Have you ever wondered what happens when a star reaches the end of its life? Some stars don’t simply fade away—they explode in one of the most powerful events in the universe: a supernova. These explosions are so bright they can outshine entire galaxies for a short time! Let’s explore the spectacular final moments of massive stars.
What is a Supernova?
A supernova is the violent death of a massive star, releasing an immense amount of energy in just a few seconds. These cosmic blasts create heavy elements, scatter stardust across space, and even seed the birth of new stars and planets.

A brilliant supernova explosion—the final act of a dying star.
Not all supernovae occur the same way. Scientists classify them into two main types:
🔵 Type I: The White Dwarf Detonation
Occurs in binary star systems (where two stars orbit each other).
A white dwarf steals too much material from its companion star and becomes unstable.
This runaway reaction leads to a thermonuclear explosion—a Type Ia supernova!
A white dwarf accumulates too much mass, triggering a powerful Type Ia supernova.
🔴 Type II: The Core Collapse Supernova
Happens when a massive star (at least 8 times the Sun’s mass) runs out of fuel.
Without fuel, the star can no longer support itself against gravity.
The core collapses in an instant, triggering a gigantic explosion that blasts the outer layers into space!
A dying massive star undergoes core collapse, leading to a spectacular Type II supernova.
Supernovae: The Universe’s Element Factories
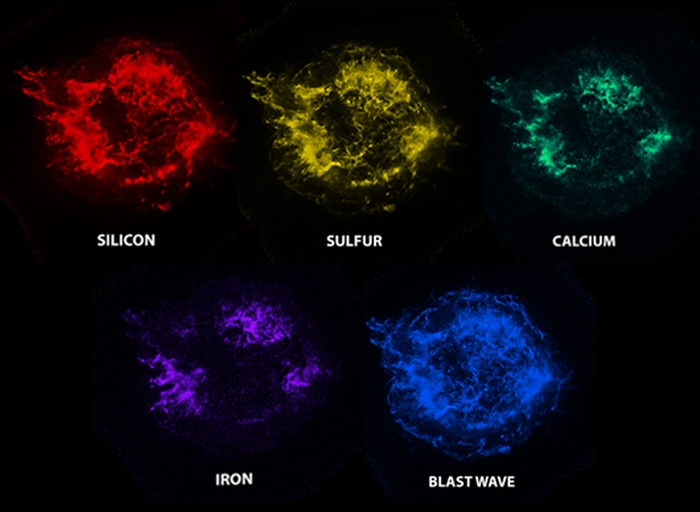
Did you know that without supernovae, life as we know it wouldn’t exist? These explosions create and scatter heavy elements like:
🌟 Carbon & Oxygen – Found in every living thing.
🪙 Iron & Nickel – Essential for planets (and even the iron in your blood!).
💎 Gold & Uranium – Precious metals forged in the hearts of dying stars!
The very atoms that make up your body, Earth, and everything around you were once formed in ancient supernovae. In a way, we are all made of stardust! ✨

Supernovae spread the building blocks of life across the universe!
What’s Left After a Supernova?
A supernova doesn’t just disappear—what remains depends on the mass of the original star:
🟣 Neutron Star – If the core is between 1.4 and 3 times the Sun’s mass, it collapses into an ultra-dense ball of neutrons. A teaspoon of neutron star material weighs billions of tons!
⚫ Black Hole – If the core is even more massive, gravity crushes it into a point of infinite density, creating a black hole that nothing—not even light—can escape.
5. Famous Supernovae in History
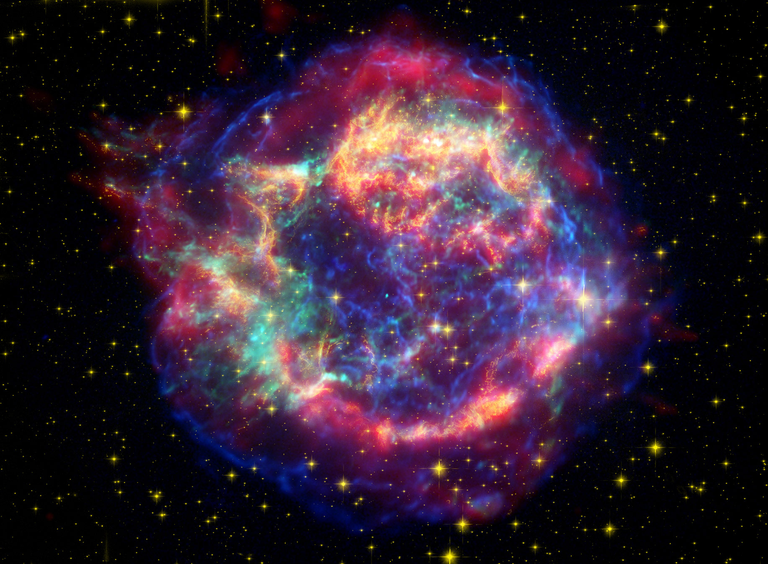
🔭 SN 1054 (Crab Nebula) – A massive explosion recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054. Today, its remains form the Crab Nebula, a bright pulsar-wind nebula.
✨ SN 1987A – One of the closest supernovae observed in modern times, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, about 168,000 light-years away.
💥 Betelgeuse – A Supernova in Waiting? – The red supergiant Betelgeuse in the Orion constellation is nearing the end of its life. Astronomers believe it could explode in the next 100,000 years—a blink of an eye in cosmic time!
📸 Image Suggestion: A comparison of Betelgeuse now vs. how it might look after going supernova.
📝 Caption: The red supergiant Betelgeuse could become the next visible supernova in our galaxy!
6. What’s Next?
Supernovae are not just cosmic fireworks—they are engines of creation, shaping the evolution of galaxies and spreading the elements necessary for life.
🔭 In upcoming posts, we’ll explore:
🕳️ How do black holes form after a supernova?
🌀 What are neutron stars and pulsars?
🌠 Could we see a supernova in our lifetime?
So keep looking up—because one day, a new supernova might light up our sky!
🚀 What do you think? If you could witness a supernova in real-time, what would you want to see? Let’s discuss in the comments!
🔭 Follow Galactic Wonders for more cosmic explorations! 🌟💥✨
Posted Using INLEO