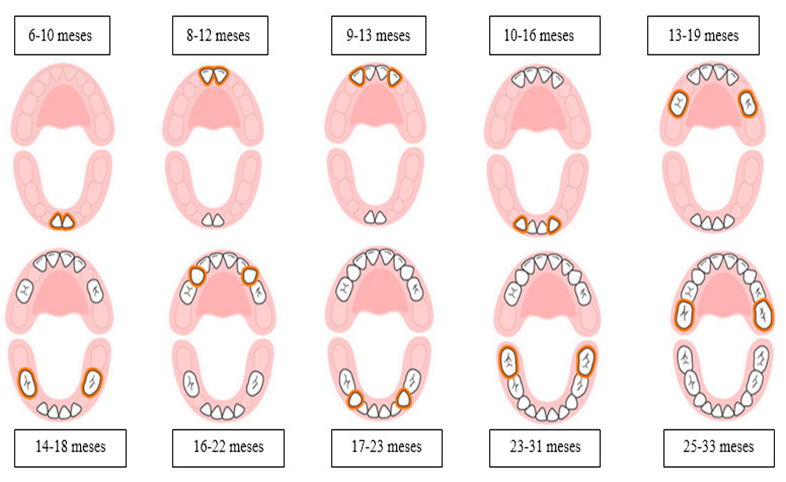
Los dientes supernumarios o Hiperdontia no es más que dientes en exceso o dientes sobrantes, que pueden aparecer en cualquier persona, suele ser más común en los dientes definitivos que en los de leche, es una patología que no presenta síntomas y no se requiere de un análisis de laboratorio o diagnóstico por imágenes sino que, por lo general es auto diagnosticable y pueden provocar alteraciones en la erupción, ya sea al ocupar el espacio de la arcada de otros dientes o al bloquearles la guía de erupción.
Supernumary teeth or Hyperdontia is nothing more than excess teeth or excess teeth, which can appear in anyone, it is usually more common in permanent teeth than in milk teeth, it is a pathology that does not present symptoms and does not require a laboratory analysis or diagnostic imaging but, in general, it is self-diagnosing and can cause alterations in the eruption, either by occupying the space of the arch of other teeth or by blocking the eruption guide.
FUENTE
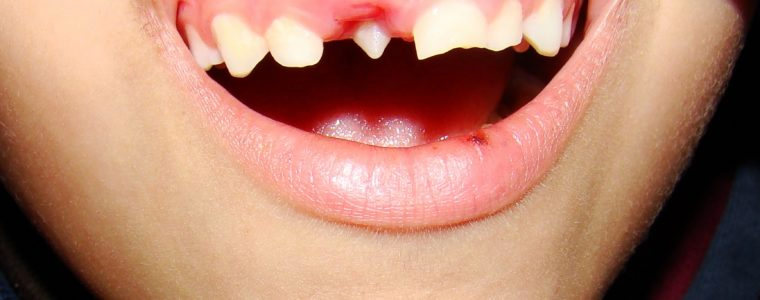
La diferencia entre dientes supernumarios y dientes suplementarios es que, los supernumarios suelen tener una forma muy diversa diferente a la forma habitual de un diente y es más parecido a un cono así como también, suelen tener diversas direcciones de erupción, mientras que los suplementarios son dientes extras que tienen la misma forma que un diente normal.
The difference between supernumary teeth and supplementary teeth is that supernumaries tend to have a very diverse shape different from the usual shape of a tooth and it is more similar to a cone as well as, they usually have different directions of eruption, while the supplementary ones are extra teeth that are the same shape as a normal tooth.
FUENTE
¿Cuáles son las causas de la aparición de los dientes supernumarios?
¿What are the causes of the appearance of supernumary teeth?
La causa de que aparezcan estos dientes es una desviación en proceso embriológico pero, también suele estar relacionada con el padecimiento de algunos síndromes como el querubismo, el síndrome de Gardner o la disostosis cleidocraneal.
The cause of these teeth appearing is a deviation in the embryological process, but it is also usually related to the suffering of some syndromes such as cherubism, Gardner's syndrome or cleidocranial dysostosis.
¿Cuáles son los síntomas?
¿What are the symptoms?
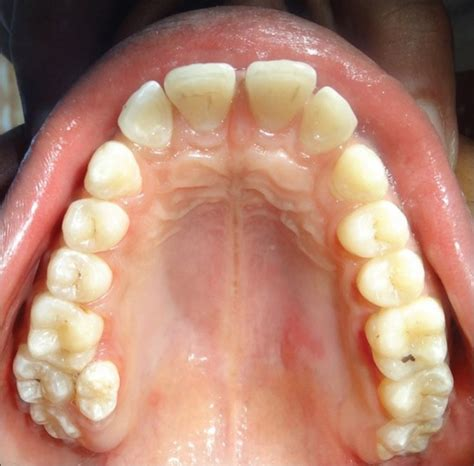
A pesar de no presentar síntomas tiene numerosas repercusiones en el estado de la boca como problemas de apiñamiento dental o desplazamiento de las piezas dentales, aparición de de caries en los dientes adyacentes, retraso en la erupción de alguna de las piezas dentales en el caso de los niños, afecta a la sonrisa, especialmente si erupcionan en la zona de los dientes centrales.
Despite not presenting symptoms, it has numerous repercussions on the state of the mouth such as problems of dental crowding or displacement of the teeth, the appearance of cavities in the adjacent teeth, delay in the eruption of any of the teeth in the case of In children, it affects the smile, especially if it erupts in the area of the central teeth.
¿Cómo se puede tratar?
¿How can it be treated?
Si los dientes supernumarios afectan a un niño con dentición mixta, debe ser evaluado por un odontopediatra quien determinara si el diente debe ser extraído o no para evitar posibles problemas en la erupción o en la colocación de los dientes en la arcada. Pero, en el caso de los niños existe el problema de que una extracción precoz, pueda dañar los dientes que aún no han terminado de formarse.
If supernumary teeth affect a child with mixed dentition, it should be evaluated by a pediatric dentist who will determine if the tooth should be extracted or not to avoid possible problems in the eruption or in the placement of the teeth in the arch. But, in the case of children, there is the problem that an early extraction can damage teeth that have not yet finished forming.